Android 7.1 ActivityManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (四)
四、Activity的更新(旋转)
sendNewConfiguration()会调用到ActivityManagerService的updateConfiguration()来update Configuration,并根据应用的配置来判断是否要重新lunch应用。
void sendNewConfiguration() {
try {
mActivityManager.updateConfiguration(null);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
public void updateConfiguration(Configuration values) {
enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION,
"updateConfiguration()");
synchronized(this) {
if (values == null && mWindowManager != null) {
// sentinel: fetch the current configuration from the window manager
values = mWindowManager.computeNewConfiguration();
}
if (mWindowManager != null) {
mProcessList.applyDisplaySize(mWindowManager);
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (values != null) {
Settings.System.clearConfiguration(values);
}
updateConfigurationLocked(values, null, false);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
先看一下总体时序图,后面详细展开:
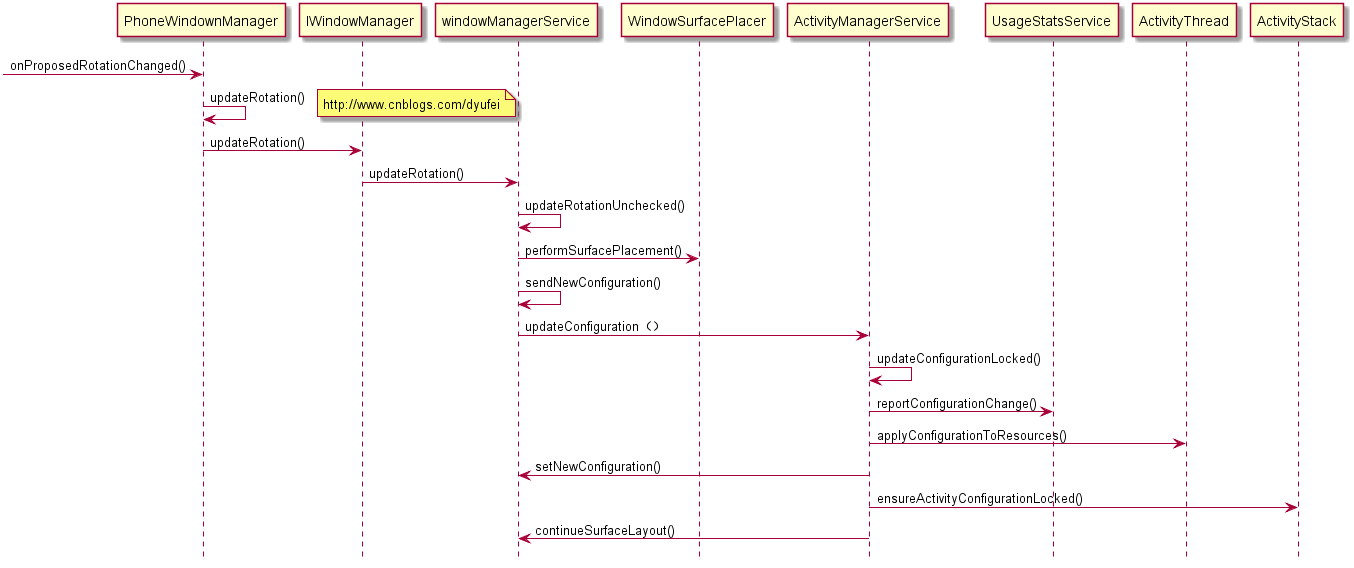
1)updateConfigurationLocked()
updateConfigurationLocked()
(1)获取Configuration数据保存在mConfiguration
(2)调用ActivityThread的scheduleConfigurationChanged()
(3)发送ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED广播
(4)获取当前最上面活动的Activity,调用ActivityStack的ensureActivityConfigurationLocked()函数根据应用配置判断是否要重新luncher应用
private boolean updateConfigurationLocked(Configuration values, ActivityRecord starting,
boolean initLocale, boolean persistent, int userId, boolean deferResume) {
int changes = 0; if (mWindowManager != null) {
mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
}
if (values != null) {
Configuration newConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
changes = newConfig.updateFrom(values);
if (changes != 0) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.i(TAG_CONFIGURATION,
"Updating configuration to: " + values); EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, changes); if (!initLocale && !values.getLocales().isEmpty() && values.userSetLocale) {
final LocaleList locales = values.getLocales();
int bestLocaleIndex = 0;
if (locales.size() > 1) {
if (mSupportedSystemLocales == null) {
mSupportedSystemLocales =
Resources.getSystem().getAssets().getLocales();
}
bestLocaleIndex = Math.max(0,
locales.getFirstMatchIndex(mSupportedSystemLocales));
}
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale",
locales.get(bestLocaleIndex).toLanguageTag());
LocaleList.setDefault(locales, bestLocaleIndex);
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(SEND_LOCALE_TO_MOUNT_DAEMON_MSG,
locales.get(bestLocaleIndex)));
} mConfigurationSeq++;
if (mConfigurationSeq <= 0) {
mConfigurationSeq = 1;
}
newConfig.seq = mConfigurationSeq;
mConfiguration = newConfig;
Slog.i(TAG, "Config changes=" + Integer.toHexString(changes) + " " + newConfig);
mUsageStatsService.reportConfigurationChange(newConfig,
mUserController.getCurrentUserIdLocked());
//mUsageStatsService.noteStartConfig(newConfig); final Configuration configCopy = new Configuration(mConfiguration); // TODO: If our config changes, should we auto dismiss any currently
// showing dialogs?
mShowDialogs = shouldShowDialogs(newConfig, mInVrMode); AttributeCache ac = AttributeCache.instance();
if (ac != null) {
ac.updateConfiguration(configCopy);
} // Make sure all resources in our process are updated
// right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
// resource values after we return will be sure to get
// the new ones. This is especially important during
// boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
// all resources have that config before following boot
// code is executed.
mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy); if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
msg.arg1 = userId;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
} final boolean isDensityChange = (changes & ActivityInfo.CONFIG_DENSITY) != 0;
if (isDensityChange) {
// Reset the unsupported display size dialog.
mUiHandler.sendEmptyMessage(SHOW_UNSUPPORTED_DISPLAY_SIZE_DIALOG_MSG); killAllBackgroundProcessesExcept(Build.VERSION_CODES.N,
ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_FOREGROUND_SERVICE);
} for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REPLACE_PENDING
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent, null, null, 0, null, null,
null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false,
MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
if ((changes&ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE) != 0) {
intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
if (initLocale || !mProcessesReady) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY);
}
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent,
null, null, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
}
}
// Update the configuration with WM first and check if any of the stacks need to be
// resized due to the configuration change. If so, resize the stacks now and do any
// relaunches if necessary. This way we don't need to relaunch again below in
// ensureActivityConfigurationLocked().
if (mWindowManager != null) {
final int[] resizedStacks = mWindowManager.setNewConfiguration(mConfiguration);
if (resizedStacks != null) {
for (int stackId : resizedStacks) {
final Rect newBounds = mWindowManager.getBoundsForNewConfiguration(stackId);
mStackSupervisor.resizeStackLocked(
stackId, newBounds, null, null, false, false, deferResume);
}
}
}
} boolean kept = true;
final ActivityStack mainStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
// mainStack is null during startup.
if (mainStack != null) {
if (changes != 0 && starting == null) {
// If the configuration changed, and the caller is not already
// in the process of starting an activity, then find the top
// activity to check if its configuration needs to change.
starting = mainStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
} if (starting != null) {
kept = mainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes, false);
// And we need to make sure at this point that all other activities
// are made visible with the correct configuration.
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(starting, changes,
!PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
}
if (mWindowManager != null) {
mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
return kept;
}
五、总结
总流程图如下

Android 7.1 ActivityManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (四)的更多相关文章
- Android 7.1 WindowManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (二)
一.概述 从上篇[Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析]知道实际的旋转由WindowManagerService来完成,这里接着上面具体详细展开. 调了三个函数完成了三件事,即首先调用update ...
- Android 7.1 WindowManagerService 屏幕旋转流程分析 (三)
三.屏幕的绘制 performSurfacePlacement()函数来触发window的绘制,这里最大的循环次数是6,当然一般不会到最大次数就会被Scheduled. final void perf ...
- Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析
Android 7.1 屏幕旋转流程分析 一.概述 Android屏幕的旋转在framework主要涉及到三个类,结构如图 PhoneWindowManager:为屏幕的横竖屏转换的管理类. Wi ...
- 【转】如何在 Android 程序中禁止屏幕旋转和重启Activity
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bluestorm/p/3665890.html 禁止屏幕随手机旋转变化 有时候我们希望让一个程序的界面始终保持在一个方向,不随手机方向旋转而变 ...
- 如何在 Android 程序中禁止屏幕旋转和重启Activity
禁止屏幕随手机旋转变化 有时候我们希望让一个程序的界面始终保持在一个方向,不随手机方向旋转而变化:在AndroidManifest.xml的每一个需要禁止转向的Activity配置中加入android ...
- Android系统分析之运营商显示流程分析之运营商信息的读取流程二
运营商显示流程分析之运营商信息的读取流程 一. SIM卡运营商信息的读取 从前面的 运营商信息的获取和赋值 可以知道SIM卡运营商的赋值最终是在 SIMRecords 中完成的, 而SIM卡信息的相关 ...
- 【Android】11.3 屏幕旋转和场景变换过程中GridView的呈现
分类:C#.Android.VS2015: 创建日期:2016-02-21 一.简介 实际上,对于布局文件中的View来说,大多数情况下,Android都会自动保存这些状态,并不需要我们都去处理它.这 ...
- 屏幕旋转时调用PopupWindow update方法更新位置失效的问题及解决方案
接到一个博友的反馈,在屏幕旋转时调用PopupWindow的update方法失效.使用场景如下:在一个Activity中监听屏幕旋转事件,在Activity主布局文件中有个按钮点击弹出一个Pop ...
- Android 4.4 Kitkat Phone工作流程浅析(六)__InCallActivity显示更新流程
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/yihongyuelan 转载请务必注明出处 本文代码以MTK平台Android 4.4为分析对象,与Google原生AOSP有些许差异,请读者知悉. ...
随机推荐
- Glance 镜像服务群集
#Glance 镜像服务群集 openstack pike 部署 目录汇总 http://www.cnblogs.com/elvi/p/7613861.html#4.Glance 镜像服务群集 ##. ...
- ThinkPHP 5 中AJAX跨域请求头设置方法
最近用thinkphp做项目,在测试环境时,存在接口的测试问题.在tp官网也没能找到相关的解决方法.自已看了一下源码,有如下的解决方案. 在项目目录下面,创建common/behavior/CronR ...
- java把html标签字符转普通字符(反转换成html标签)(摘抄)
下面是java把html标签字符转换,我用了spring 包中的 org.springframework.web.util.HtmlUtils 了解了源代码并且进步了使用,发现写得真不错...同时也可 ...
- 【福利】十一起,小冰科技所有UWP产品免费半个月
从十月一日起(UTC协调世界时),至十月十五,小冰科技所有UWP产品免费半个月!!!!!! 注意是UTC哦,中国区,比UTC早8个小时,要等到十月一号早晨八点开始... 现在小冰科技旗下一共发布了 5 ...
- Postgres中表和元组的组织方式
PG version 9.5.3 PG中四种堆文件: 普通堆 临时堆 序列堆 TOAST表 PageHeaderData长度为24(截图为8.4版本,20字节)个字节包含的内容如下: 空闲空间的起始和 ...
- 使用PowerApps快速构建基于主题的轻业务应用 —— 入门篇
作者:陈希章 发表于 2017年12月12日 前言 在上一篇文章 基于Office 365的随需应变业务应用平台 中我提到,随着随需应变的业务需要,以及技术的发展,业务应用的开发的模式也有了深刻的变化 ...
- vue2入门之vue-cli
vue-cli vue在web前端可谓是大放异彩,尤其在国内与angular.react有三足鼎立之势.很多人想入门vue2而又苦于不知从何下手.因为vue2是以组件化开发的,最好要搭配webpack ...
- 【tyvj P4879】骰子游戏
http://www.tyvj.cn/p/4879 首先,投一个骰子,每个数字出现的概率都是一样的.也就是不算小A的话,n个人投出x个骰子需要的次数和点数无关. 计数问题考虑dp,令f(i,j)为前i ...
- em标签和strong标签的区别
今天模拟面试,第一个问题就是这个,然后我回答说就是表示强调,然后老师说还有吗,我说不知道了,然后,就没有然后了... 第一个层次的区别: <em>标签是告诉浏览器把其中的文本表示为强调的内 ...
- Mysql的安装和图形化界面的使用
访问mysql网址:https://dev.mysql.com/ 下面需要登录你的oracle账号进行下载就好~ 下载之后是一解压包形式存在的~ 解压之后的文件 这里我新建了my.ini的文件~将my ...
