Structure And Representation Of MIB Object Names - SNMP Tutorial
30.8 Structure And Representation Of MIB Object Names
We said that ASN.1 specifies how to represent both data items and names. However, understanding the names used for MIBvariables requires us to know about the underlying namespace. Names used for MIB variables are taken from the object identifier namespace administered by ISO and ITU. The key idea behind the object identifier namespace is that it provides a namespace in which all possible objects can be designated. The namespace is not restricted to variables used in network management -- it includes names for arbitrary objects (e.g., each international protocol standard document has a name).
The object identifier namespace is absolute (global), meaning that names are structured to make them globally unique. Like most namespaces that are large and absolute, the object identifier namespace is hierarchical. Authority for parts of the namespace is subdivided at each level, allowing individual groups to obtain authority to assign some of the names without consulting a central authority for each assignment4.
The root of the object identifier hierarchy is unnamed, but has three direct descendants managed by ISO, ITU, and jointly by ISO and ITU. The descendants are assigned both short text strings and integers that identify them (the text strings are used by humans to understand object names; computer software uses the integers to form compact, encoded representations of the names). ISO has allocated one subtree for use by other national or international standards organizations (including U.S. standards organizations), and the U.S. National Institute for Standards and Technology5 has allocated a subtree for the U.S. Department of Defense. Finally, the IAB has petitioned the Department of Defense to allocate it a subtree in the namespace. Figure 30.4 illustrates pertinent parts of the object identifier hierarchy and shows the position of the node used by TCP/IP network management protocols.
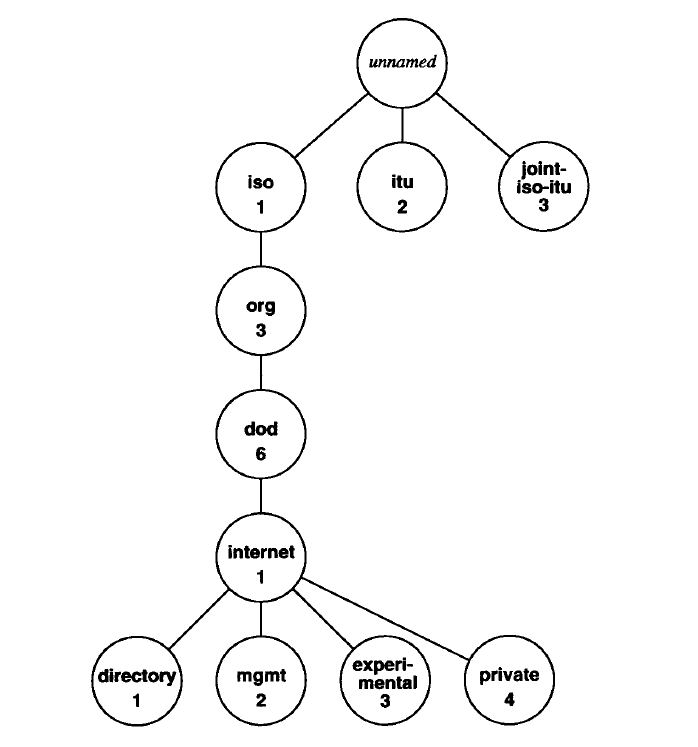

The name of an object in the hierarchy is the sequence of numeric labels on the nodes along a path from the root to the object. The sequence is written with periods separating the individual components. For example, the name 1.3.6.1.2 denotes the node labeled mgmt, the Internet management subtree. The MIBhas been assigned a node under the mgmt subtree with label mib and numeric value 1. Because all MIB variables fall under that node, they all have names beginning with the prefix 1.3.6.1.2.1.
Earlier we said that the MIB groups variables into categories. The exact meaning of the categories can now be explained: they are the subtrees of the mib node of the object identifier namespace. Figure 30.5 illustrates the idea by showing part of the naming subtree under the mib node.


Two examples will make the naming syntax clear. Figure 30.5 shows that the category labeled ip has been assigned the numeric value 4. Thus, the names of all MIB variables corresponding to IP have an identifier that begins with the prefix 1.3.6.1.2.1.4. If one wanted to write out the textual labels instead of the numeric representation, the name would be:
iso . org . dod. internet. mgmt . mib . ip
A MIB variable named ipInReceives has been assigned numeric identifier 3 under the ip node in the namespace, so its name is:
iso . org . dod. internet. mgmt . mib . ip . ipInReceives
and the corresponding numeric representation is:
1 . 3 . 6 . 1 . 2 . 1 . 4 . 3
When network management protocols use names of MIBvariables in messages, each name has a suffix appended. For simple variables, the suffix 0 refers to the instance of the variable with that name. So, when it appears in a message sent to a router, the numeric representation of iplnReceives is:
1 . 3 . 6 . 1 . 2 . 1 . 4 . 3 . 0
which refers to the instance of ipInReceives on that router. Note that there is no way to guess the numeric value or suffix assigned to a variable. One must consult the published standards to find which numeric values have been assigned to each object type.
Thus, programs that provide mappings between the textual form and underlying numeric values do so entirely by consulting tables of equivalences -- there is no closed-form computation that performs the transformation.
As a second, more complex example, consider the MIBvariable ipAddrTable, which contains a list of the IP addresses for each network interface. The variable existsin the namespace as a subtree under ip, and has been assigned the numeric value 20. Therefore, a reference to it has the prefix:
iso . org . dod . internet. mgmt . mib . ip . ipAddrTable
with a numeric equivalent:
1 . 3 . 6 . 1 . 2 . 1 . 4 . 20
In programming language terms, we think of the IP address table as a one-dimensional array, where each element of the array consists of a structure (record) that contains five items: an IP address, the integer index of an interface corresponding to the entry, an IP subnet mask, an IP broadcast address, and an integer that specifies the maximum datagram size that the router will reassemble. Of course, it is unlikely that a router has such an array in memory. The router may keep this information in many variables or may need to follow pointers to find it. However, the MIBprovides a name for the array as if it existed, and allows network management software on individual routers to map table references into appropriate internal variables. The point is:
Although they appear to specify details about data structures, MIB standards donot dictate the implementation. Instead, MIB definitions provide a uniform, virtual interface that managers use to access data; an agent must translate between the virtual items in a MIB and the internal implementation.
Using ASN.1 style notation, we can define ipAddrTable:
ipAddrTable ::= SEQUENCE OF IpAddrEntry
where SEQUENCE and OF are keywords that define an ipAddrTable to be a one dimensional array of IpAddrEntrys. Each entry in the array is defined to consist of five fields (the definition assumes that IpAddresshas already been defined).
IpAddrEntry ::= SEQUENCE {
ipAdEntAddr
IpAddress,
ipAdEntIflndex
INTEGER,
ipAdEntNetMask
IpAddress,
ipAdEntBcastAddr
IpAddress,
ipAdEntReasmMaxSize
INTEGER (0..65535)
}
Further definitions must be given to assign numeric values to ipAddrEntry and to each item in the IpAddrEntry sequence. For example, the definition:
ipAddrEntry { ipAddrTable 1 }
specifies that ipAddrEntryfalls under ipAddrTableand has numeric value 1. Similarly, the definition:
ipAdEntNetMask { ipAddrEntry 3 }
assigns ipAdEntNetMasknumeric value 3 under ipAddrEntry.
We said that ipAddrTablewas like aone-dimensional array. However, there is a significant difference in the way programmers use arrays and the way network management software uses tables in the MIB. Programmers think of an array as a set of elements that have an index used to select a specific element. For example, the programmer might write xyz[3] to select the third element from array xyz. ASN.1 syntax does not use integer indices. Instead, MIB tables append a suffix onto the name to select a specific element in the table. For our example of an IP address table, the standard specifies that the suffix used to select an item consists of an IPaddress. Syntactically, the IP address (in dotted decimal notation) is concatenated onto the end of the object name to form the reference. Thus, to speclfy the network mask field in the IP address table entry corresponding to address 128.10.2.3, one uses the name:
iso.org.dod. internet.mgmt.mib. ip. ipAddrTable. ipAddrEntry. ipAdEntNetMask. 128.10.2.3
which, in numeric form, becomes:
1 . 3 . 6 . 1 . 2 . 1 . 4 . 20 . 1 . 3 . 128 . 10 . 2 . 3
Although concatenating an index to the end of a name may seem awkward, it provides a powerful tool that allows clients to search tables without knowing the number of items or the type of data used as an index. The next section shows how network management protocols use this feature to step through a table one element at a time.
3 ASN.1 is usually pronounced by reading the dot: "A-S-N dot 1".
4 Readers should recall from the Domain Name System discussion in Chapter 24 how authority for a hierarchical namespace is subdivided.
5 NIST was formerly the National Bureau of Standards.
Abstract from Internetworking With TCP/IP Vol I: Principles, Protocols, and Architecture Fourth Edition,
DOUGLAS E. COMER,
Department of Computer Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907,
PRENTICE HALL,
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
Structure And Representation Of MIB Object Names - SNMP Tutorial的更多相关文章
- SNMP Tutorial
Applications: Internet Management (SNMP) 30.1 Introduction 30.2 The Level Of Management Protocols 30 ...
- Examples of MIB Variables - SNMP Tutorial
30.5 Examples of MIB Variables Versions 1 and 2 of SNMP each collected variables together in a singl ...
- Structure Of Management Information - SNMP Tutorial
30.6 The Structure Of Management Information In addition to the standards that specify MIB variables ...
- Simple Network Management Protocol - SNMP Tutorial
30.9 Simple Network Management Protocol Network management protocols specify communication between t ...
- Summary - SNMP Tutorial
30.13 Summary Network management protocols allow a manager to monitor and control routers and hosts. ...
- Formal Definitions Using ASN.1 - SNMP Tutorial
30.7 Formal Definitions Using ASN.1 The SMI standard specifies that all MIB variables must be define ...
- Protocol Framework - SNMP Tutorial
30.4 Protocol Framework TCP/IP network management protocols2 divide the management problem into two ...
- Example: Encoded SNMP Message - SNMP Tutorial
30.11 Example Encoded SNMP Message The encoded form of ASN.1 uses variable-length fields to represen ...
- SNMP Message Format - SNMP Tutorial
30.10 SNMP Message Format Unlike most TCP/IP protocols, SNMP messages do not have fixed fields. Inst ...
随机推荐
- [AlwaysOn Availability Groups]AlwaysOn健康诊断日志
AlwaysOn健康诊断日志 为了监控primary可用副本的健康状况,SQL Server资源DLL使用SQL Server2012的过程sp_server_diagnostics. SQL Ser ...
- TCP三次握手建立连接
基本过程: ISN(初始序号)随时间变化,每一个连接具有不同的ISN,防止在网络延迟中分组被重新发送. 请求端发送SYN(同步序号 )=1,seq=ISN(32bits序号,每4ms+ ...
- jq attr()改变checkbox的checked无效!!!!
今天做项目发现用attr()改变checked,实现全选功能的时候发现,第一次点击有效,之后点击全选功能便实效. 一开始以为是自己写错了,在各种碰壁之后,才猛然发现,原来这是jq的一个小bug. 在j ...
- lmap
1.lamp组件安装 sudo apt-get install apache2 sudo apt-get install php5 sudo apt-get install mysql-server ...
- amCharts图表中的JavaScript中文注释引起的浏览器兼容性问题
近期用amCharts做图表.一切都很顺利,然后演示的时候掉链子了,平时开发的时候都是用的火狐和谷歌,加上这种图表框架本来就号称兼容性极好,也没有在ie上测试,演示的机器上恰巧用的是ie11,发现一个 ...
- EF继承关系映射
继承映射策略的三种策略 There are following three different approaches to represent an inheritance hierarchy in ...
- Azure机器学习入门(一)
我们开始深入学习Azure机器学习的基本原理并为您开启伟大的数据科学之门.Azure 机器学习的一个重要特征就是在构建预测分析方案时,它能够方便地将开发模式集成为可重复的工作流模式.这就使得Azure ...
- Caffe源码解析5:Conv_Layer
转载请注明出处,楼燚(yì)航的blog,http://home.cnblogs.com/louyihang-loves-baiyan/ Vision_layer里面主要是包括了一些关于一些视觉上的操 ...
- 基于网格的分割线优化算法(Level Set)
本文介绍一种网格分割线的优化算法,该方法能够找到网格上更精确.更光滑的分割位置,并且分割线能够自由地合并和分裂,下面介绍算法的具体原理和过程. 曲面上的曲线可以由水平集(level set)形式表示, ...
- angular的跨域(angular百度下拉提示模拟)和angular选项卡
1.angular中$http的服务: $http.get(url,{params:{参数}}).success().error(); $http.post(url,{params:{参数}}).su ...
