【思维题 线段树】cf446C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
我这种maintain写法好zz。考试时获得了40pts的RE好成绩
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
F1 = 1; F2 = 1; Fn = Fn - 1 + Fn - 2 (n > 2).
DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of n integers: a1, a2, ..., an. Moreover, there are mqueries, each query has one of the two types:
- Format of the query "1 l r". In reply to the query, you need to add Fi - l + 1 to each element ai, where l ≤ i ≤ r.
- Format of the query "2 l r". In reply to the query you should output the value of
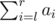 modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
Help DZY reply to all the queries.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300000). The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — initial array a.
Then, m lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n holds.
Output
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
题目分析
注意到形如Fib的数列$a_{n+2}=a_{n+1}+a_n$有相当好的性质。
- $a_n=F_{n−2}a_1+F_{n−1}a_2$
- $\sum_{i=1}^na_i=a_{n+2}−a_2$
第一条可以用数学归纳法证明;第二条就是将$2\sum_{i=1}^na_i$展开,得到$\sum_{i=1}^na_i+a_{n+2}-a_2$.
回到这一道题上,利用了这两条性质,那么对于每一个修改的区间只需要保留区间前两项增加的Fib值就可以记录下这个操作。所以现在就可以用线段树来维护这一系列询问了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define MO 1000000009
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = ; struct node
{
ll tag1,tag2,sum;
}f[maxn<<];
int n,m;
ll sum[maxn],fib[maxn]; int read()
{
char ch = getchar();
int num = , fl = ;
for (; !isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
if (ch=='-') fl = -;
for (; isdigit(ch); ch=getchar())
num = (num<<)+(num<<)+ch-;
return num*fl;
}
void maintain(int rt, int lens)
{
f[rt].tag1 %= MO, f[rt].tag2 %= MO;
f[rt].sum = f[rt<<].sum+f[rt<<|].sum;
f[rt].sum = (f[rt].sum+f[rt].tag1*fib[lens]+f[rt].tag2*fib[lens+]-f[rt].tag2)%MO;
}
void pushdown(int rt, int l, int r)
{
if (!f[rt].tag1&&!f[rt].tag2) return;
int mid = (l+r)>>, ls = rt<<, rs = rt<<|;
f[ls].tag1 += f[rt].tag1, f[ls].tag2 += f[rt].tag2;
f[rs].tag1 += f[rt].tag1*fib[mid-l]+f[rt].tag2*fib[mid-l+];
f[rs].tag2 += f[rt].tag1*fib[mid-l+]+f[rt].tag2*fib[mid-l+];
f[rt].tag1 = f[rt].tag2 = ;
maintain(ls, mid-l+);
maintain(rs, r-mid);
}
void modify(int rt, int L, int R, int l, int r)
{
if (L <= l&&r <= R){
f[rt].tag1 += fib[l-L+];
f[rt].tag2 += fib[l-L+];
maintain(rt, r-l+);
return;
}
int mid = (l+r)>>;
pushdown(rt, l, r);
if (L <= mid) modify(rt<<, L, R, l, mid);
if (R > mid) modify(rt<<|, L, R, mid+, r);
maintain(rt, r-l+);
}
ll query(int rt, int L, int R, int l, int r)
{
if (L <= l&&r <= R) return f[rt].sum;
pushdown(rt, l, r);
int mid = (l+r)>>;
ll ret = ;
if (L <= mid) ret += query(rt<<, L, R, l, mid);
if (R > mid) ret += query(rt<<|, L, R, mid+, r);
return ret%MO;
}
int main()
{
n = read(), m = read(), fib[] = fib[] = ;
for (int i=; i<=n; i++) sum[i] = (sum[i-]+read())%MO;
for (int i=; i<=; i++) fib[i] = (fib[i-]+fib[i-])%MO;
for (int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int opt = read(), l = read(), r = read();
if (opt==) modify(, l, r, , n);
else printf("%lld\n",(query(, l, r, , n)+(sum[r]-sum[l-])%MO+MO)%MO);
}
return ;
}
END
【思维题 线段树】cf446C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers的更多相关文章
- cf446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- CF446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 线段树 + 数学
有两个性质需要知道: $1.$ 对于任意的 $f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2]$ 的数列,都有 $f[i]=fib[i-2]\times f[1]+fib[i-1]\times f[2]$ 其中 ...
- codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(数学 or 数论+线段树)(两种方法)
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation F1 ...
- Codeforces 446-C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 同余 线段树 斐波那契数列
C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- ACM学习历程—Codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(线段树 && 数论)
Description In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence ...
- Codeforces 446C —— DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(线段树)
题目:DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 题意比較简单,不解释了. 尽管官方的题解也是用线段树,但还利用了二次剩余. 可是我没有想到二次剩余,然后写了个感觉非常复杂度的线段树,还是 ...
- codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 数论+线段树成段更新
DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers Time Limit:4000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d &a ...
- 「CF446C」 DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
「CF446C」 DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 这里提供一种优美的根号分治做法. 首先,我们考虑一种不太一样的暴力.对于一个区间加斐波那契数的操作 \([a,b]\),以及一 ...
- Codeforces446C - DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
Portal Description 给出一个\(n(n\leq3\times10^5)\)个数的序列,进行\(m(m\leq3\times10^5)\)次操作,操作有两种: 给区间\([L,R]\) ...
随机推荐
- java.sql.SQLException: Could not commit with auto-commit set on
This kind of exceptions occur when the Oracle JDBC Driver (ojdbc6.jar) version 12 or above will be u ...
- python 5 条件判断
条件判断 计算机之所以能做很多自动化的任务,因为它可以自己做条件判断. 比如,输入用户年龄,根据年龄打印不同的内容,在Python程序中,用if语句实现: age = 20 if age >= ...
- SpringBoot---Web开发---WebSocket
[广播式] 1. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="ht ...
- 如何安装使用windows自带的telnet服务
控制面板->程序和功能->打开或关闭Windows功能->Telnet 客户端 [ Telnet 服务器 ] 安装完成后重启cmd telnet ip port
- 开发工具~nuget配置本地源
我们在本地部署了自己的nuget服务器,有时可以需要用到nuget restore命令去恢复包包,它会从下面的nuget.config里读你的配置源信息,就是在这里,我们要把内测的nuget服务器路径 ...
- 高效的设计可视化UI
http://www.uimaker.com/uimakerdown/uitutorial/35990.html http://maqetta.org/downloads/ .Data.js Data ...
- JavaWeb_05_xml相关&dtd快速入门
学东西怎么学,是什么,能做什么,怎么去做!! 1.xml的简介 1.eXtensible Markup Language:可扩展标记型语言 标记型语言:html是标记型语言 也是使用标签来操作 可扩展 ...
- zblog忘记后台密码怎么办 官方解决方案
刚装的zblog还没开始研究,结果发现密码弄错了进不去后台,也是醉了 为节省时间,直接用官方方案,就是一个无密码进后台的文件.下载后把文件上传至网站根目录,然后直接访问后台修改密码 zblog密码找回 ...
- get_user
Name get_user -- Get a simple variable from user space. Synopsis get_user ( x, ptr); Arguments x ...
- EasyUI Tabs + Yii2.0实现iframe方式打开页面(解决共用静态文件引入加载的问题)
在项目实际开发中,有将打开的各个链接页面隔离的需求(防止静态资源起冲突),这个时候常规思路就是使用iframe来实现!但遇到一个比较棘手的问题,当用easyui Tabs打开一个iframe页面时,怎 ...
