CodeForces 228D. Zigzag(线段树暴力)
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The court wizard Zigzag wants to become a famous mathematician. For that, he needs his own theorem, like the Cauchy theorem, or his sum, like the Minkowski sum. But most of all he wants to have his sequence, like the Fibonacci sequence, and his function, like
the Euler's totient function.
The Zigag's sequence with the zigzag factor z is an infinite sequence Siz (i ≥ 1; z ≥ 2),
that is determined as follows:
- Siz = 2,
when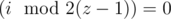 ;
; 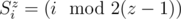 ,
,
when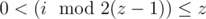 ;
; ,
,
when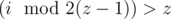 .
.
Operation  means
means
taking the remainder from dividing number x by number y.
For example, the beginning of sequence Si3(zigzag
factor 3) looks as follows: 1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1.
Let's assume that we are given an array a, consisting of n integers.
Let's define element number i (1 ≤ i ≤ n) of
the array as ai.
The Zigzag function is function 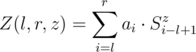 ,
,
where l, r, z satisfy the inequalities 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, z ≥ 2.
To become better acquainted with the Zigzag sequence and the Zigzag function, the wizard offers you to implement the following operations on the given array a.
- The assignment operation. The operation parameters are (p, v). The operation denotes assigning value v to
the p-th array element. After the operation is applied, the value of the array element ap equals v. - The Zigzag operation. The operation parameters are (l, r, z). The operation denotes calculating the Zigzag function Z(l, r, z).
Explore the magical powers of zigzags, implement the described operations.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) —
The number of elements in array a. The second line contains n space-separated
integers: a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) —
the elements of the array.
The third line contains integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 105) —
the number of operations. Next m lines contain the operations' descriptions. An operation's description starts with integer ti (1 ≤ ti ≤ 2) —
the operation type.
- If ti = 1 (assignment
operation), then on the line follow two space-separated integers: pi, vi (1 ≤ pi ≤ n; 1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) —
the parameters of the assigning operation. - If ti = 2 (Zigzag
operation), then on the line follow three space-separated integers: li, ri, zi (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ n; 2 ≤ zi ≤ 6) —
the parameters of the Zigzag operation.
You should execute the operations in the order, in which they are given in the input.
For each Zigzag operation print the calculated value of the Zigzag function on a single line. Print the values for Zigzag functions in the order, in which they are given in the input.
Please, do not use the %lld specifier to read or write 64-bit integers in С++. It is preferred to use cin, cout streams
or the %I64dspecifier.
5
2 3 1 5 5
4
2 2 3 2
2 1 5 3
1 3 5
2 1 5 3
5
26
38
Explanation of the sample test:
- Result of the first operation is Z(2, 3, 2) = 3·1 + 1·2 = 5.
- Result of the second operation is Z(1, 5, 3) = 2·1 + 3·2 + 1·3 + 5·2 + 5·1 = 26.
- After the third operation array a is equal to 2, 3, 5, 5, 5.
- Result of the forth operation is Z(1, 5, 3) = 2·1 + 3·2 + 5·3 + 5·2 + 5·1 = 38.
大致思路:Z从2到6,按循环节分别维护一棵线段树,一共维护30棵线段树。查询复杂度logn的。改动的复杂度是30*logn
时限3s,毕竟codeforces可过
//137924k 1372ms GNU G++ 4.9.2 2761B
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
#define ALL(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
#define foreach(i, v) for (__typeof((v).begin()) i = (v).begin(); i != (v).end(); ++ i)
#define REP(i,n) for ( int i=1; i<=int(n); i++ )
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll; #define root 1,n,1
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
const int N = 1e5+100;
ll sum[35][N<<2];
ll val[N],mul[35][N];
int n; inline void pushup(int rt,ll *sum)
{
sum[rt] = sum[rt<<1]+sum[rt<<1|1];
}
void build(int l,int r,int rt,ll sum[],ll mul[])
{
if(l == r)
{
sum[rt] = val[l]*mul[l];
return ;
}
int m = (l+r)>>1;
build(lson,sum,mul);
build(rson,sum,mul);
pushup(rt,sum);
}
void update(int pos,ll x,int l,int r,int rt,ll sum[],ll mul[])
{
if(l == r)
{
sum[rt] = x*mul[l];
return ;
}
int m = (l+r)>>1;
if(pos <= m) update(pos,x,lson,sum,mul);
else update(pos,x,rson,sum,mul);
pushup(rt,sum);
}
ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt,ll sum[])
{
if(L <= l && r <= R)
{
return sum[rt];
}
ll ans = 0;
int m = (l+r)>>1;
if(L <= m) ans += query(L,R,lson,sum);
if(R > m) ans += query(L,R,rson,sum);
return ans;
} inline int getid(int l,int z)
{
int buf = 0;
REP(i,z-2) buf += 2*i;
int k = 2*(z-1);
l = (l-1)%k+1;
if(l == 1) return l+buf;
return k-l+2+buf;
} int main()
{
//......................
ll a[15];
a[1] = 1,a[2] = 2;
REP(i,2)REP(j,N-10) mul[i][j] = a[(j-1+i-1)%2+1];
a[3] = 3,a[4] = 2;
REP(i,4)REP(j,N-10) mul[2+i][j] = a[(j-1+i-1)%4+1];
a[4] = 4,a[5] = 3,a[6] = 2;
REP(i,6)REP(j,N-10) mul[6+i][j] = a[(j-1+i-1)%6+1];
a[5] = 5,a[6] = 4,a[7] = 3,a[8] = 2;
REP(i,8)REP(j,N-10) mul[12+i][j] = a[(j-1+i-1)%8+1];
a[6] = 6,a[7] = 5,a[8] = 4,a[9] = 3,a[10] = 2;
REP(i,10)REP(j,N-10) mul[20+i][j] = a[(j-1+i-1)%10+1];
//....................... cin>>n;
REP(i,n) scanf("%I64d",&val[i]);
REP(i,30) build(root,sum[i],mul[i]);
int Q;
cin>>Q;
REP(i,Q)
{
int op;
scanf("%d",&op);
if(op == 1)
{
int pos;ll x;
scanf("%d%I64d",&pos,&x);
REP(i,30) update(pos,x,root,sum[i],mul[i]);
}
else
{
int l,r,z;
scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&r,&z);
int id = getid(l,z);
printf("%I64d\n",query(l,r,root,sum[id]));
}
}
}
CodeForces 228D. Zigzag(线段树暴力)的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence (线段树 暴力)
传送门 题目大意: 给你一个序列,要求在序列上维护三个操作: 1)区间求和 2)区间取模 3)单点修改 这里的操作二很讨厌,取模必须模到叶子节点上,否则跑出来肯定是错的.没有操作二就是线段树水题了. ...
- hdu 4288 线段树 暴力 **
题意: 维护一个有序数列{An},有三种操作: 1.添加一个元素. 2.删除一个元素. 3.求数列中下标%5 = 3的值的和. 解题思路: 看的各种题解,今天终于弄懂了. 由于线段树中不支持添加.删除 ...
- 【BZOJ】3038: 上帝造题的七分钟2(线段树+暴力)
http://www.lydsy.com:808/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3038 这题我就有得吐槽了,先是线段树更新写错,然后不知哪没pushup导致te,精度问题sq ...
- Vasya and a Tree CodeForces - 1076E(线段树+dfs)
I - Vasya and a Tree CodeForces - 1076E 其实参考完别人的思路,写完程序交上去,还是没理解啥意思..昨晚再仔细想了想.终于弄明白了(有可能不对 题意是有一棵树n个 ...
- Codeforces 765F Souvenirs 线段树 + 主席树 (看题解)
Souvenirs 我们将询问离线, 我们从左往右加元素, 如果当前的位置为 i ,用一棵线段树保存区间[x, i]的答案, 每次更新完, 遍历R位于 i 的询问更新答案. 我们先考虑最暴力的做法, ...
- Codeforces 787D. Legacy 线段树建模+最短路
D. Legacy time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input out ...
- hdu 6430 线段树 暴力维护
Problem E. TeaTree Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Oth ...
- 【Vjudge】P558E A Simple Task(线段树暴力)
题目链接 这题……太暴力了吧…… 开二十六棵线段树维护l到r字符i出现的次数,然后修改的时候暴力修改,输出的时候暴力输出……就过了…… 然后我还没想到…… qwq #include<cstdio ...
- Almost Regular Bracket Sequence CodeForces - 1095E (线段树,单点更新,区间查询维护括号序列)
Almost Regular Bracket Sequence CodeForces - 1095E You are given a bracket sequence ss consisting of ...
随机推荐
- C# 模拟提交带附件(input type=file)的表单
今天调用某API时,对于文档中的传入参数:File[] 类型,感觉很陌生,无从下手! 按通常的方式在json参数中加入file的二进制数据提交,一直报错(参数错误)!后来经过多方咨询,是要换一种 表单 ...
- HTML5 总结-音频-2
HTML5 音频 音频格式 当前,audio 元素支持三种音频格式: IE 9 Firefox 3.5 Opera 10.5 Chrome 3.0 Safari 3.0 Ogg Vorbis ...
- (IOS)签名Demo
思路是将每一次按下屏幕的touch move时的点存到一个数组里,即一个数组相当于一个笔画:再将该代表笔画的数组保存到一个大数组中,每组每次touch的移动都历遍大数组和笔画数组,将点于点之间连接起来 ...
- vs2010 调试中监视变量
在msdn中写了如何查看调试的数据,网址: http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/vstudio/esta7c62(v=vs.100).aspx Visual ...
- MFC中SDI程序创建流程的回顾
SDI程序创建流程的回顾 从CWinApp.InitialInstance()开始, 1.首先应用程序对象创建文档模板; CSingleDocTemplate* pDocTemplate; pDocT ...
- MSSQLServer的备份与还原
最近用到了mssql2000的数据备份还原到2008上, 在备份2000时,一定注意要备份成一个文件,就是目标那里只添加一个就好,(否则待会还原数据库时要添加这两个文件,要不就报“备份了几个簇,只提供 ...
- ASP.NET路由
ASP.NET 路由使您可以使用不必映射到网站中特定文件的 URL. 由于该 URL 不必映射到文件,因此可以使用对用户操作进行描述因而更易于被用户理解的 URL. ASP.NET MVC 框架和 A ...
- POJ 3384 Feng Shui 凸包直径 + 半平面交
G++一直没有过了 换成 C++果断A掉了...It's time to bet RP. 题意:给一个多边形,然后放进去两个圆,让两个圆的覆盖面积尽量最大,输出两个圆心的坐标. 思路:将多边形的边向里 ...
- Java Pattern Matcher 正则应用
转自:http://www.itzhai.com/java-notes-regex-matches-and-lookingat.html#read-more 1.基本语法 2.String内建的正则表 ...
- Win7 x64安装Paramiko出问题
今天上午windows下配置paramiko环境时出现问题,随手记录下来. 先说一下我的环境: win7 x64 旗舰版.Python3.5.0.pip8.1.0 pip install para ...
