Codeforces--615B--Longtail Hedgehog(贪心模拟)
This Christmas Santa gave Masha a magic picture and a pencil. The picture consists ofn points connected by
m segments (they might cross in any way, that doesn't matter). No two segments connect the same pair of points, and no segment connects the point to itself. Masha wants to color some segments in order paint a hedgehog.
In Mashas mind every hedgehog consists of a tail and some spines. She wants to paint the tail that satisfies the following conditions:
- Only segments already presented on the picture can be painted;
- The tail should be continuous, i.e. consists of some sequence of points, such that every two neighbouring points are connected by a colored segment;
- The numbers of points from the beginning of the tail to the end should strictly increase.
Masha defines the length of the tail as the number of points in it. Also, she wants to paint some spines. To do so, Masha will paint all the segments, such that one of their ends is theendpoint of the tail. Masha defines
the beauty of a hedgehog as the length of the tail multiplied by the number of spines. Masha wants to color the most beautiful hedgehog. Help her calculate what result she may hope to get.
Note that according to Masha's definition of a hedgehog, one segment may simultaneously serve as a spine and a part of the tail (she is a little girl after all). Take a look at the picture for further clarifications.
First line of the input contains two integers n andm(2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000,1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number
of points and the number segments on the picture respectively.
Then follow m lines, each containing two integersui andvi
(1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n,ui ≠ vi) —
the numbers of points connected by corresponding segment. It's guaranteed that no two segments connect the same pair of points.
Print the maximum possible value of the hedgehog's beauty.
8 6
4 5
3 5
2 5
1 2
2 8
6 7
9
4 6
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 4
3 4
12
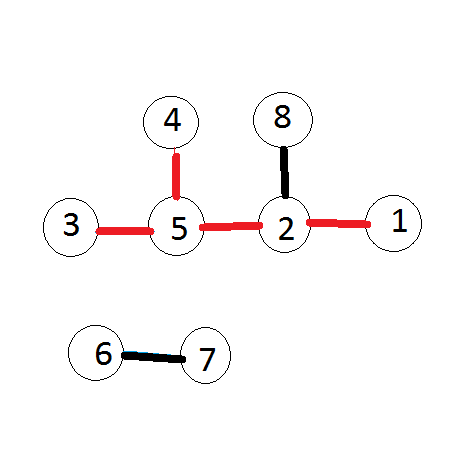
The picture below corresponds to the first sample. Segments that form the hedgehog are painted red. The tail consists of a sequence of points with numbers1,
2 and 5. The following segments are spines: (2,
5), (3,
5) and (4,5). Therefore, the beauty of the hedgehog is equal to3·3 = 9.
n个点,m条无向边,在连成的链中找一条递增的链,使得末尾节点的度数乘以深度最大,因为是无向边,又要求递增的链,所以尽量使小的数做起点,并且将所有的边按照节点大小进行排序,从最小的点开始遍历,记录每一个点最大的深度,然后找到最大的乘积
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int u,v;
}edge[200000+10];
bool cmp(node s1,node s2)
{
if(s1.u==s2.u)
return s1.v<s2.v;
return s1.u<s2.u;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
__int64 dp[100100],dre[100100];
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
memset(dre,0,sizeof(dre));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>edge[i].u>>edge[i].v;
if(edge[i].u>edge[i].v)
swap(edge[i].u,edge[i].v);//¾¡Á¿Ê¹Ð¡µÄµã×öÆðµã
dre[edge[i].u]++,dre[edge[i].v]++;
}
sort(edge,edge+m,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)//¼Ç¼ÿһ¸öµãµÄ×î´óÉî¶È
dp[edge[i].v]=max(dp[edge[i].v],dp[edge[i].u]+1);
__int64 ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans=max(ans,(dp[i]+1)*dre[i]);//Ñ°ÕÒ×î´ó³Ë»ý
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Codeforces--615B--Longtail Hedgehog(贪心模拟)的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 615B Longtail Hedgehog
题目: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/615/B 题意:题目描述很复杂,但实际上很简单.大意就是连续的几个点组成尾巴,要求尾巴的长度乘以尾巴终点的分 ...
- CodeForces ---596B--Wilbur and Array(贪心模拟)
Wilbur and Array Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 262144KB 64bit IO Format: %I64d & %I64u Su ...
- Codeforces 158 B. Taxi[贪心/模拟/一辆车最多可以坐4人同一个群的小朋友必须坐同一辆车问最少需要多少辆车]
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/158/B B. Taxi time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit pe ...
- 贪心+模拟 Codeforces Round #288 (Div. 2) C. Anya and Ghosts
题目传送门 /* 贪心 + 模拟:首先,如果蜡烛的燃烧时间小于最少需要点燃的蜡烛数一定是-1(蜡烛是1秒点一支), num[g[i]]记录每个鬼访问时已点燃的蜡烛数,若不够,tmp为还需要的蜡烛数, ...
- Codeforces Round #338 (Div. 2) B. Longtail Hedgehog dp
B. Longtail Hedgehog 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/615/problem/B Description This Christma ...
- codeforces 615 B. Longtail Hedgehog (DFS + 剪枝)
题目链接: codeforces 615 B. Longtail Hedgehog (DFS + 剪枝) 题目描述: 给定n个点m条无向边的图,设一条节点递增的链末尾节点为u,链上点的个数为P,则该链 ...
- Codeforces Round #338 (Div. 2) B. Longtail Hedgehog 记忆化搜索/树DP
B. Longtail Hedgehog This Christmas Santa gave Masha a magic picture and a pencil. The picture con ...
- codeforces 704B - Ant Man 贪心
codeforces 704B - Ant Man 贪心 题意:n个点,每个点有5个值,每次从一个点跳到另一个点,向左跳:abs(b.x-a.x)+a.ll+b.rr 向右跳:abs(b.x-a.x) ...
- Longtail Hedgehog(DP)
Longtail Hedgehog time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
随机推荐
- Android基础TOP2_1:输出系统时间
Activity: <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" ...
- jsp 中包含 一个路径为变量的文件
<head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <% String fileroot="MyJsp.jsp ...
- c++枚举变量初始值
#include <iostream> // std::cout, std::boolalpha, std::noboolalpha enum foo { c = -1, a = 1, b ...
- cocos creator destroy方法
node.destroy(),Node.destroyAllChildren并不会立即销毁,实际销毁操作会延迟到当前帧渲染前执行. 这段话可能不明白,但是在Node.destroyAllChildre ...
- 中望CAD VBA检测文件是否存在
Option Explicit Private Declare Function PathFileExists Lib "shlwapi.dll" Alias "Path ...
- IntentService和HandlerThread的使用以及源码阅读
使用MyIntentService.java public class MyIntentService extends IntentService { /** * 是否正在运行 */ private ...
- 通过git向github提交项目
按顺序学习 https://www.cnblogs.com/forget406/p/6045499.html#top https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoputao0903/artic ...
- python爬虫19 | 遇到需要的登录的网站怎么办?用这3招轻松搞定!
你好 由于你是游客 无法查看本文 请你登录再进 谢谢合作 当你在爬某些网站的时候 需要你登录才可以获取数据 咋整? 莫慌 小帅b把这几招传授给你 让你以后从容应对 那么 接下来就是 学习 python ...
- redis 和 memcached的区别
redis和memcached的区别 Redis 和 Memcache 都是基于内存的数据存储系统.Memcached是高性能分布式内存缓存服务:Redis是一个开源的key-value存储系统. ...
- 【模板】RMQ问题 ST表
洛谷3865 #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; ; ...
