<转>SQL Server CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY
Problem
SQL Server 2005 introduced the APPLY operator, which is like a join clause and it allows joining between two table expressions i.e. joining a left/outer table expression with a right/inner table expression. The difference between the join and APPLY operator becomes evident when you have a table-valued expression on the right side and you want this table-valued expression to be evaluated for each row from the left table expression. In this tip I am going to demonstrate the APPLY operator, how it differs fromregular JOINs and some uses.
Solution
The APPLY operator allows you to join two table expressions; the right table expression is processed every time for each row from the left table expression. As you might have guessed, the left table expression is evaluated first and then the right table expression is evaluated against each row of the left table expression for the final result set. The final result set contains all the selected columns from the left table expression followed by all the columns of the right table expression.
SQL Server APPLY operator has two variants; CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY
- The CROSS APPLY operator returns only those rows from the left table expression (in its final output) if it matches with the right table expression. In other words, the right table expression returns rows for the left table expression match only.
- The OUTER APPLY operator returns all the rows from the left table expression irrespective of its match with the right table expression. For those rows for which there are no corresponding matches in the right table expression, it contains NULL values in columns of the right table expression.
- So you might conclude, the CROSS APPLY is equivalent to an INNER JOIN (or to be more precise its like a CROSS JOIN with a correlated sub-query) with an implicit join condition of 1=1 whereas the OUTER APPLY is equivalent to a LEFT OUTER JOIN.
You might be wondering if the same can be achieved with a regular JOIN clause, so why and when do you use the APPLY operator? Although the same can be achieved with a normal JOIN, the need of APPLY arises if you have a table-valued expression on the right part and in some cases the use of the APPLY operator boosts performance of your query. Let me explain with some examples.
Create Sample Data for CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY examples
Script #1 creates a Department table to hold information about departments. Then it creates an Employee table which holds information about the employees. Please note, each employee belongs to a department, hence the Employee table has referential integrity with the Department table.
--Script #1 - Creating some temporary objects to work on... USE [tempdb]
GO IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE OBJECT_ID = OBJECT_ID(N'[Employee]') AND type IN (N'U'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE [Employee]
END
GO IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE OBJECT_ID = OBJECT_ID(N'[Department]') AND type IN (N'U'))
BEGIN
DROP TABLE [Department]
END CREATE TABLE [Department](
[DepartmentID] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[Name] VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
) ON [PRIMARY] INSERT [Department] ([DepartmentID], [Name])
VALUES (1, N'Engineering')
INSERT [Department] ([DepartmentID], [Name])
VALUES (2, N'Administration')
INSERT [Department] ([DepartmentID], [Name])
VALUES (3, N'Sales')
INSERT [Department] ([DepartmentID], [Name])
VALUES (4, N'Marketing')
INSERT [Department] ([DepartmentID], [Name])
VALUES (5, N'Finance')
GO CREATE TABLE [Employee](
[EmployeeID] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[FirstName] VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
[LastName] VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
[DepartmentID] [int] NOT NULL REFERENCES [Department](DepartmentID),
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO INSERT [Employee] ([EmployeeID], [FirstName], [LastName], [DepartmentID])
VALUES (1, N'Orlando', N'Gee', 1 )
INSERT [Employee] ([EmployeeID], [FirstName], [LastName], [DepartmentID])
VALUES (2, N'Keith', N'Harris', 2 )
INSERT [Employee] ([EmployeeID], [FirstName], [LastName], [DepartmentID])
VALUES (3, N'Donna', N'Carreras', 3 )
INSERT [Employee] ([EmployeeID], [FirstName], [LastName], [DepartmentID])
VALUES (4, N'Janet', N'Gates', 3 )
SQL Server CROSS APPLY vs INNER JOIN example
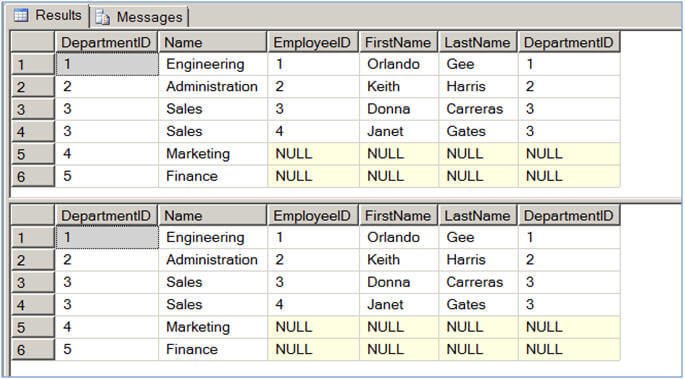
The first query in Script #2 selects data from the Department table and uses a CROSS APPLY to evaluate the Employee table for each record of the Department table. The second query simply joins the Department table with the Employee table and all matching records are produced.
--Script #2 - CROSS APPLY and INNER JOIN SELECT * FROM Department D
CROSS APPLY
(
SELECT * FROM Employee E
WHERE E.DepartmentID = D.DepartmentID
) A
GO SELECT * FROM Department D
INNER JOIN Employee E ON D.DepartmentID = E.DepartmentID
GO
f you look at the results, you can see see they are the same.

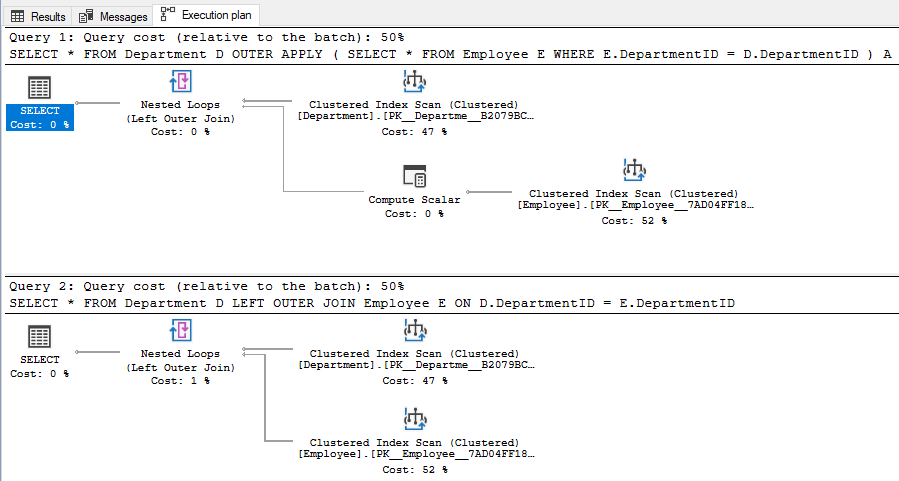
Also, the execution plans for these queries are similar and they have an equal query cost, as you can see in the image below.

So what is the use of APPLY operator? How does it differ from a JOIN and how does it help in writing more efficient queries? I will discuss this later.
SQL Sever OUTER APPLY vs LEFT OUTER JOIN example
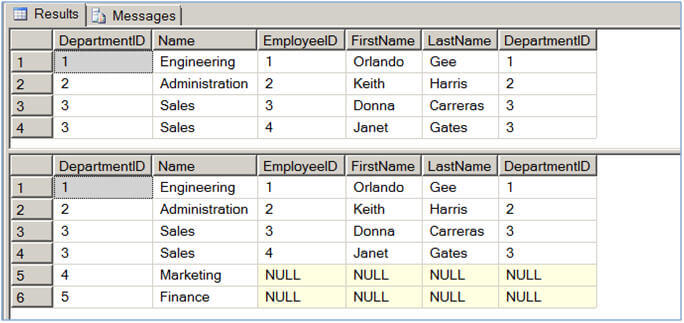
The first query in Script #3 selects data from Department table and uses an OUTER APPLY to evaluate the Employee table for each record of the Department table. For those rows for which there is not a match in the Employee table, those rows contain NULL values as you can see in case of row 5 and 6 below. The second query simply uses a LEFT OUTER JOIN between the Department table and the Employee table. As expected the query returns all rows from Department table, even for those rows for which there is no match in the Employee table.
--Script #3 - OUTER APPLY and LEFT OUTER JOIN SELECT * FROM Department D
OUTER APPLY
(
SELECT * FROM Employee E
WHERE E.DepartmentID = D.DepartmentID
) A
GO SELECT * FROM Department D
LEFT OUTER JOIN Employee E ON D.DepartmentID = E.DepartmentID
GO
Even though the above two queries return the same information, the execution plan is a bit different. Although cost wise there is not much difference, the query with the OUTER APPLY uses a Compute Scalar operator (with estimated operator cost of 0.0000103 or around 0%) before the Nested Loops operator to evaluate and produce the columns of the Employee table.
Joining table valued functions and tables using APPLY operators
In Script #4, I am creating a table-valued function which accepts DepartmentID as its parameter and returns all the employees who belong to this department. The next query selects data from the Department table and uses a CROSS APPLY to join with the function we created. It passes the DepartmentID for each row from the outer table expression (in our case Department table) and evaluates the function for each row similar to a correlated subquery. The next query uses the OUTER APPLY in place of the CROSS APPLY and hence unlike the CROSS APPLY which returned only correlated data, the OUTER APPLY returns non-correlated data as well, placing NULLs into the missing columns.
--Script #4 - APPLY with table-valued function IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE OBJECT_ID = OBJECT_ID(N'[fn_GetAllEmployeeOfADepartment]') AND type IN (N'IF'))
BEGIN
DROP FUNCTION dbo.fn_GetAllEmployeeOfADepartment
END
GO CREATE FUNCTION dbo.fn_GetAllEmployeeOfADepartment(@DeptID AS INT)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN
(
SELECT * FROM Employee E
WHERE E.DepartmentID = @DeptID
)
GO SELECT * FROM Department D
CROSS APPLY dbo.fn_GetAllEmployeeOfADepartment(D.DepartmentID)
GO SELECT * FROM Department D
OUTER APPLY dbo.fn_GetAllEmployeeOfADepartment(D.DepartmentID)
GO
 ]]
]]
You might be wondering if we can use a simple join in place of the above queries, the answer is NO. If you replace the CROSS/OUTER APPLY in the above queries with an INNER JOIN/LEFT OUTER JOIN, specifying the ON clause with 1=1 and run the query, you will get the error "The multi-part identifier "D.DepartmentID" could not be bound.". This is because with JOINs the execution context of the outer query is different from the execution context of the function (or a derived table), and you cannot bind a value/variable from the outer query to the function as a parameter. Hence the APPLY operator is required for such queries.
So in summary the APPLY operator is required when you have to use a table-valued function in the query, but it can also be used with inline SELECT statements.
Joining table valued system functions and tables using APPLY operators
Let me show you another query with a Dynamic Management Function (DMF). Script #5 returns all the currently executing user queries except for the queries being executed by the current session. As you can see in the script below, the sys.dm_exec_requestsdynamic management view is being CROSS APPLY'ed with the sys.dm_exec_sql_text dynamic management function which accepts a "plan handle" for the query and the "plan handle" is being passed from the left/outer expression to the function to return the data.
--Script #5 - APPLY with Dynamic Management Function (DMF) USE master
GO SELECT DB_NAME(r.database_id) AS [Database], st.[text] AS [Query]
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests r
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(r.plan_handle) st
WHERE r.session_Id > 50 -- Consider spids for users only, no system spids.
AND r.session_Id NOT IN (@@SPID) -- Don't include request from current spid.
Note, for the above query, the [text] column in the query returns all queries submitted in a batch. If you want to see only the active (currently executing) query you can use the statement_start_offset and statement_end_offset columns to trim the active part of the query. Refer to this tip How to isolate the current running commands in SQL Server for a good example.
Other Notes
As I told you before there are certain scenarios where a query with an APPLY operator performs better than a query with regular joins. I am not going to delve into much details rather here are some articles that discuss this topic in greater detail.
Please note, the APPLY operator is not an ANSI operator but rather an extension of SQL Server T-SQL (available in SQL Server 2005 and later), so if you plan to port your database to some other DBMS take this into consideration.
<转>SQL Server CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY的更多相关文章
- sql server cross/outer apply 用法
这是 sql server 帮助文档关于apply的描述: 使用 APPLY 运算符(2005或以上版本)可以为实现查询操作的外部表表达式返回的每个行调用表值函数.表值函数作为右输入,外部表表达式作为 ...
- SQL Server连接查询之Cross Apply和Outer Apply的区别及用法(转载)
先简单了解下cross apply的语法以及会产生什么样的结果集吧!示例表: SELECT * FROM tableA CROSS APPLY tableB 两张表直接连接,不需要任何的关联条件,产生 ...
- SQL Server中CROSS APPLY和OUTER APPLY应用
1.什么是Cross Apply和Outer Apply ? 我们知道SQL Server 2000中有Cross Join用于交叉联接的.实际上增加Cross Apply和Outer Apply是用 ...
- SQL Server 关于CROSS APPLY 和 OUTER APPLY应用
先看看语法: <left_table_expression> {cross|outer} apply<right_table_expression> 再让我们了解一下appl ...
- SQL SERVER使用 CROSS APPLY 与 OUTER APPLY 连接查询
概述 CROSS APPLY 与 OUTER APPLY 可以做到: 左表一条关联右表多条记录时,我需要控制右表的某一条或多条记录跟左表匹配的情况. 有两张表:Student(学生表)和 S ...
- SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 outer apply
SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 outer apply 例子: CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Customers]( ) COLLATE Chinese_PRC_ ...
- SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 outer apply(转)
转载链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/shuangnet/archive/2013/04/02/2995798.html apply有两种形式: cross apply 和 oute ...
- SQL关于apply的两种形式cross apply和outer apply(转载)
SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 outer apply apply有两种形式: cross apply 和 outer apply 先看看语法: <lef ...
- 转:SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 outer apply
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Leo_wl/archive/2013/04/02/2997012.html SQL 关于apply的两种形式cross apply 和 out ...
随机推荐
- html-定位
概述: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8 ...
- miniui中可以设置是否让页面进行分页 <div id="datagrid1" class="mini-datagrid" style="width:100%" allowAlternating="true" showpager="true"/> 就是设置showpager属性为true
<div id="datagrid1" class="mini-datagrid" style="width:100%" allowA ...
- Scala-Unit-2-Scala基础语法1
一.Scala程序的开始->HelloScala 这里的操作如同java的helloworld程序,直接放代码! object HelloScala{ def main(args:Array[S ...
- HDU 3861 The King’s Problem (强连通缩点+DAG最小路径覆盖)
<题目链接> 题目大意: 一个有向图,让你按规则划分区域,要求划分的区域数最少. 规则如下:1.所有点只能属于一块区域:2,如果两点相互可达,则这两点必然要属于同一区域:3,区域内任意两点 ...
- PhantomJS在Selenium中被标记为过时的应对措施
今天使用PhantomJS时,Selenium提示PhantomJS被标记不赞成,我就蒙了.PhantomJS可是Headless浏览器中相当知名的一款,标记为过时,代表着将在未来版本摒弃掉这个支持. ...
- 【ABP】ABP跨域调用API时出现的问题
public override void Initialize() { IocManager.RegisterAssemblyByConvention(Assembly.GetExecutingAss ...
- QtQuick自定义主题以及控件样式指引
自定义控件样式 请在Qt帮助索引中输入Customizing a Control进行查看 不过实际用下来感觉除非你想自己实现一套效果复杂的UI或是创造一个全新控件,比如:给UI添加模糊.虚化等Shad ...
- Codeforces Round #538 (Div. 2)
目录 Codeforces 1114 A.Got Any Grapes? B.Yet Another Array Partitioning Task C.Trailing Loves (or L'oe ...
- C语言实现密码修改
/* *修改密码 *描述: *1.本来已经存在密码 *2.很多时候需要输入两次密码,对比是否正确,才能确认修改密码正确 *敲代码思路: *1.输入旧的密码判断是否正确 *2.提示输入修改后的密码 *3 ...
- 获取当前泛型类的传入,BaseDaoImpl<T> implements BaseDao<T>
public abstract class BaseDaoImpl<T> implements BaseDao<T> { private Class<T> claz ...
