netfilter-在内核态操作网络数据包
一.概述
netfilter是自2.4内核的一个数据包过滤框架。可以过滤数据包,网络地址和端口转换(nat和napt技术),以及其他操作数据包的功能。主要工作原理是在内核模块注册回调函数(hook函数)到内核,内核执行到相关点时会触发这个回调函数,然后根据回调函数里的逻辑,对包含网络协议栈的sk_buff结构进行操作!!!iptables的内核模块就是使用的netfilter。netfilter官方网站:http://www.netfilter.org/
二.基本函数接口
1.把hook函数注册到内核需要使用结构体nf_hook_ops来关联,该结构体定义在内核头文件目录的linux/netfilter.h里面,这里以2.6.39内核为例:
struct nf_hook_ops {
struct list_head list;
/* User fills in from here down. */
nf_hookfn *hook;
struct module *owner;
u_int8_t pf;
unsigned int hooknum;
/* Hooks are ordered in ascending priority. */
int priority;
};
nf_hookfn就是要填充的hook函数。pf时8位协议族,如ipv4就是PF_INET。hooknum是指定hook函数注册的数据包的路径地点。priority是该hook的优先级,当有多个hook在同一个点注册的时候,会按照优先级来执行hook。
2.nf_hookfn函数声明也是在linux/netfilter.h里面:
typedef unsigned int nf_hookfn(unsigned int hooknum,
struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in,
const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *));
sk_buff是内核维护的网络协议栈结构,里面可以取出各协议栈信息。该函数的返回值:
/* Responses from hook functions. */ #define NF_DROP 0 #define NF_ACCEPT 1 #define NF_STOLEN 2 #define NF_QUEUE 3 #define NF_REPEAT 4 #define NF_STOP 5
NF_ACCEPT:接收数据包,由内核继续正常的报文传送
NF_DROP:丢弃数据包
NF_STOLEN:数据包的操作全部由hook函数处理
NF_QUEUE:将报文入队,通常交由用户程序处理
NF_REPEAT:再次调用该hook函数。
3.hooknum的5个通用注册点也是定义在linux/netfilter.h
enum nf_inet_hooks {
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
NF_INET_FORWARD,
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
NF_INET_NUMHOOKS
};
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING:系统收到数据后,且没有经过路由
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN:系统收到数据,经过路由后,如果数据的目标地址是本机就经过该点
NF_INET_FORWARD:系统收到数据,经过路由后,如果数据的目标地址是其他地方就经过该点
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT:系统发送数据时,未经过路由
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING:系统发送数据时,经过了路由阶段,马上就发出去了
对于ipv4的注册点值跟上面一样,只是用的宏定义:
/* IP Hooks */ /* After promisc drops, checksum checks. */ #define NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING 0 /* If the packet is destined for this box. */ #define NF_IP_LOCAL_IN 1 /* If the packet is destined for another interface. */ #define NF_IP_FORWARD 2 /* Packets coming from a local process. */ #define NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT 3 /* Packets about to hit the wire. */ #define NF_IP_POST_ROUTING 4 #define NF_IP_NUMHOOKS 5 #endif /* ! __KERNEL__ */
4.注册和撤销注册函数:
/* Function to register/unregister hook points. */ int nf_register_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg); void nf_unregister_hook(struct nf_hook_ops *reg);
参数都是nf_hook_ops结构指针。
三.简单例子
我们用一个简单例子观察vxlan的数据包在各hook点的ip情况,vxlan环境可以参考Docker+OpenvSwitch搭建VxLAN实验环境
本例子是内核模块编程,可以参考初探linux内核编程,参数传递以及模块间函数调用
/**
* @file netfilter_hook.c
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("yuuyuu");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("netfilter");
MODULE_VERSION("1.0");
/* 打印点分制ip地址 */
#define printk_ip(info, be32_addr) \
printk("%s %d.%d.%d.%d\n", \
info, \
((unsigned ], \
((unsigned ], \
((unsigned ], \
((unsigned ])
int filter_ip(__be32 addr)
{
unsigned ];
unsigned ];
|| host_num == || host_num == )
;
;
}
int filter_src_dst_ip(__be32 s_addr, __be32 d_addr)
{
int i = filter_ip(s_addr) && filter_ip(d_addr);
return i;
}
/* NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING */
unsigned int pre_routing_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
ip_header = ip_hdr(skb);
if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr))
{
printk("pre_routing_hook()==================================\n");
printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr);
printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr);
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
struct nf_hook_ops pre_routing_ops =
{
.hook = pre_routing_hook,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST
};
/* NF_INET_LOCAL_IN */
unsigned int local_in_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
ip_header = ip_hdr(skb);
if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr))
{
printk("local_in_hook()========================================\n");
printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr);
printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr);
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
struct nf_hook_ops local_in_ops =
{
.hook = local_in_hook,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_LOCAL_IN,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST
};
/* NF_INET_FORWARD */
unsigned int forward_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
ip_header = ip_hdr(skb);
if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr))
{
printk("forward_hook=========================================\n");
printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr);
printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr);
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
struct nf_hook_ops forward_ops =
{
.hook = forward_hook,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_FORWARD,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST
};
/* NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT */
unsigned int local_out_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
ip_header = ip_hdr(skb);
if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr))
{
printk("local_out_hook===========================================\n");
printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr);
printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr);
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
struct nf_hook_ops local_out_ops =
{
.hook = local_out_hook,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST
};
/* NF_INET_POST_ROUTING */
unsigned int post_routing_hook(unsigned int hooknum, struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff *))
{
struct iphdr *ip_header;
ip_header = ip_hdr(skb);
if (filter_src_dst_ip(ip_header->saddr, ip_header->daddr))
{
printk("post_routing_hook====================================\n");
printk_ip("src ip:", ip_header->saddr);
printk_ip("dst ip:", ip_header->daddr);
}
return NF_ACCEPT;
}
struct nf_hook_ops post_routing_ops =
{
.hook = post_routing_hook,
.pf = PF_INET,
.hooknum = NF_INET_POST_ROUTING,
.priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST
};
/* 注册 */
static int hook_init(void)
{
printk("hook_init()======================\n");
nf_register_hook(&pre_routing_ops);
nf_register_hook(&local_in_ops);
nf_register_hook(&forward_ops);
nf_register_hook(&local_out_ops);
nf_register_hook(&post_routing_ops);
;
}
static void hook_exit(void)
{
printk("hook_exit()=====================\n");
nf_unregister_hook(&pre_routing_ops);
nf_unregister_hook(&local_in_ops);
nf_unregister_hook(&forward_ops);
nf_unregister_hook(&local_out_ops);
nf_unregister_hook(&post_routing_ops);
}
module_init(hook_init);
module_exit(hook_exit);
第27,34行简单过滤下本环境的IP,方便查看结果。
Makefile文件
KERNEL_DIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
obj-m := netfilter_hook.o
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(PWD) modules
四.验证
vxlan环境:
host1:eth0:192.168.2.1,虚拟网桥10.1.2.10
host2:eth0:192.168.2.2,虚拟网桥10.1.2.11
编译后插入模块,在host1里面ping一次host2的虚拟网桥10.1.2.11
然后参看内核输出信息:
sudo dmesg
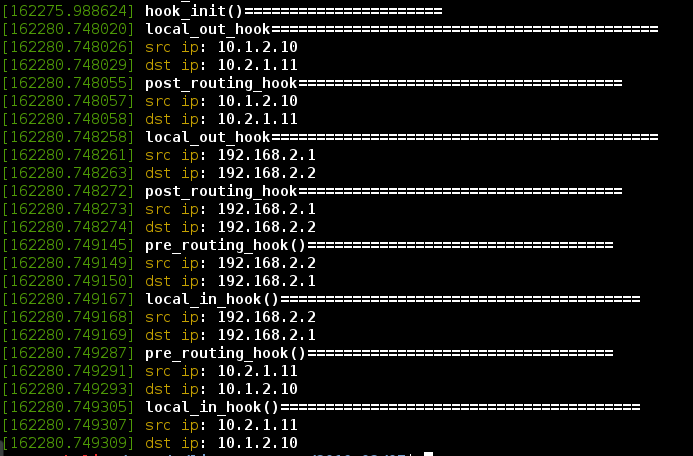
可以看到vxlan的icmp请求有2个IP在工作,分别经过local_out_hook和post_routing_hook。
同理host2的icmp应答进入本机也是2个IP都经过了pre_routing_hook和local_in_hook。
netfilter-在内核态操作网络数据包的更多相关文章
- Linux内核中网络数据包的接收-第一部分 概念和框架
与网络数据包的发送不同,网络收包是异步的的.由于你不确定谁会在什么时候突然发一个网络包给你.因此这个网络收包逻辑事实上包括两件事:1.数据包到来后的通知2.收到通知并从数据包中获取数据这两件事发生在协 ...
- Linux内核网络数据包处理流程
Linux内核网络数据包处理流程 from kernel-4.9: 0. Linux内核网络数据包处理流程 - 网络硬件 网卡工作在物理层和数据链路层,主要由PHY/MAC芯片.Tx/Rx FIFO. ...
- linux2.6.24内核源代码分析(2)——扒一扒网络数据包在链路层的流向路径之一
在2.6.24内核中链路层接收网络数据包出现了两种方法,第一种是传统方法,利用中断来接收网络数据包,适用于低速设备:第二种是New Api(简称NAPI)方法,利用了中断+轮询的方法来接收网络数据包, ...
- Linux 中的网络数据包捕获
Linux 中的网络数据包捕获 Ashish Chaurasia, 工程师 简介: 本教程介绍了捕获和操纵数据包的不同机制.安全应用程序,如 VPN.防火墙和嗅探器,以及网络应用程序,如路由程序,都依 ...
- sk_buff封装和解封装网络数据包的过程详解(转载)
http://dog250.blog.51cto.com/2466061/1612791 可以说sk_buff结构体是Linux网络协议栈的核心中的核心,几乎所有的操作都是围绕sk_buff这个结构体 ...
- sk_buff封装和解封装网络数据包的过程详解
转自:http://www.2cto.com/os/201502/376226.html 可以说sk_buff结构体是Linux网络协议栈的核心中的核心,几乎所有的操作都是围绕sk_buff这个结构体 ...
- 用C++实现网络编程---抓取网络数据包的实现方法
一般都熟悉sniffer这个工具,它可以捕捉流经本地网卡的所有数据包.抓取网络数据包进行分析有很多用处,如分析网络是否有网络病毒等异常数据,通信协议的分析(数据链路层协议.IP.UDP.TCP.甚至各 ...
- Android利用tcpdump和wireshark抓取网络数据包
Android利用tcpdump和wireshark抓取网络数据包 主要介绍如何利用tcpdump抓取andorid手机上网络数据请求,利用Wireshark可以清晰的查看到网络请求的各个过程包括三次 ...
- 网络数据包信息收集工具ferret-sidejack
网络数据包信息收集工具ferret-sidejack 网络数据包传递用户的各种操作和对应的信息.但是由于各种数据混在一起,不利于渗透测试人员分析.Kali Linux提供了一款信息搜集工具ferr ...
随机推荐
- servlet同一用户不同页面共享数据
如何实现不同页面之间的数据传递,实现页面的数据共享?常见的方法有以下4种: 1)表单提交(form) 2)sendRedirect()跳转 3)session技术 4)Cookie技术 表单提交 这是 ...
- (原) 1.1 Zookeeper单机安装
本文为原创文章,转载请注明出处,谢谢 zookeeper 单机安装配置 1.安装前准备 linux系统(此文环境为Centos6.5) Zookeeper安装包,官网https://zookeeper ...
- Ionic 今天发布了Windows 桌面版的IDE Ionic Lab
Ionic简介: Ionic 是一个强大的 HTML5 应用程序开发框架,号称 Advanced HTML5 Hybrid Mobile AppFramework 是 AngularJS 移动端解决方 ...
- jquery.sobox 经典版弹窗控件
sobox 是一款非常实用的,基于 jQuery 的弹窗控件.功能非常完整,而代码量又非常少(压缩完仅8k不到)的一款弹窗控件,如果你熟悉ext的弹窗控件,那么sobox的使用对你来说应该是愉悦而完全 ...
- URL(统一资源定位符)结构和注意事项
URL的常见结构: http://localhost/项目名称/文件1/文件2... 注意事项: 当我们在项目中在书写URL的时候,一般会出现两种情况: 第一种:在路径前面加上/,表示直接连在loca ...
- js获取页面中图片的总数
查看效果:http://keleyi.com/keleyi/phtml/image/9.htm 下面是完整代码: <html><body><div id="ke ...
- angularjs 指令—— 绑定策略(@、=、&)
angularjs 指令—— 绑定策略(@.=.&) 引入主题背景:angular 的指令配置中的template可以直接使用硬编码写相应的代码,不过也可以根据变量,进行动态更新.那么需要用到 ...
- JavaScript基础系列(变量与类型)
以下内容将JavaScript简称为JS 打开本文时不管你是零基础的初学者还是其他语言的老兵,我都想说程序语言的基础支撑起了整个网络世界,不把这些基础学透之后稍复杂的内容会让你寸步难行. 现在先给编程 ...
- android键盘弹出头部上移处理
<ScrollView android:id="@+id/top_bar" android:layout_width="fill_parent" andr ...
- mac jdk 6设置
新装的mac 系统10.10 ,jdk是1.8,因为一些工具要使用 jdk 6,以下是设置过程 查看版本 java -version 查看java是再哪:在/usr/bin/java whereis ...
