Spring Security中异常上抛机制及对于转型处理的一些感悟
在使用Spring Security的过程中,我们会发现框架内部按照错误及问题出现的场景,划分出了许许多多的异常,但是在业务调用时一般都会向外抛一个统一的异常出来,为什么要这样做呢,以及对于抛出来的异常,我们又该如何分场景进行差异化的处理呢,今天来跟我一起看看吧。
一个登陆场景下的外层代码
@PostMapping("/login")
public void login(@NotBlank String username,
@NotBlank String password, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
request.login(username, password);
System.out.println("login success");
} catch (ServletException authenticationFailed) {
System.out.println("a big exception authenticationFailed");
}
}
request.login(username,password)跳入到了HttpServlet3RequestFactory类中,点击去发现login方法只是统一向外抛出了一个ServletException异常。
public void login(String username, String password) throws ServletException {
if (this.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new ServletException("Cannot perform login for '" + username + "' already authenticated as '" + this.getRemoteUser() + "'");
} else {
AuthenticationManager authManager = HttpServlet3RequestFactory.this.authenticationManager;
if (authManager == null) {
HttpServlet3RequestFactory.this.logger.debug("authenticationManager is null, so allowing original HttpServletRequest to handle login");
super.login(username, password);
} else {
Authentication authentication;
try {
authentication = authManager.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password));
} catch (AuthenticationException var6) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
throw new ServletException(var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
}
}
但是在ProviderManager类中的public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {}
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
Iterator var6 = this.getProviders().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
AuthenticationProvider provider = (AuthenticationProvider)var6.next();
if (provider.supports(toTest)) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using " + provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
this.copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
} catch (AccountStatusException var11) {
this.prepareException(var11, authentication);
throw var11;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var12) {
this.prepareException(var12, authentication);
throw var12;
} catch (AuthenticationException var13) {
lastException = var13;
}
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
try {
result = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
} catch (ProviderNotFoundException var9) {
;
} catch (AuthenticationException var10) {
lastException = var10;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && result instanceof CredentialsContainer) {
((CredentialsContainer)result).eraseCredentials();
}
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
} else {
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound", new Object[]{toTest.getName()}, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
this.prepareException((AuthenticationException)lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
}
这里就涉及到了多态的知识点,异常的多态。如子异常AccountStatusException都可以向上转型为统一的验证异常AuthenticationException。
在设计之初的时候,验证类统一的父级异常是AuthenticationException。然后根据业务需求向下拓展出了很多个场景性质的异常,可能有十个、一百个、一千个。
- 密码不正确 BadCredentialsException
- 账号是否被锁定 LockedException
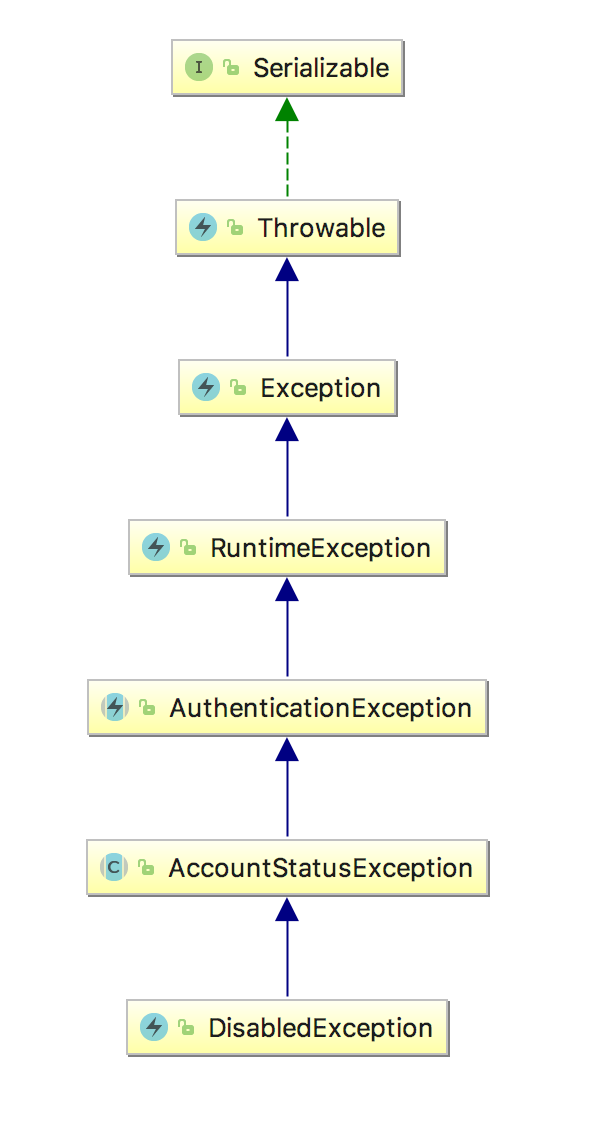
- 账号是否被禁用 DisabledException
- 账号是否在有效期内 AccountExpiredException
- 密码失效 CredentialsExpiredException
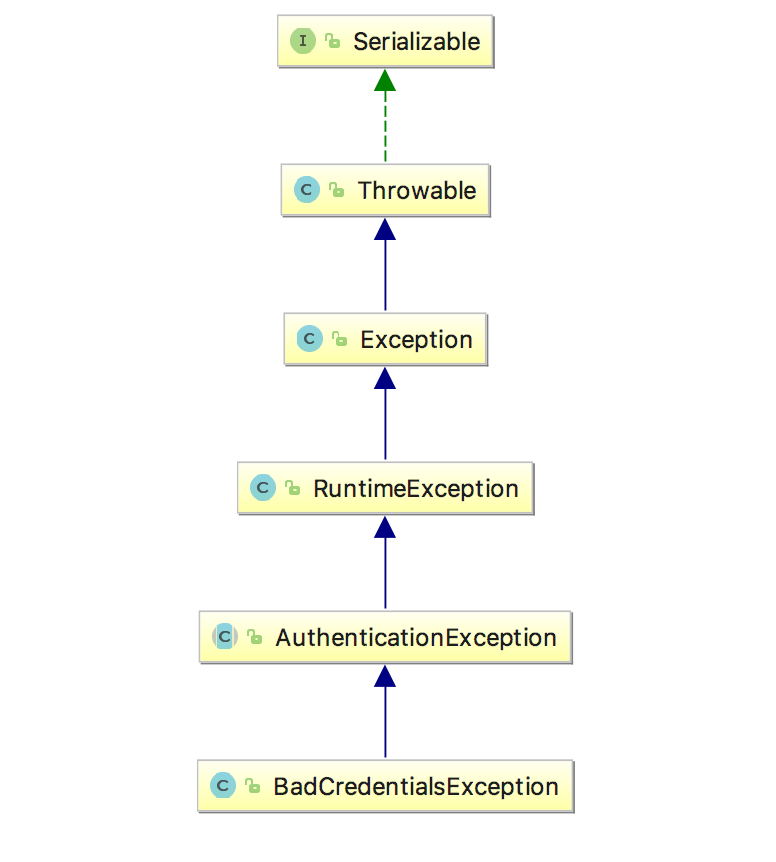
两个场景下的异常类关系图谱
ServletException
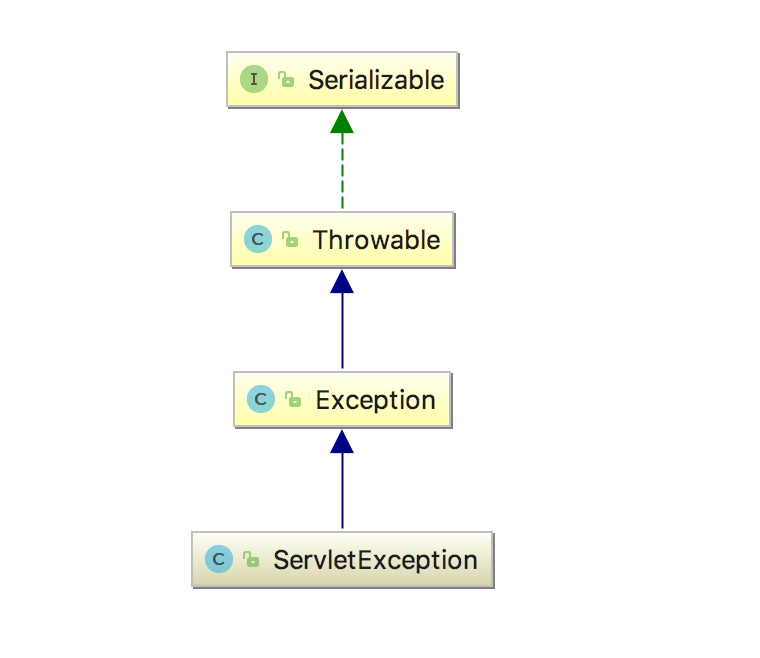
BadCredentialsException,密码错误
账号被禁用,DisabledException
public void login(String username, String password) throws ServletException{
...
catch (AuthenticationException loginFailed) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
throw new ServletException(loginFailed.getMessage(), loginFailed);
}
}
// 在捕获到异常之后会构建一个ServletException并将AuthenticationException统一的包装进去,比如说内部报了BadCredentialsException,那么在这里就会向上转型为Throwable
public ServletException(String message, Throwable rootCause) {
super(message, rootCause);
}
// 在Throwable类中会将最下面冒出来的异常传给cause,getRootCause就能获得异常的具体原因
public Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
}
// Throwable向下转型BadCredentialsException
if (throwable instanceof BadCredentialsException)
调整后的代码
在外层根据不同异常而做不同的业务处理的代码就可以改造为如下
@PostMapping("/login")
public void login(@NotBlank String username,
@NotBlank String password, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
request.login(username, password);
System.out.println("login success");
} catch (ServletException authenticationFailed) {
Throwable throwable = authenticationFailed.getRootCause();
if (throwable instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
System.out.println("user password is wrong");
}else if (throwable instanceof DisabledException){
System.out.println("user is disabled");
}else {
System.out.println("please contact the staff");
}
}
}
Spring Security中异常上抛机制及对于转型处理的一些感悟的更多相关文章
- Spring Security 中的过滤器
本文基于 spring-security-core-5.1.1 和 tomcat-embed-core-9.0.12. Spring Security 的本质是一个过滤器链(filter chain) ...
- [收藏]Spring Security中的ACL
ACL即访问控制列表(Access Controller List),它是用来做细粒度权限控制所用的一种权限模型.对ACL最简单的描述就是两个业务员,每个人只能查看操作自己签的合同,而不能看到对方的合 ...
- Spring Security中实现微信网页授权
微信公众号提供了微信支付.微信优惠券.微信H5红包.微信红包封面等等促销工具来帮助我们的应用拉新保活.但是这些福利要想正确地发放到用户的手里就必须拿到用户特定的(微信应用)微信标识openid甚至是用 ...
- java中异常的抛出:throw throws
java中异常的抛出:throw throws Java中的异常抛出 语法: public class ExceptionTest{ public void 方法名(参数列表) throws 异常列表 ...
- Spring Security 中的 Bcrypt
最近在写用户管理相关的微服务,其中比较重要的问题是如何保存用户的密码,加盐哈希是一种常见的做法.知乎上有个问题大家可以先读一下: 加盐密码保存的最通用方法是? 对于每个用户的密码,都应该使用独一无二的 ...
- 看源码,重新审视Spring Security中的角色(roles)是怎么回事
在网上看见不少的博客.技术文章,发现大家对于Spring Security中的角色(roles)存在较大的误解,最大的误解就是没有搞清楚其中角色和权限的差别(好多人在学习Spring Security ...
- 六:Spring Security 中使用 JWT
Spring Security 中使用 JWT 1.无状态登录 1.1 什么是有状态? 1.2 什么是无状态 1.3 如何实现无状态 2.JWT 2.1 JWT数据格式 2.2 JWT交互流程 2.3 ...
- 五:Spring Security 中的角色继承问题
Spring Security 中的角色继承问题 以前的写法 现在的写法 源码分析 SpringSecurity 在角色继承上有两种不同的写法,在 Spring Boot2.0.8(对应 Spring ...
- Spring Security中html页面设置hasRole无效的问题
Spring Security中html页面设置hasRole无效的问题 一.前言 学了几天的spring Security,偶然发现的hasRole和hasAnyAuthority的区别.当然,可能 ...
随机推荐
- Openstack 在VMware虚拟机ESXI和Workstation下安装需要更改参数
[vmware vsphere] 要在esxi 5i的系统文件/etc/vmware/config最后添加vhv.allow = “TRUE” 一行.重启 VMware ESXi 后编辑虚拟机选项(需 ...
- parted分区脚本
#!/bin/bash #Used to fomat 6 disks PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin export PATH disk_to_parted=&qu ...
- 【BZOJ3456】城市规划 多项式求逆
[BZOJ3456]城市规划 Description 刚刚解决完电力网络的问题, 阿狸又被领导的任务给难住了. 刚才说过, 阿狸的国家有n个城市, 现在国家需要在某些城市对之间建立一些贸易路线, 使得 ...
- 【CF802L】Send the Fool Further! (hard) 高斯消元
[CF802L]Send the Fool Further! (hard) 题意:给你一棵n个节点的树,每条边有长度,从1号点开始,每次随机选择一个相邻的点走,走到一个叶子时就停止,问期望走的总路程. ...
- 【CF850E】Random Elections FWT
[CF850E]Random Elections 题意:有n位选民和3位预选者A,B,C,每个选民的投票方案可能是ABC,ACB,BAC...,即一个A,B,C的排列.现在进行三次比较,A-B,B-C ...
- spring-boot 学习笔记一
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/ityouknow/p/5662753.html 1.构建项目: 访问http://start.spring.io/,下载demo: 下载解压 ...
- PHPStorm 注册码&主题皮肤
JetBrains PhpStorm 注册方法: 用浏览器打开 http://idea.lanyus.com/ 点击页面中的“获得注册码” 然后打开PhpStorm,在注册时切换至Activation ...
- CBV之详解
一,CBV,基于反射实现根据请求方式不同,执行不同的方法. 1. 开发模式 - 普通开发方式(前后端放在一起写) - 前后端分离 2. 后端开发 为前端提供URL(API/接口的开发) 注:永远返回H ...
- win10拖拽的问题
以前很多可以支持托砖的到了win10都不行了 解决 按Windows键+R,打开“运行”对话框:输入regedit,回车或确定. 依次找到以下键值HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWA ...
- js生成二维码以及点击下载二维码
js生成二维码 jquery.qrcode.js可以快速使用页面生成二维码.但改项目有两个小问题:1.不支持中文:2.不支持二维码中间生成图片. 支持中文的jquery-qrcode jquery.q ...
