树的平衡 AVL Tree
本篇随笔主要从以下三个方面介绍树的平衡:
1):BST不平衡问题
2):BST 旋转
3):AVL Tree
一:BST不平衡问题的解析
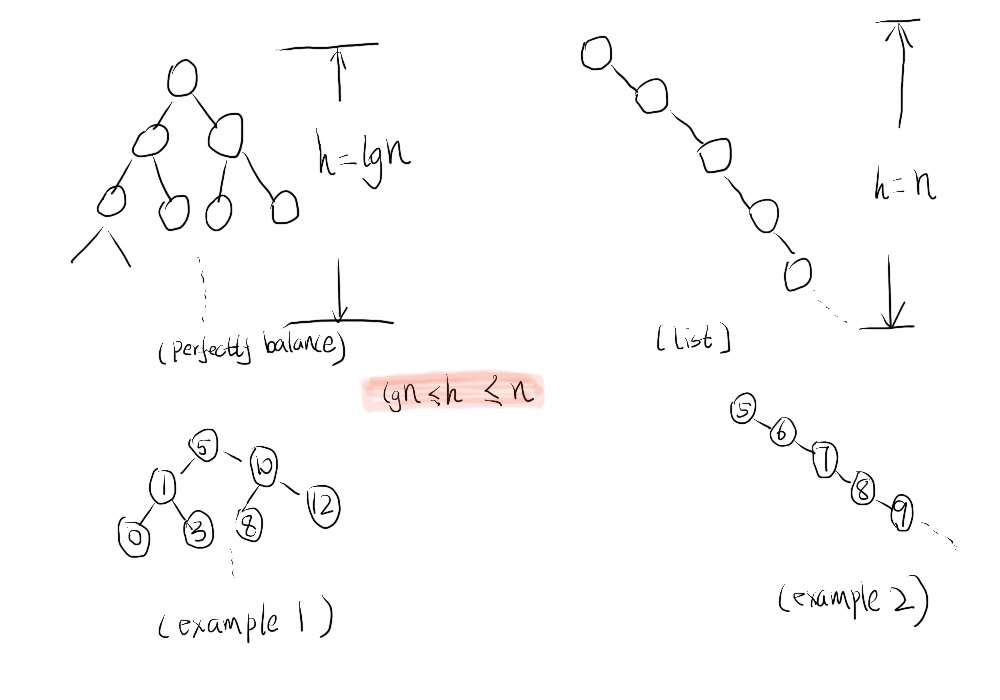
之前有提过普通BST的一些一些缺点,例如BST的高度是介于lgN和N之间的,如果是N的的话,显然效率很低,不是我们需要的;但是在实际情况中,BST的高度h = N的情况却经常出现,例如下图所示。在BST中search,insert的running time都等于BST的高度h,我们肯定希望高度h越小越好,best case就是lgN。下图的example 2的情况,我们会称之为这个BST是不平衡的。 所以如果遇到这种不平衡的BST,我们如何解决呢?如何将不平衡的BST转化成平衡的BST呢?如何将BST的高度h从N转化成lgN呢?
二:树的平衡
下面我们就来介绍一下树的旋转 rotation。BST是可以经过一些旋转操作后,仍然保持BST的结构不变的,即对于每一个node,该node的left child的值总是小于这个node的值,而该node的right child的值总是大于这个node的值。经过总结,这个旋转主要可以分为4中模式,这四种模式如下面的两图所示:
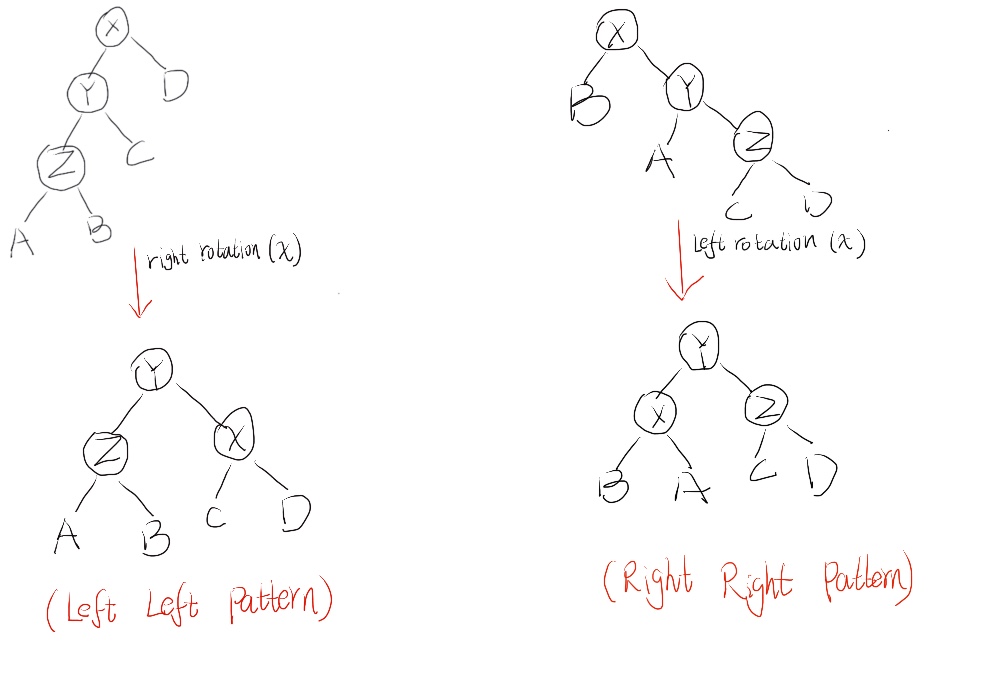
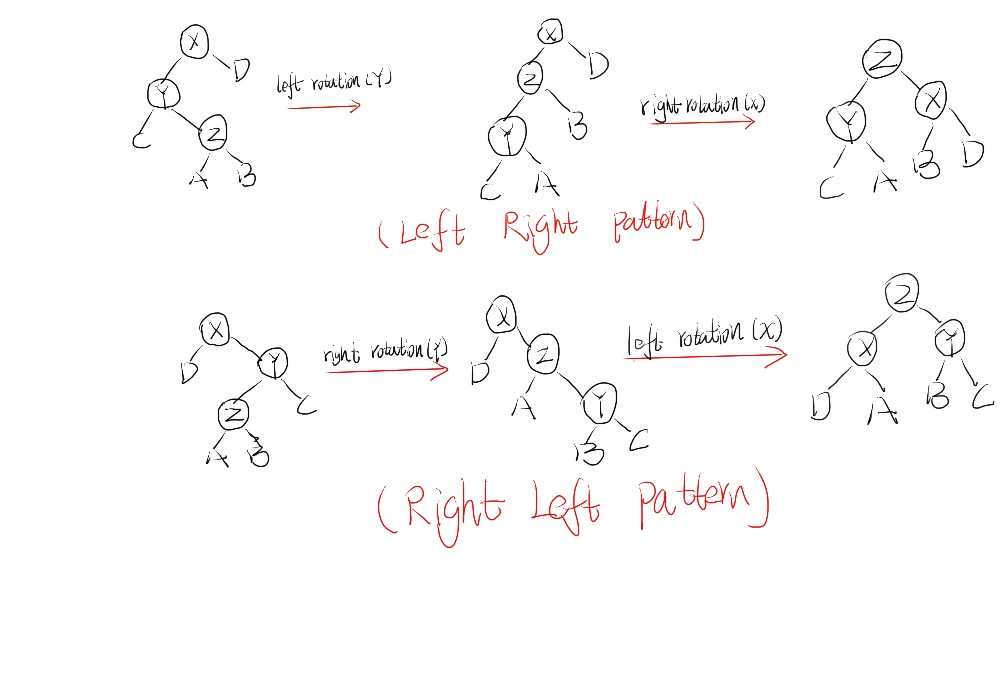
这四种rotation的方式是由BST的特性所决定的,至于为什么这样旋转是是正确的,也是由BST的特点所确定的,我在这就不证明了。只要大家记住BST可以有这4中旋转模式即可。其实上面所示的rotation过程,都是为了平衡树的目的。 那么现在有一个问题来了,我们说了这么多平衡,不平衡的概念,前面我们都是通过直观的感受来体味平衡或者不平衡,那么到底有什么明确的指标可以指明一个BST到底是平衡还是不平衡的呢???这个指标到底是什么呢?那么下面就要解释AVL Tree的概念了。
三:AVL Tree
首先AVL Tree要满足以下2个条件:
1. AVL Tree遵循BST的结构;即left child 小于当前node, right child大于当前node。
2.每一个node的2个 child nodes的高度相差不大于1。
根据上面的条件,我们可以看出AVL Tree其本质是一种特殊的BST。所以我们现在有一个定性的指标来判断一个BST是不是平衡的了,这个指标就是上面2个条件。当然了BST中有很多指标来判读一个BST是不是平衡的,我们这里只是用AVL Tree作为其中之一个指标,你也可以用其他的指标方法。
所以AVL Tree是平衡的,其高度是h=lgN;
在AVL Tree中,每一个node的高度等于取其2个child node 的较大的高度值加1,即max[left child height, right child height]+1; 若node==NULL,则其高度默认为-1.
当在构建AVL Tree的过程中,向其中insert node的时候,首先第一步跟BST insert一样,然后第二步是要检查insert后node的2个children之间的高度差,然后根据相应的高度差来判断相应的rotation的pattern,经过旋转后,使整个Tree仍然保持AVL Tree的特性,即满足上面的2个条件,所以仍然是平衡的。由于insert,search的操作的时间复杂度在BST中都是等于树的高度,AVL Tree作为一种特殊的BST,insert, search的操作的时间复杂度自然也是等于AVL的高度h=lgN. 这样的时间复杂度还是可以让我们满意的,其效率也要远远高于O(N)。AVL Tree的C++ 实现过程如下面的代码所示,以下代码实现了AVL Tree的insertion, sorting, rotation等功能。代码仅供学习交流等非盈利使用,不能用于商业目的,作者保留追溯的权利。
#include "AVLTree.hpp"
using namespace std; AVL_Tree::AVL_Tree(){ this->root = NULL;
} void AVL_Tree::setRoot(Node *root){ this->root = root;
}
Node *AVL_Tree::getRoot(){ return this->root;
} /*
* height of tree or subtree
*
* a node's height equals the max of node's left child's height and node's right child's height plus 1
*
*parameters:
1, node;//the node that we want to measure with
*
*return: the height of the node
*/
int AVL_Tree::height(Node *node){ int h = -; if (node != NULL) { int l_height = height(node->getLeft());
int r_height = height(node->getRight());
h = std::max(l_height,r_height) + ;
} return h;
}
/*
* the height difference of two children nodes
*
*parameters:
* 1, node;//the node which we want to know the differences of its two children
*
*return: int; the height difference of the two children nodes
*/ int AVL_Tree::heightDiff(Node *node){ int l_height = height(node->getLeft());
int r_height = height(node->getRight()); return l_height-r_height; } /*
*
*4 types of rotations
*
*1)left left pattern
*2)left right pattern
*3)right right pattern
*4)right left pattern
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::ll_rotation(Node *node){ int value = node->getData();
Node *temp = node->getLeft(); node->setData(temp->getData());
node->setLeft(temp->getLeft()); temp->setData(value);
temp->setLeft(temp->getRight());
temp->setRight(node->getRight());
node->setRight(temp); }
void AVL_Tree::lr_rotation(Node *node){ Node *temp = node->getLeft();
node->setLeft(temp->getRight());
temp->setRight(temp->getRight()->getLeft());
node->getLeft()->setLeft(temp);
ll_rotation(node); }
void AVL_Tree::rr_rotation(Node *node){ int value = node->getData();
Node *temp = node->getRight(); node->setData(temp->getData());
node->setRight(temp->getRight()); temp->setData(value);
temp->setRight(temp->getLeft());
temp->setLeft(node->getLeft());
node->setLeft(temp); }
void AVL_Tree::rl_rotation(Node *node){ Node *temp = node->getRight();
node->setRight(temp->getLeft());
temp->setLeft(node->getRight()->getRight());
node->getRight()->setRight(temp);
rr_rotation(node); } /*
*Description: balancing the node whoes two children nodes' height difference is greater than 1 or smaller than -1
*
*parameters:
* 1, node;//the node which we want to rotate with, it is the polar point of the rotation
*
*
*return: void
*
*
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::balance(Node *node){ int balance_factor = heightDiff(node);//differences of the node's two sub nodes. if (balance_factor>) {//left side is heavy if (heightDiff(node->getLeft())>) {//left left case ll_rotation(node); }else{//left right case lr_rotation(node);
} }else if (balance_factor<-){//right side heavy if (heightDiff(node->getRight())<) {//right right case rr_rotation(node); }else{//right left case rl_rotation(node);
} }
} /*
* Description: insert a node into the AVL tree and keep the whole structure balanced after inserting
*
*Parameters:
* 1, Node *node;//the node which needs to be inserted
* 2, Node *root;//the root of the tree or subtree;
*
*Return: Node *;//the parent node of the inserted node;
*/ Node *AVL_Tree::insert(Node *node, Node *root){ if (this->root == NULL) { Node *root = new Node();
root->setLeft(NULL);
root->setRight(NULL);
root->setData(node->getData());
this->root = root; return root;
} if (root == NULL) { return node; }else if(node->getData() < root->getData()){ root->setLeft(insert(node, root->getLeft()));
balance(root); }else if (node->getData()>=root->getData()){ root->setRight(insert(node, root->getRight()));
balance(root);
} return root;
} /*
*Description: print out the sorted nodes of the AVL tree of AVL subtree
*
*parameters:
* 1, Node *node;//the root of the AVL tree of AVL subtree
*
*
*/
void AVL_Tree::inorderSort(Node *node){ if (node == NULL) { return;
} inorderSort(node->getLeft());
std::cout<<node->getData()<<" ";
inorderSort(node->getRight()); }
树的平衡 AVL Tree的更多相关文章
- PAT Advanced 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25) [平衡⼆叉树(AVL树)]
题目 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child ...
- AVL树 高度平衡的二叉查找树
1.What is AVL tree? AVL tree 是一种特殊的二叉查找树,,首先我们要在树中引入平衡因子balance,表示结点右子树的高度减去左子树的高度差(右-左),对于一棵AVL树要么它 ...
- AVL树(平衡二叉查找树)
首先要说AVL树,我们就必须先说二叉查找树,先介绍二叉查找树的一些特性,然后我们再来说平衡树的一些特性,结合这些特性,然后来介绍AVL树. 一.二叉查找树 1.二叉树查找树的相关特征定义 二叉树查找树 ...
- PAT 1066 Root of AVL Tree[AVL树][难]
1066 Root of AVL Tree (25)(25 分) An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, ...
- PAT甲级——1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree (完全AVL树的判断)
嫌排版乱的话可以移步我的CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44385565/article/details/89390802 An AVL tree is a sel ...
- 树的平衡之AVL树——错过文末你会后悔,信我
学习数据结构应该是一个循序渐进的过程: 当我们学习数组时,我们要体会数组的优点:仅仅通过下标就可以访问我们要找的元素(便于查找). 此时,我们思考:假如我要在第一个元素前插入一个新元素?采用数组需要挪 ...
- 04-树5 Root of AVL Tree + AVL树操作集
平衡二叉树-课程视频 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the tw ...
- 判断AVL树是否平衡
AVL树是高度的平衡二插搜索树,其左子树和右子树的高度之差不超过1(树中的左子树和右子树都是AVL树),维持这个高度之差就要控制它的平衡因子.那么判断一颗AVL树是否平衡就需要判断它的左子树和右子树高 ...
- 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)(AVL树的实现)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
随机推荐
- Linux系统安装_Centos6.9
第1章 虚拟机安装 1.1 镜像下载 1.1.1 新版本下载 http://mirrors.aliyun.com #阿里云官方镜像站点 1.1.2 旧版本下载 http://vault.cento ...
- svg snap 笔记
路径中的字母,大写相对于左上角绝对定位,小写相对定位 M110,95,95,110M115,100,100,115 pattern 类似于图片拼贴,可以把指定位置的图案用来填充 var patt ...
- Scrum Meeting Alpha - 6
Scrum Meeting Alpha - 6 NewTeam 2017/10/31 地点:主南203 任务反馈 团队成员 完成任务 计划任务 安万贺 完成了个人博客和班级列表部分API的包装 完成个 ...
- Servlet编程实例2
上次实验中利用HttpServletRespon.sendRedict()方法来实现页面的转跳,而这种重定向请求的方法无法传递缓存的内容. 所以为了做出改进,这次使用RequestDispatcher ...
- python进阶------进程线程(三)
python中的进程 1.multiprocessing模块 由于GIL的存在,python中的多线程其实并不是真正的多线程,如果想要充分地使用多核CPU的资源,在python中大部分情况需要使用多进 ...
- 深入理解ES6之——迭代器与生成器
迭代器 迭代器是被设计专用于迭代的对象,带有特定接口.所有的迭代器对象都有next方法,会返回一个结果对象.该结果对象有两个属性:对应下一个值的value,以及一个布尔类型的done,其值为true时 ...
- phpcms实现全站搜索
如果制作的静态页面中有搜索功能,那么使用phpcms进行替换怎么替换呢?会不会越到很多的麻烦呢?接下来进行phpcms替换静态页面中的搜索功能. 第一步:搜索页面的form表单提交书写,form表单怎 ...
- 【朝花夕拾】朝花夕拾-Robot Framework实战演练之开篇
(原创文章,转载请注明出处.) 开博了,简单感慨两句. 前些年一直在做质量体系建设及团队管理的事,忽略了对测试技术热度的保持,这两年有幸重回开发测试第一线,颇感欣喜. 近期随着公司新业务的开展,需要快 ...
- [拓扑排序]Ordering Tasks UVA - 10305
拓扑排序模版题型: John has n tasks to do.Unfortunately, the tasks are not independent and the execution of o ...
- [NOIP]玩具装箱
题目:(非常经典的模拟赛题,适合动规入门的OIer) 简要分析: 动态规划,用一维数组 f[i] 表示从位置1 到 位置i 的最优花费 ,由于 f[i ] 以前的最优花费都是确定的,故只需要在 1 ...
