dubbo服务引用与集群容错
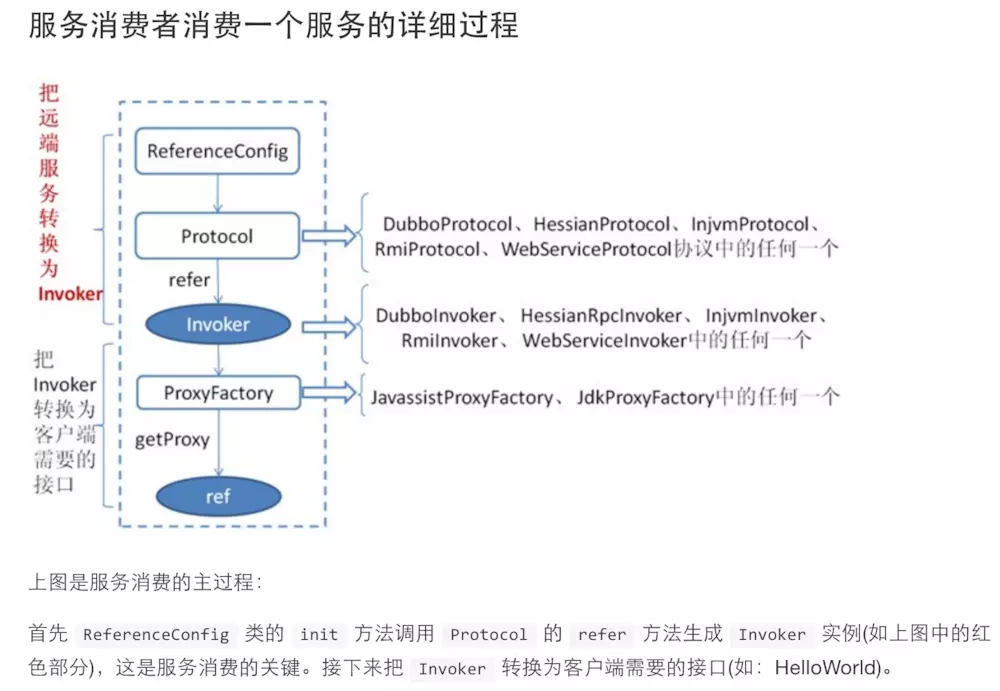
服务引用无非就是做了两件事
将spring的schemas标签信息转换bean,然后通过这个bean的信息,连接、订阅zookeeper节点信息创建一个
invoker将
invoker的信息创建一个动态代理对象
时序图:
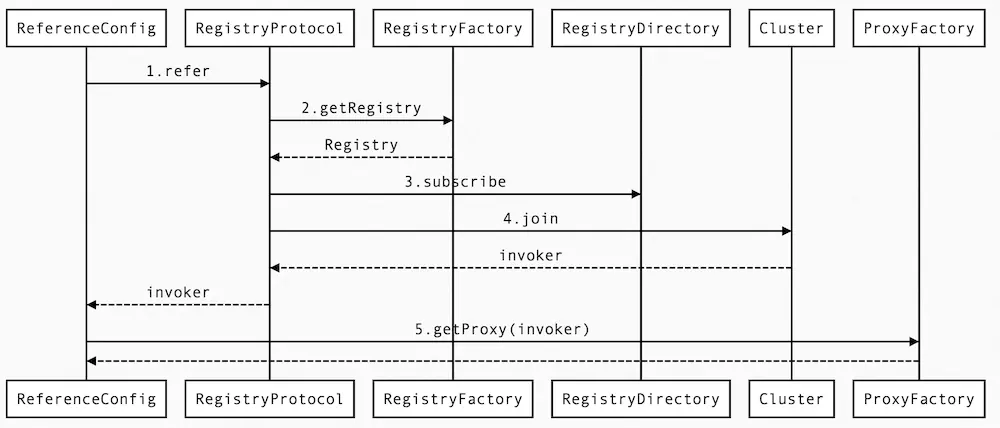
最终返回一个被调用接口的动态代理对象。
在调用代理对象的方法时,会进入InvokerInvocationHandle类的逻辑。
跟踪源码的时候,发现消费端调用invoke的时候要调用一连串的Invoker实现类,一直纠结这些Invoker是用来做什么的?
Invoker的创建应该是入口,也就是从referenceConfig类开始
然后找到RegistryProtocol.doRefer方法
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.getLocalHost(), 0, type.getName(), directory.getUrl().getParameters());
if (! Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())
&& url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)));
}
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY,
Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
return cluster.join(directory);
}
也就是这一行:
cluster.join(directory);
但是调试发现第一步创建的实例化对象是MockClusterWrapper类而不是FailoverCluster
但是ExtensionLoader在实例化对象时,有个比较特殊的地方,那就是在实例化完成之后,会自动套上当前的ExtensionLoader中的Wrapper类,上面的mock所对应的MockClusterWrapper就是这样的一个Wrapper:也就是实例化出来的FailoverCluster会被套上一层MockClusterWrapper,总结一下就是:
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) {
//no mock
//执行到这一行的时候开始进入集群 cluster -> AbstractClusterInvoker
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
//fail-mock
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
} else {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl(), e);
}
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
}
return result;
}
AbstractClusterInvoker.java
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
// binding attachments into invocation.
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
//选择出可用的invoker集合
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
// 初始化负载均衡策略
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
protected List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// -> AbstractDirectory.java
return directory.list(invocation);
}
AbstractDirectory.java
public List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (destroyed) {
throw new RpcException("Directory already destroyed .url: " + getUrl());
}
// 模板方法,由子类实现
// -> RegistryDirectory.java 或者 StaticDirectory.java
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = doList(invocation);
List<Router> localRouters = this.routers; // local reference
if (localRouters != null && !localRouters.isEmpty()) {
for (Router router : localRouters) {
try {
if (router.getUrl() == null || router.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.RUNTIME_KEY, false)) {
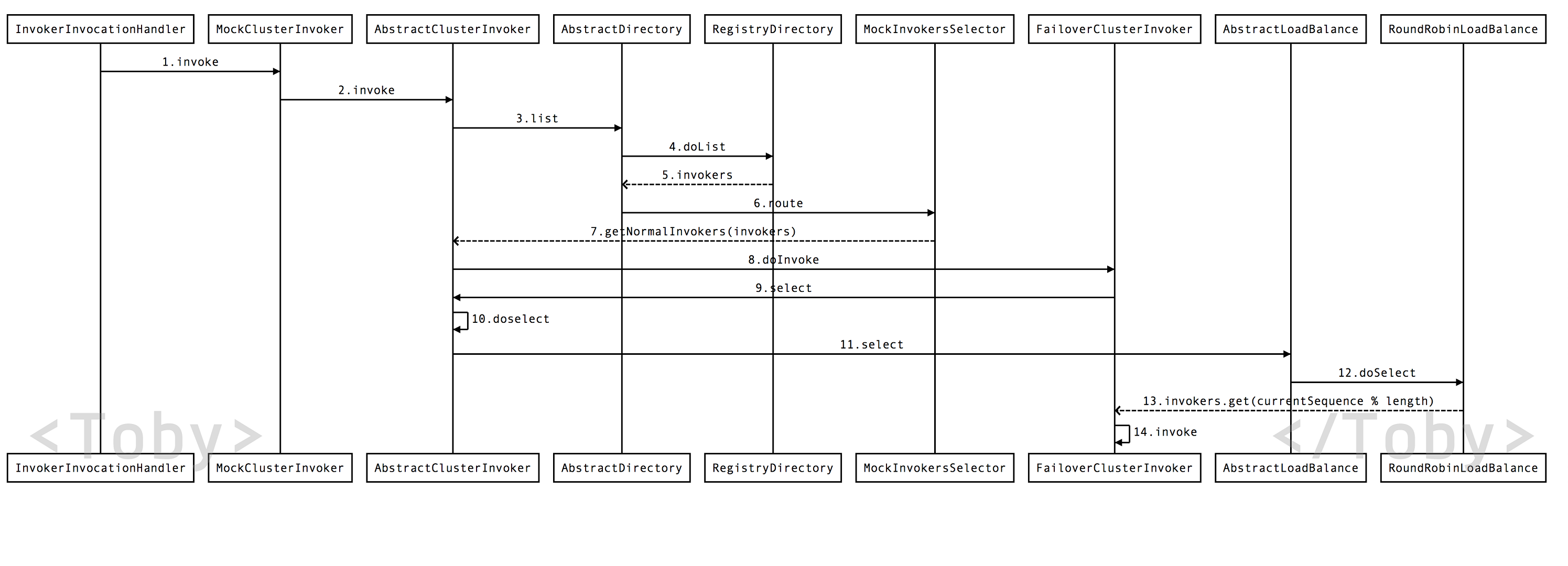
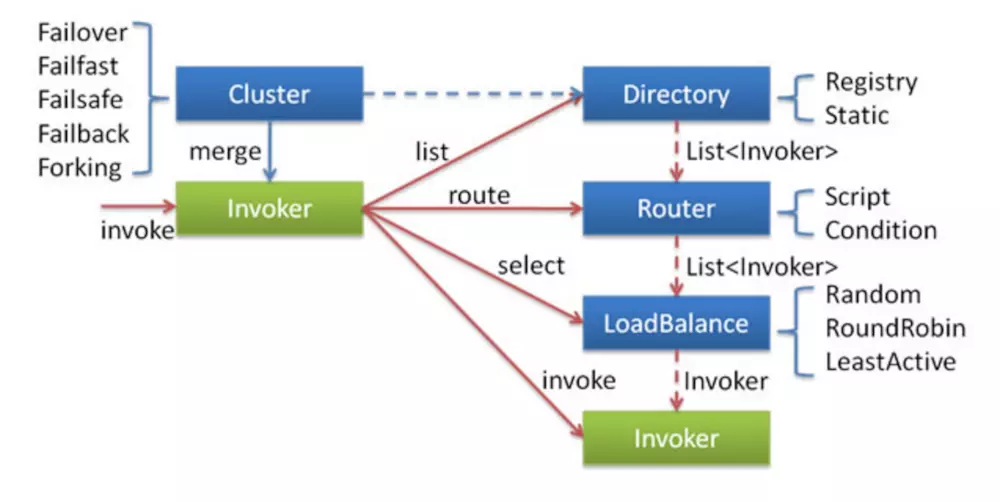
//将invokers返回后,下面来到了Router,开始进入路由,现在我们到了序号6,此时到了MockInvokersSelector类,
//他是Router接口的实现类,从官网的介绍图中我们也可以看到Router分为Script和Condition两种,翻译过来也就是脚本路由和条件路由
invokers = router.route(invokers, getConsumerUrl(), invocation);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to execute router: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
return invokers;
}
RegistryDirectory.java
public List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
// 1. No service provider 2. Service providers are disabled
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION,
"No provider available from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " for service " + getConsumerUrl().getServiceKey() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please check status of providers(disabled, not registered or in blacklist).");
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // The routing can be enumerated according to the first parameter
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if (invokers == null) {
Iterator<List<Invoker<T>>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(0) : invokers;
}
MockInvokersSelector.java
public <T> List<Invoker<T>> route(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers,
URL url, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (invocation.getAttachments() == null) {
return getNormalInvokers(invokers);
} else {
String value = invocation.getAttachments().get(Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK);
if (value == null) {
//拿到能正常执行的invokers,并将其返回
return getNormalInvokers(invokers);
} else if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
return getMockedInvokers(invokers);
}
}
return invokers;
} private <T> List<Invoker<T>> getNormalInvokers(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
if (!hasMockProviders(invokers)) {
return invokers;
} else {
List<Invoker<T>> sInvokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(invokers.size());
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (!invoker.getUrl().getProtocol().equals(Constants.MOCK_PROTOCOL)) {
sInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
return sInvokers;
}
}
在Router中,将上一步的全部invokers挑选出能正常执行的invokers
......
//选择出可用的invoker集合
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
// 初始化负载均衡策略
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
在集群调用失败时,Dubbo 提供了多种容错方案,缺省为 failover 重试。
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
// retry loop.
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
// check again
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
// 通过负载均衡算法选择一个Invoker,然后调用
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "Failed to invoke the method "
+ methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
+ Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
}
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY);
{
//ignore overloaded method
if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore concurrency problem
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
}
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (sticky) {
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//If the `invoker` is in the `selected` or invoker is unavailable && availablecheck is true, reselect.
if ((selected != null && selected.contains(invoker))
|| (!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null && availablecheck)) {
try {
Invoker<T> rinvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck);
if (rinvoker != null) {
invoker = rinvoker;
} else {
//Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
//Avoid collision
invoker = index < invokers.size() - 1 ? invokers.get(index + 1) : invokers.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t);
}
}
return invoker;
}
dubbo服务引用与集群容错的更多相关文章
- Dubbo 源码分析 - 集群容错之 LoadBalance
1.简介 LoadBalance 中文意思为负载均衡,它的职责是将网络请求,或者其他形式的负载"均摊"到不同的机器上.避免集群中部分服务器压力过大,而另一些服务器比较空闲的情况.通 ...
- Dubbo 源码分析 - 集群容错之 Cluster
1.简介 为了避免单点故障,现在的应用至少会部署在两台服务器上.对于一些负载比较高的服务,会部署更多台服务器.这样,同一环境下的服务提供者数量会大于1.对于服务消费者来说,同一环境下出现了多个服务提供 ...
- Dubbo 源码分析 - 集群容错之 Router
1. 简介 上一篇文章分析了集群容错的第一部分 -- 服务目录 Directory.服务目录在刷新 Invoker 列表的过程中,会通过 Router 进行服务路由.上一篇文章关于服务路由相关逻辑没有 ...
- Dubbo 源码分析 - 集群容错之 Directory
1. 简介 前面文章分析了服务的导出与引用过程,从本篇文章开始,我将开始分析 Dubbo 集群容错方面的源码.这部分源码包含四个部分,分别是服务目录 Directory.服务路由 Router.集群 ...
- Dubbo工作原理,集群容错,负载均衡
Remoting:网络通信框架,实现了sync-over-async和request-response消息机制. RPC:一个远程过程调用的抽象,支持负载均衡.容灾和集群功能. Registry:服务 ...
- Dubbo负载均衡与集群容错机制
1 Dubbo简介 Dubbo是一款高性能.轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现. 作为一个轻量级RPC框架,D ...
- dubbo源码分析- 集群容错之Cluster(一)
1.集群容错的配置项 failover - 失败自动切换,当出现失败,重试其他服务器(缺省),通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长的延时. failfast - 快速失效,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错.通 ...
- Dubbo的10种集群容错模式
学习Dubbo源码的过程中,首先看到的是dubbo的集群容错模式,以下简单介绍10种集群容错模式 1.AvailableCluster 顾名思义,就是可用性优先,遍历所有的invokers,选择可用的 ...
- kubernetes实战-交付dubbo服务到k8s集群(六)使用blue ocean流水线构建dubbo-consumer服务
我们这里的dubbo-consumer是dubbo-demo-service的消费者: 我们之前已经在jenkins配置好了流水线,只需要填写参数就行了. 由于dubbo-consumer用的gite ...
随机推荐
- windows server2012部署apache项目访问后台管理系统时tomcat就停了是怎么回事
是由于环境变量没有配好的原因,找不到jre目录 tomcat的运行需要JRE,一般启动闪退都是因为找不到JRE,也就是说环境安装JDK时环境变量没有配置好. 我们首先打开”命令提示符“窗口,输入jav ...
- io.fabric8.kubernetes对pv和pvc的增删查改
1.新建maven项目k8stest,pom.xml如下: <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns: ...
- UVa 1025 A Spy in the Metro (DP动态规划)
题意:一个间谍要从第一个车站到第n个车站去会见另一个,在是期间有n个车站,有来回的车站,让你在时间T内时到达n,并且等车时间最短, 也就是尽量多坐车,最后输出最少等待时间. 析:这个挺复杂,首先时间是 ...
- HDU 1286 找新朋友 (欧拉phi函数打表)
题意:你懂得. 析:一看这个题应该是欧拉phi函数,也就说欧拉phi函数是指求从 1 到 n 中与 n 互素的数的个数,这个题很明显是这个意思嘛,不多说了. 代码如下: #include <io ...
- HITS
HITS 1 概述 HITS(hypertext induced topic search)超链接归纳主题搜索是由kleinbers在90年代提出的基于链接分析的网页排名算法.Hits算法是利用Hub ...
- (一)ElasticSearch-入门
目录:一.前言二.安装三.索引四.搜索五.聚合六.分布式的特性 一.前言Elasticsearch是一个基于Apache Lucene(TM)的开源搜索引擎.无论在开源还是专有领域,Lucene可以被 ...
- [C#学习笔记]C#中的decimal类型——《CLR via C#》
System.Decimal是非常特殊的类型.在CLR中,Decimal类型不是基元类型.这就意味着CLR没有知道如何处理Decimal的IL指令. 在文档中查看Decimal类型,可以看到它提供了一 ...
- 利用反射(Reflection)处理对象
创建一个学生类: public class Student { public int Id { set; get; } public string Name { set; get; } public ...
- 【cocos2d-x 手游研发小技巧(3)Android界面分辨率适配方案】
先感叹一下吧~~android的各种分辨率各种适配虐我千百遍,每次新项目我依旧待它如初恋···· 每家公司都有自己项目工程适配的方案,这种东西就是没有最好,只有最适合!!! 这次新项目专项针对andr ...
- DOS文件操作命令
内部命令 COPY---文件固执命令 格式:COPY [源盘:][路径]<源文件名> [目标盘][路径]<目标文件名> 拷贝一个或多个文件到指定盘上 1)COPY是文件对文件的 ...
