HDU 3103 Shoring Up the Levees(计算几何 搜寻区域)
主题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3103
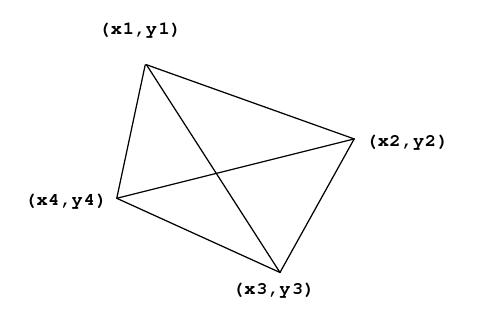
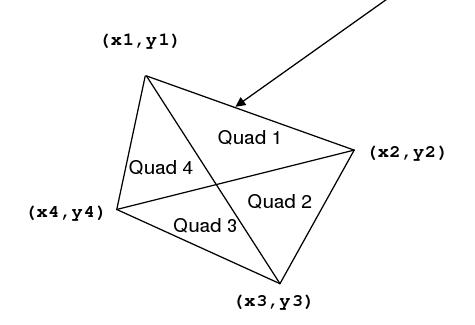
The quadrilateral is defined by four vertices. The levees partition the country into four quadrants. Each quadrant is identified by a pair of vertices representing the outside edge of that quadrant. For example, Quadrant 1 shown below is defined by the points
(x1, y1) and (x2, y2) .
It happens very often that the country of Waterlogged becomes flooded, and the levees need to be reinforced, but their country is poor and they have limited resources. They would like to be able to reinforce those levees that encompass the largest area first,
then the next largest second, then the next largest third, and the smallest area fourth.
Help Waterlogged identify which quadrants are the largest, and the length of the levees around them.
X1 Y1 X2 Y2 X3 Y3 X4 Y4
The four points are guaranteed to form a convex quadrilateral when taken in order -- that is, there will be no concavities, and no lines crossing. Every number will be in the range from -1000.0 to 1000.0 inclusive. No Quadrant will have an area or a perimeter
smaller than 0.001. End of the input will be a line with eight 0.0's.
A1 P1 A2 P2 A3 P3 A4 P4
Print them in order from largest area to smallest -- so A1 is the largest area. If two Quadrants have the same area when rounded to 3 decimal places, output the one with the largest perimeter first. Print all values with 3 decimal places of precision (rounded).
Print spaces between numbers. Do not print any blank lines between outputs.
1 2 1 5 5 2 2 0
3.5 2.2 4.8 -9.6 -1.2 -4.4 -8.9 12.4
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
5.100 11.459 3.400 9.045 0.900 6.659 0.600 4.876
44.548 38.972 21.982 25.997 20.342 38.374 10.038 19.043
题意:
给出四个点,连接对角线后,分为四个象限。依照面积大小依次输出,假设面积同样则依照周长大小输出(注意:比較面积是否同样是比較保留了三位后是否同样);
代码例如以下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-5;
const double PI = acos(-1.0); struct point
{
double x, y;
};
struct gao
{
double mz,zc;
};
struct gao gg[10]; bool cmp(gao a,gao b)
{
if(a.mz!=b.mz)
return a.mz>b.mz;
return a.zc>b.zc;
}
double xmult(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x0,double y0)
{
return (x1-x0)*(y2-y0)-(x2-x0)*(y1-y0);
} //判两点在线段同側,点在线段上返回0
int same_side(point p1,point p2,point l1,point l2)
{
return xmult(l1.x,l1.y,p1.x,p1.y,l2.x,l2.y)*xmult(l1.x,l1.y,p2.x,p2.y,l2.x,l2.y)>0;
} //两点距离
double dis(point a,point b)
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
//两线段的交点
point intersection(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2)
{
point ret=u1;
double t=((u1.x-v1.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-v1.y)*(v1.x-v2.x))
/((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-u2.y)*(v1.x-v2.x));
ret.x+=(u2.x-u1.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u2.y-u1.y)*t;
return ret;
} //三点面积
double aera(point a,point b,point c)
{
double aa,bb,cc,q;
aa=dis(c,b);
bb=dis(a,c);
cc=dis(b,a);
q=(aa+bb+cc)/2;
double h=sqrt(q*(q-aa)*(q-bb)*(q-cc));
h=(int)(h*1000+0.5);
return h*0.001;
} //三点周长
double get_zc(point a,point b,point c)
{
double aa,bb,cc,q;
aa=dis(c,b);
bb=dis(a,c);
cc=dis(b,a);
q=(aa+bb+cc);
return q;
} int main()
{
int i;
double x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4;
point a,b,c,d,e;
while(scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2,&x3,&y3,&x4,&y4)!=EOF)
{
if(x1==0 && y1==0 && x2==0 && y2==0 && x3==0 && y3==0 && x4==0 && y4==0)
break;
a.x=x1;
a.y=y1;
b.x=x2;
b.y=y2;
c.x=x3;
c.y=y3;
d.x=x4;
d.y=y4;
if(same_side(a, b, c,d)==0)
e = intersection(d,c,a,b);
else if(same_side(d, b, c, a)==0)
e = intersection(d,b,c,a);
else
e = intersection(b,c,d,a);
gg[0].mz=aera(a,b,e);
gg[1].mz=aera(b,c,e);
gg[2].mz=aera(c,d,e);
gg[3].mz=aera(a,d,e);
gg[0].zc=get_zc(a,b,e);
gg[1].zc=get_zc(b,c,e);
gg[2].zc=get_zc(c,d,e);
gg[3].zc=get_zc(a,d,e);
sort(gg,gg+4,cmp);
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
printf("%.3lf %.3lf ",gg[i].mz,gg[i].zc);
printf("%.3lf %.3lf\n",gg[i].mz,gg[i].zc);
}
return 0;
}
/*
2 0 2 2 0 2 0 0
*/
版权声明:本文博主原创文章,博客,未经同意不得转载。
HDU 3103 Shoring Up the Levees(计算几何 搜寻区域)的更多相关文章
- HDU 5572 An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何+对称点模板)
HDU 5572 An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何) 题目链接http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5572 Descripti ...
- hdu 1115:Lifting the Stone(计算几何,求多边形重心。 过年好!)
Lifting the Stone Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- HDU 6697 Closest Pair of Segments (计算几何 暴力)
2019 杭电多校 10 1007 题目链接:HDU 6697 比赛链接:2019 Multi-University Training Contest 10 Problem Description T ...
- HDU 1392 Surround the Trees(凸包*计算几何)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1392 这里介绍一种求凸包的算法:Graham.(相对于其它人的解释可能会有一些出入,但大体都属于这个算 ...
- HDU 3264 Open-air shopping malls (计算几何-圆相交面积)
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3264 题意:给你n个圆,坐标和半径,然后要在这n个圆的圆心画一个大圆,大圆与这n个圆相交的面积必须大于等 ...
- hdu 1392:Surround the Trees(计算几何,求凸包周长)
Surround the Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 1140:War on Weather(计算几何,水题)
War on Weather Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
- hdu 2857:Mirror and Light(计算几何,点关于直线的对称点,求两线段交点坐标)
Mirror and Light Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 1756:Cupid's Arrow(计算几何,判断点在多边形内)
Cupid's Arrow Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
随机推荐
- plist文件读写
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; NSDictionary *dictionary1 = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithO ...
- http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?打开很慢解决方案
最近, 在写一个demo的时候突然发现加载超级慢, 寻找之下发现了"罪魁祸首", 系引用了http://fonts.googleapis.com/css. 接着在网上看到有网友反映 ...
- MySQL 改动用户password及重置rootpassword
为数据库用户改动password是DBA比較常见的工作之中的一个.对于MySQL用户账户的password改动,有几种不同的方式.推荐的方式使用加密函数来改动password. 本文主要描写叙述了通过 ...
- html网页特殊符号代码
HTML特殊字符编码大全:往网页中输入特殊字符,需在html代码中加入以&开头的字母组合或以&#开头的数字.下面就是以字母或数字表示的特殊符号大全. ...
- linux free
在Linux下查看内存我们一般用command free [root@nonamelinux ~]# free total used free s ...
- git pull VS git fetch&merge(good)
从图中可以看到,git fetch和git pull的区别, git fetch 不会自动的将结果merge到本地,只是将远程版本同步到本地版本库,而不会merge到本地副本. git pull 将 ...
- Axuer 网页
http://www.webppd.com/axure/
- Linux 下卸载MySQL 5
对于在Linux下通过rpm方式的mysql,我们能够通过移除这些rpm包以及删除项目的文件夹来达到卸载的目的.本文演示了在SUSE Linux 10下下载MySQL 5.5.37.详细见下文. 1. ...
- windows azure Vm、cloud service、web application 如何选择可用的服务
windows azure 的web应用和虚拟机都经常用.我们经常把我们的网站部署上去.一般选择web应用或者开一个虚拟机.开一个虚拟机就会按照虚拟机的使用时间进行计费. 那么我们选择web部署在哪里 ...
- sql中 in 、not in 、exists、not exists 使用方法和区别
% 的一类. NOT IN:通过 NOT IN keyword引入的子查询也返回一列零值或很多其它值. 以下查询查找没有出版过商业书籍的出版商的名称. SELECT pub_name FROM pub ...
