Tree Traversals Again
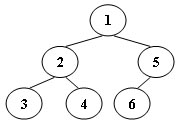
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
Push
Push
Push
Pop
Pop
Push
Pop
Pop
Push
Push
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
可以使用堆栈以非递归方式实现顺序二进制树遍历。你的任务是给出这棵树的后序遍历序列。
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。对于每种情况,第一行包含正整数N(≤ 3 0),它是节点的总数量在树(并且因此节点编号从1到N)。然后接下来是N行,每行描述一种堆栈操作,格式为:“Push X”,其中X是被推入堆栈的节点的索引; 或“Pop”表示从堆栈中弹出一个节点。
对于每个测试用例,在一行中打印相应树的后序遍历序列。保证存在解决方案。所有数字必须用一个空格分隔,并且在行的末尾不能有额外的空格。
先给出大神的思路
对二叉树的中序遍历可以通过使用栈来避免迭代的方法,对于figure1中的6节点树而言,它的栈操作为push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop()。依据这个输入可以生成这个二叉树,要求打印出该树的后序遍历。
解法:
该题要求我们通过中序遍历的栈实现的栈操作来生成二叉树。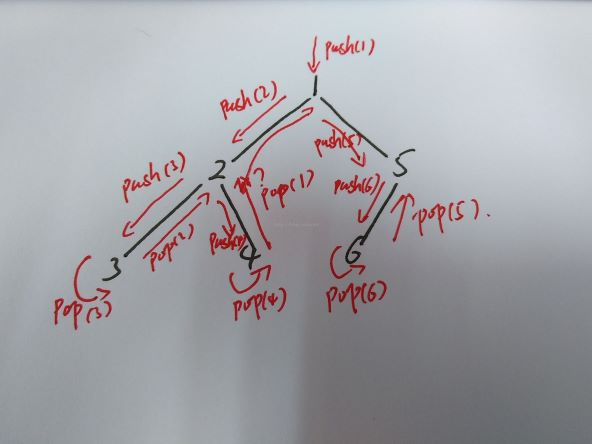
如上图,中序遍历的操作流程(其中箭头代表遍历流),我们可以看出:
1.每次push都指向一个新的节点。
2.每次pop都指向一个被抛出的节点。
3.连续的pop-pop或push-push流的方向都相同。
4.连续的push-pop指向同一个叶节点,同时执行方向转弯。(节点3)
5.连续的pop-push经过一个父节点,同时执行方向转弯。(节点2)
6.每个节点只能pop指向一次,push指向一次。(节点4到2直接跳到1)
于是我们就可以通过这些特性来构建二叉树:
1.读入第一次push构建根节点,根节点入栈。
2.读入下一个操作,有两种情况:
(1)push
说明有一个新节点出现,构建一个节点。如果上次操作为push,把该节点设为栈顶的左儿子,节点入栈。如果上次是pop,经过一个父节点,说明应该是生成了父节点的一个儿子,所以将该节点设为上次pop出来的节点的右儿子。
(2)pop
说明正在pop一个节点,不论上次操作是,该次都抛出一个节点。
这是我写的,有点菜
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#define MaxTree 31
#define Null -1
using namespace std; int P[MaxTree];
int num=;
int NUM=;
stack<int> st; struct TreeNode
{
int date;
int Left;
int Right;
}T[MaxTree]; int BuildTree(struct TreeNode T[])
{
int N,m,p,i;
string str,pre;
int Root;
cin>>N;
for(i=;i<*N;i++)
{
cin>>str;
if(str=="Push")
{
cin>>m;
if(i==)
{
Root=;
T[num].date=m;
T[num].Left=Null;
T[num].Right=Null;
st.push(num);
pre=str;
}
else if(pre=="Push")
{
T[num].Left=num+;
num++;
T[num].date=m;
T[num].Left=Null;
T[num].Right=Null;
st.push(num);
pre=str;
}
else if(pre=="Pop")
{
T[p].Right=num+;
num++;
T[num].date=m;
T[num].Left=Null;
T[num].Right=Null;
st.push(num);
pre=str;
}
}
else if(str=="Pop")
{
p=st.top();
st.pop();
pre=str;
}
}
if(N==)
{
Root=Null;
}
return Root;
} void search(int Tree)
{
if(Tree==Null)
return;
search(T[Tree].Left);
search(T[Tree].Right);
P[NUM++]=T[Tree].date;
} int main()
{
int Tree;
Tree=BuildTree(T);
search(Tree);
int i;
for(i=;i<NUM;i++)
{
if(i==)
cout<<P[i];
else
cout<<' '<<P[i];
}
return ;
}
下面是别人用动态链表实现的,值得一看
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
using namespace std; int preorder[], inorder[];
int n, preid = , inid = , cnt = ;
int get(){
char s[];
scanf("%s", s);
if (s[] == 'o') return -;
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
return a;
}
void build(int preb, int pree, int inb, int ine){
if (preb > pree) return;
int root = preorder[preb];
int inroot = inb;
while (inorder[inroot] != root) ++inroot;
build(preb+, preb+inroot-inb, inb, inroot-);
build(preb+inroot-inb+, pree, inroot+, ine);
if (cnt++ != ) putchar(' ');
printf("%d", root);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
stack<int> st;
for (int i = ; i < n*; ++i){
int a = get();
if (a != -){
st.push(a);
preorder[preid++] = a;
}else{
inorder[inid++] = st.top();
st.pop();
}
}
build(, n-, , n-);
return ;
}
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std; const string PUSH("Push");
const string POP("Pop"); typedef struct Node
{
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int d):data(d), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
}Node; void PostOrderTraverse(Node *root)
{
Node* temp = root;
Node* pre = NULL;
stack<Node*> S;
int flag = ; while(temp || !S.empty())
{
if(temp)
{
S.push(temp);
temp = temp->left;
}
else
{
temp = S.top();
if(temp->right && temp->right != pre)
temp = temp->right;
else
{
if(!flag)
{
flag = ;
cout<< temp->data;
}
else
cout<<" "<<temp->data;
S.pop();
pre = temp;
temp = NULL;
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
} int main()
{
int n, data;
string act;
stack<Node*> S;
Node* root = NULL, *pre = NULL;
int l = , r = ;
cin >> n; //First, build the tree , root of tree is *root.
for(int i=; i <= *n; i++)
{
Node* temp;
cin >> act;
if(act == PUSH)
{
cin >> data;
temp = new Node(data);
if(i == )
{
root = temp;
} S.push(temp);
if(pre)
{
if(l == )
pre->left = temp;
else
pre->right = temp;
}
l = ;
pre = temp;
}
else if(act == POP)
{
pre = S.top();
S.pop();
l = ;
}
} PostOrderTraverse(root); system("pause");
return ;
}
Tree Traversals Again的更多相关文章
- Tree Traversals
Tree Traversals 原题链接 常见的二叉树遍历的题目,根据后序遍历和中序遍历求层次遍历. 通过后序遍历和中序遍历建立起一棵二叉树,然后层序遍历一下,主要难点在于树的建立,通过中序遍历和后序 ...
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- hdu1710(Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals
HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals 题目大意:给一个树的前序遍历和中序遍历,要求输出后序遍历. (半年前做这道题做了两天没看懂,今天学了二叉树,回来AC了^ ^) 首先介绍一下 ...
- HDU-1701 Binary Tree Traversals
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 已知先序和中序遍历,求后序遍历二叉树. 思路:先递归建树的过程,后后序遍历. Binary Tree Tr ...
- 03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25)
03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- HDU 1710-Binary Tree Traversals(二进制重建)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- PAT1086:Tree Traversals Again
1086. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- Binary Tree Traversals(HDU1710)二叉树的简单应用
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- 【PAT】1020 Tree Traversals (25)(25 分)
1020 Tree Traversals (25)(25 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive int ...
随机推荐
- python3学习笔记及常见问题
1,mac自带的python是2.7版本,我们需要按照python3,这样在terminal下可以直接使用,但是编译打包的时候会默认使用python2.7 解决办法:安装virtualenv,一个管理 ...
- @RequestParam 和 @ PathVariable 的区别
@RequestParam 和 @ PathVariable 的区别http://localhost:8080/Springmvc/user/page.do?pageSize=3&pageNo ...
- Lesson Learned
最近,中兴ZTE违反美国商务部禁令,向伊朗出售敏感技术,被美国下达长达7年的禁止令,教训十分深刻.以诚待人,信守承诺,才能在商业社会站稳脚跟. 还是说说最近自己上的一课吧.上了港台服以后,奇奇怪怪的问 ...
- sync.Pool的使用
一定要搞明白sync.Pool的正确用法,避免出现以下问题: kline := this.pool.Get() defer this.pool.Put(kline) kline.UnMarshal(d ...
- UVA10562(看图写树,dfs)
这个题过的好艰难,不过真的学到好多. 关于fgets的用法真的是精髓.!isspace(c)和c!=' '是有区别的. 其它的看代码吧 #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- html基础js
HTML中的三把利器的JS 又称为JavaScript,看着好像和Java有点联系,实际上他和java半毛钱关系都没有,JavaScript和我们学习的Python.Go.Java.C++等,都是一种 ...
- NYOJ-15:括号匹配(二)
内存限制:64MB 时间限制:1000ms 特判: No 通过数:54 提交数:158 难度:6 题目描述: 给你一个字符串,里面只包含"(",")",&quo ...
- JS处理日期&字符串格式相互转换
之前找过一些获取系统日期以及日期&字符串格式相互转换的方式,但总体自我感觉来说还是以下的方式会更适合一些. 如有更好的方式,望大家多多赐教和交流,谢谢! 2016年曾写过一次,不过只是发了一下 ...
- 设计模式—模板方法(template method)
一.定义 百度百科给的定义:定义一个操作中的算法骨架(稳定),而将一些步骤延迟到子类中(变化).Template Method使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤. 如何做到 ...
- 使用feign出现 java.lang.IllegalStateException: Service id not legal hostname
检查spring. application.name是否使用了_