Edge Detection
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 22604 | Accepted: 5311 |
Description
A simple edge detection algorithm sets an output pixel's value to be the maximum absolute value of the differences between it and all its surrounding pixels in the input image. Consider the input image below:

The upper left pixel in the output image is the maximum of the values |15-15|,|15-100|, and |15-100|, which is 85. The pixel in the 4th row, 2nd column is computed as the maximum of |175-100|, |175-100|, |175-100|, |175-175|, |175-25|, |175-175|,|175-175|, and |175-25|, which is 150.
Images contain 2 to 1,000,000,000 (109) pixels. All images are encoded using run length encoding (RLE). This is a sequence of pairs, containing pixel value (0-255) and run length (1-109). Input images have at most 1,000 of these pairs. Successive pairs have different pixel values. All lines in an image contain the same number of pixels.
Input
Output
Sample Input
7
15 4
100 15
25 2
175 2
25 5
175 2
25 5
0 0
10
35 500000000
200 500000000
0 0
3
255 1
10 1
255 2
10 1
255 2
10 1
255 1
0 0
0
Sample Output
7
85 5
0 2
85 5
75 10
150 2
75 3
0 2
150 2
0 4
0 0
10
0 499999990
165 20
0 499999990
0 0
3
245 9
0 0
0
Hint
Source

题意
使用一种叫做“run length encoding”的方式来储存大尺寸图片,该方法是通过记录编码值和编码长度的对(number,length)来存储图片。有一种简单的edge detection算法是将图像中的每一个点的值与他周围的八个点求差,然后取绝对值的最大值。
现在的任务就是实现这个算法,输入的图片是以run length encoding的形式表示的,同时也要求转换后的图片也以run length encoding的形式表示。
思路
题意中说明图片的长度为10^9,因此不可能采用暴力计算法。从答案中可以看出,会有连续一段的相同输入输出,输入的pair number不超过1000,数量上是很少的,因此可以采用跳跃编码。
run length encoding编码方法是记录编码值和该值的编码长度,这里长度可以用开始和结束位置代替,结束位置可以用下一个值的开始位置表示。这样就变成记录每一个出现的新值和出现的位置即可。
而edge detection中每一个新值的出现都是因为输入图片中新值的出现。因此,只要对输入图片的每一个pair计算这个新值开始位置周围8个像素值,并记录位置即可。然后对所有计算的像素值根据位置排序,并且对像素值相同的格子进行合并就是所求结果。

上图来自 POJ 1009 Edge Detection(图像边缘检测)
我们使用跳跃编码,记录起始格子的num值和它的长度len,自然可以通过计算得到一个虚拟很长的输入或是输出数组(一维),再将一维数组转换为虚拟二维数组,即对len进行累加,即为一维数组的索引值,像素值num即为一位数组中存储的值,而转换为二维数组,即为一位数组索引值对n取余或是取整,之所以说是虚拟,就是不开辟空间进行存储……
考虑到这里,想到了使用map,map<int,int>,其中只存储连续段的起始格,对于输入map<int,int> InMap和输出map<int,int> OutMap,其key值用来存储一位数组的索引值,value则用来存储像素值num,为什么用map呢,最重要的是它可以按照key值自动升序排列,计算每一个连续段起始格周围的8个格子后,将计算得到的像素值和数组索引值插入map,他自动帮我们按照数组索引值排序了,这样,当我们计算完毕之后,向前迭代输出,省去了排序吧啦吧啦的麻烦,只要向前迭代,并把像素值相同的格子忽略掉(因为他们应该属于同一连续段的)就可以了。本小白感觉map大法好!
关于map==》C++ STL 中 map 容器
这时候,需要考虑一下特殊的格子,对于在二维数组边界的格子,他的周围不足8个格子,计算的时候当然要注意。
我们可以用简单的取余运算就把在最左边一列、最右边一列给筛选出来。这里我们把连续段的长度进行求和为Max,即数组索引从0开始,且最大索引值不会超过Max,所以可以把最上面一行和最下面一行计算中的越界格子排掉。这里需要考虑到每行只有一列和两列的情况!!
还有更值得我们注意的!!这里也让本小白WA了几次,百思不得其解了好久……
那就是最后一行的第一个格子,由于它没有下一行,所以它的像素值会发生变化
有朋友问为什么最后一行的第一个格子需要考虑而别的行的第一个格子不需要考虑呢?
首先,如果像这样像素值发生变化,自然会进行计算。
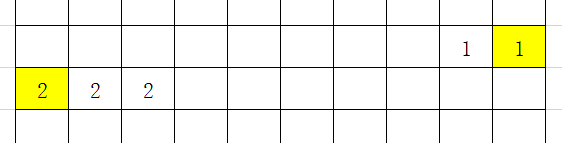
其次,如果像素值没有发生变化,那无非就是担心换行之后,格子上方和下方的格子的数值变化,拿上方格子数值变化为例,如果两个格子(黄色)上方格子数值不一样,那紫色格子的数值发生变化时,必然会计算黄色格子的数值,所以此处不需计算。其他情况同理。
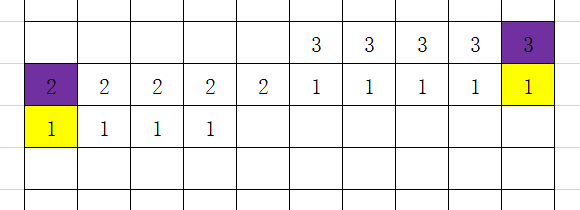
而最下面一行的第一个格子,它的下面的格子不是数值发生变化,而是消失了,即可以理解为,它下面的格子数值发生了变化但是不会启动计算过程,所以最下面一行的第一个格子是特殊的。
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
/*
可以利用map<int,int>的first为下标,second为像素值
一个输入map,一个输出map
利用map的特性,输出map插入后自动以first排序
输出的时候遍历输出map,如果second不同,则进行输出 代码很乱包括了我的测试代码……
*/
void Print(map<int,int> OutMap,int n,int Max)
{
long tempFirst = ,tempSecond=;
/*
map<int,int>::iterator iter = OutMap.begin();
for(iter;iter != OutMap.end();iter++)
{
cout<<iter->first<<" "<<iter->second<<endl;
}
*/
map<int,int>::iterator iter1 = OutMap.begin();//向前迭代
tempFirst = iter1->first;tempSecond = iter1->second;
for(iter1;iter1 != OutMap.end();iter1++)
{
if(iter1->second != tempSecond)
{
cout<<tempSecond<<" "<<iter1->first-tempFirst<<endl; tempSecond = iter1->second;
tempFirst = iter1->first;
}
}
cout<<tempSecond<<" "<<Max-tempFirst<<endl; cout<<<<" "<<<<endl;
}
void Compute(map<int,int> In,int n,int Max)
{//计算输出数组
/**/
map<int,int> OutMap;
int Count=;//记录数组下
int temp=;
int arr[] = {,-n-,-n,-n+,-,,n-,n,n+,Max-n};
///对In进行遍历
map<int,int>::iterator iter = In.begin();
for(iter;iter != In.end();iter++)
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
if(i == ) Count = arr[i];
else Count = iter->first + arr[i];//周围8个像素的下标,包括自己
if(Count < || Count >= Max)
{//下标越界
continue;
}
else if(Count%n == n- && iter->first%n == && n!=&& n!=)
{//在最左边一列,没有左边像素
continue;
}
else if(Count%n == && iter->first%n == n- && n!=&& n!=)
{//在最右边一列,没有右边像素
continue;
}
else{
map<int,int>::iterator CountIter = In.begin();//指针定位到中心
CountIter = In.upper_bound(Count);
CountIter--;
//cout<<"测试CountIter:"<<CountIter->first<<" "<<CountIter->second<<endl;
///计算当前像素的值
int Num = ;
int tempNum = ;
for(int j =;j<;j++)//考察周围的八个点
{
temp = Count + arr[j];
if(temp< || temp>=Max || temp%n==n-&&Count%n==&&n!= || temp%n==&&Count%n==n-&&n!=)
{
continue;
}else{
map<int,int>::iterator tempIter;
tempIter = In.upper_bound(temp);//第一个大于temp的位置
//cout<<"测试tempIter:"<<tempIter->first<<" "<<tempIter->second<<endl;
tempIter--;
//cout<<"测试tempIter2:"<<tempIter->first<<" "<<tempIter->second<<endl;
tempNum = CountIter->second - tempIter->second;
if(tempNum < ) tempNum = - * tempNum;
}
if(tempNum > Num) Num = tempNum;
}
///插入到OutMap
OutMap.insert(pair<int,int>(Count,Num));
}
}
}
Print(OutMap,n,Max);
OutMap.clear();
} int main()
{
int n;
map<int,int> InMap; cin>>n;
cout<<n<<endl;
while(n)
{ int num,len;
long Count = ;
///获取输入数组
cin>>num>>len;
while(len)
{
InMap.insert(pair<int,int>(Count,num));
Count += len;//虚拟数组下标增加
cin>>num>>len;
}
InMap.insert(pair<int,int>(,));
/*
map<int,int>::iterator iter;//向前迭代
for(iter = InMap.begin();iter != InMap.end();iter++)
{
cout<<iter->first<<","<<iter->second<<endl;
}
*/
///输入结束,进行输出数组的计算
Compute(InMap,n,Count);
InMap.clear();
cin>>n;
cout<<n<<endl;
} return ;
}
Edge Detection的更多相关文章
- Edge detection using LoG
intensity梯度值分布跟图片的大小有关, 比如将一张小图片放大后会变得很模糊, 原先清晰的edge, 即大的梯度值变得模糊. 但是原有的边缘通常还是肉眼可分辨的. 但用Sobel 算子可能就检测 ...
- 计算机视觉中的边缘检测Edge Detection in Computer Vision
计算机视觉中的边缘检测 边缘检测是计算机视觉中最重要的概念之一.这是一个很直观的概念,在一个图像上运行图像检测应该只输出边缘,与素描比较相似.我的目标不仅是清晰地解释边缘检测是怎样工作的,同时也提 ...
- 【数字图像分析】基于Python实现 Canny Edge Detection(Canny 边缘检测算法)
Canny 边缘检测算法 Steps: 高斯滤波平滑 计算梯度大小和方向 非极大值抑制 双阈值检测和连接 代码结构: Canny Edge Detection | Gaussian_Smoothing ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_21_Scale Space:Edge Detection and Ridge Detection with Automatic Scale Selection——1998
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Edge Detection Revisited ——2004
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Local Scale Control for Edge Detection and Blur Estimation——1998
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection: Optimal edge detection in two-dimensional images ——1996
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Multiresolution edge detection techniques ——1995
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion——1990
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
- Image Processing and Analysis_8_Edge Detection:A Computational Approach to Edge Detection——1986
此主要讨论图像处理与分析.虽然计算机视觉部分的有些内容比如特 征提取等也可以归结到图像分析中来,但鉴于它们与计算机视觉的紧密联系,以 及它们的出处,没有把它们纳入到图像处理与分析中来.同样,这里面也有 ...
随机推荐
- 记录一次k8s环境尝试过程(初始方案,现在已经做过很多完善,例如普罗米修斯)
记录一次Team k8s环境搭建过程(初始方案,现在已经做过很多完善,例如普罗米修斯) span::selection, .CodeMirror-line > span > span::s ...
- MobileNet系列
最近一段时间,重新研读了谷歌的mobilenet系列,对该系列有新的认识. 1.MobileNet V1 这篇论文是谷歌在2017年提出了,专注于移动端或者嵌入式设备中的轻量级CNN网络.该论文最大的 ...
- Mac OSX编译安装php7.1.8
laravel中用到ldap认证包,要求php7.0以上版本,而且安装Mews\Captcha包的时候 验证码无法显示 报错如下: Call to undefined function Interve ...
- kotlin函数式编程入门及图片处理
函数式编程入门: 对于面向对象编程[OOP]和函数式编程[FP] 由于在JAVA8的学习中系统的学习过了,所以这里对其概念就不过多解释了,下面直接用代码来看下在kotlin中函数式编程是如何编写的: ...
- Java 实现《编译原理》中间代码生成 -逆波兰式生成与计算 - 程序解析
Java 实现<编译原理>中间代码生成 -逆波兰式生成与计算 - 程序解析 编译原理学习笔记 (一)逆波兰式是什么? 逆波兰式(Reverse Polish notation,RPN,或逆 ...
- Python CGI编程Ⅳ
使用POST方法传递数据 使用POST方法向服务器传递数据是更安全可靠的,像一些敏感信息如用户密码等需要使用POST传输数据. 以下同样是hello_get.py ,它也可以处理浏览器提交的POST表 ...
- 29. ClustrixDB 分布式架构/并发控制
介绍 ClustrixDB使用多版本并发控制(MVCC)和2阶段锁(2PL)的组合来支持混合的读写工作负载.在我们的系统中,读取器享受无锁快照隔离,而写入器使用2PL来管理冲突.并发控制的组合意味着读 ...
- CSS层定位——固定定位,相对定位,绝对定位
主要写关于层定位的相关知识 ㈠定位概述 ⑴像图像软件中的图层一样可以对每一个layer能够精确定位操作 ⑵层定位的position属性决定了当前的一个网页元素,可以叠加到另一个网页元素上面,那么我们把 ...
- docker部署war+tomcat8
注意:本文只是将jenkins.war作为一个war包来操作,实际上要使用jenkins还要同时安装git.maven等. 1.购买阿里云服务器(Ubuntu 18.04), 设置密码,root+pa ...
- Nowcoder Playing Games ( FWT 优化 DP && 博弈论 && 线性基)
题目链接 题意 : 给出 N 个数.然后问你最多取出多少石子使得在 NIM 博弈中.后手必胜 分析 : Nim 博弈模型,后手必胜当且仅当各个堆的石子的数目的异或和为 0 转化一下.变成最少取多少石 ...
