k8s replicaset controller 分析(3)-expectations 机制分析
replicaset controller分析
replicaset controller简介
replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的一个,是 replicaset 资源对象的控制器,其通过对replicaset、pod 2种资源的监听,当这2种资源发生变化时会触发 replicaset controller 对相应的replicaset对象进行调谐操作,从而完成replicaset期望副本数的调谐,当实际pod的数量未达到预期时创建pod,当实际pod的数量超过预期时删除pod。
replicaset controller主要作用是根据replicaset对象所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量做比较,然后根据比较结果创建/删除pod,最终使得replicaset对象所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量相等。
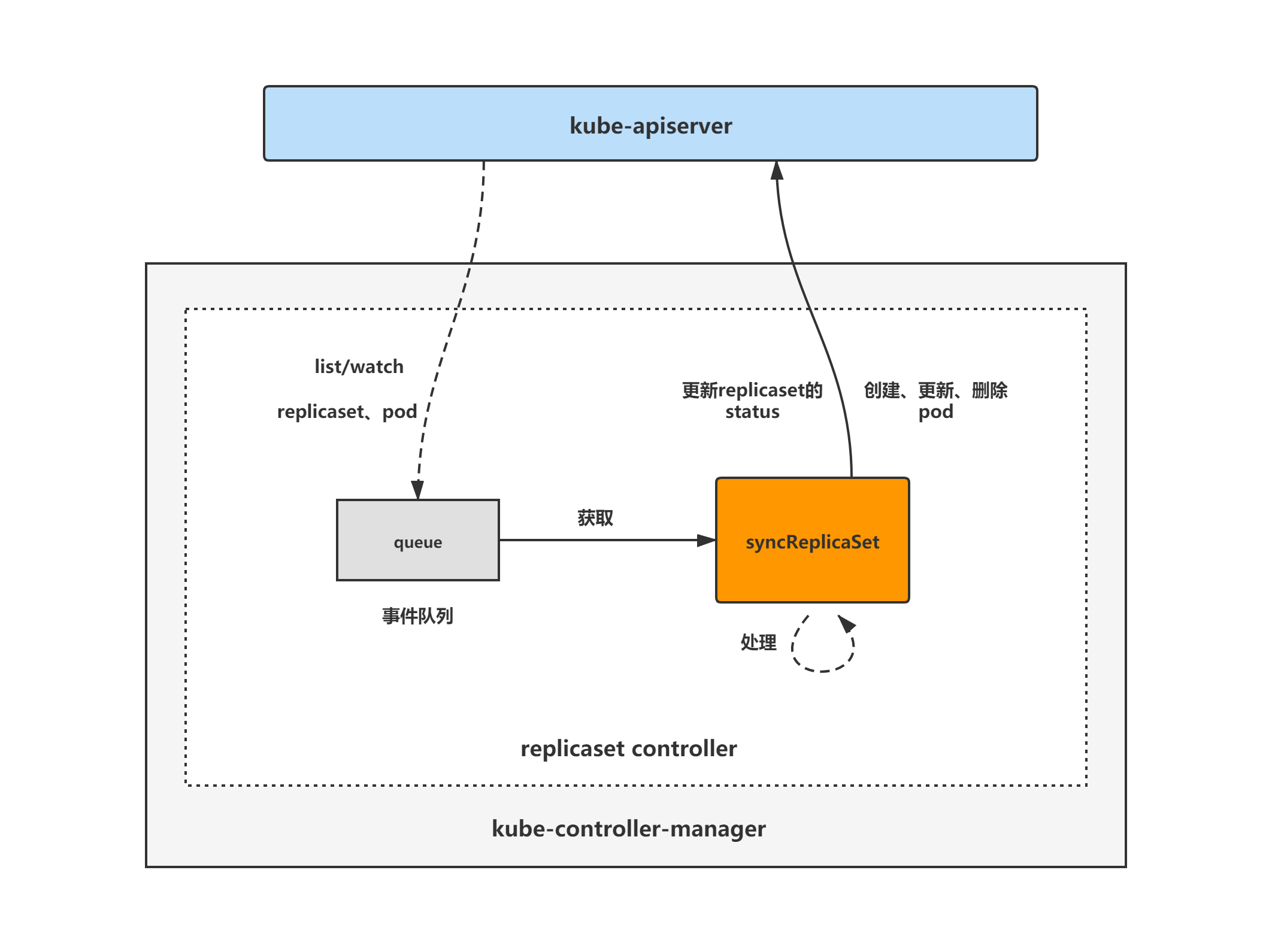
replicaset controller架构图
replicaset controller的大致组成和处理流程如下图,replicaset controller对pod和replicaset对象注册了event handler,当有事件时,会watch到然后将对应的replicaset对象放入到queue中,然后syncReplicaSet方法为replicaset controller调谐replicaset对象的核心处理逻辑所在,从queue中取出replicaset对象,做调谐处理。
replicaset controller分析分为3大块进行,分别是:
(1)replicaset controller初始化和启动分析;
(2)replicaset controller核心处理逻辑分析;
(3)replicaset controller expectations机制分析。
本篇博客进行replicaset controller expectations机制分析。
expectations机制概述
expectations记录了replicaset对象在某一次调谐中期望创建/删除的pod数量,pod创建/删除完成后,该期望数会相应的减少,当期望创建/删除的pod数量小于等于0时,说明上一次调谐中期望创建/删除的pod数量已经达到,调用rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法返回true。
根据前面的分析,在replicaset controller对replicaset对象进行调谐操作时,首先会调用rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法,返回true且replicaset对象的deletetimestamp为空,才会调用rsc.manageReplicas方法进行期望副本数的调谐操作,也即pod的创建/删除操作。
replicaset controller expectations机制分析
这个 expectations 机制的作用是什么?下面来分析一下。
以创建1000个副本的replicaset为例,分析下expectations的作用。根据前面对replicaset controller的核心处理分析可以得知,1000个pod将通过两次对replicaset对象的调谐,每次500个进行创建。
直接看到replicaset controller的核心处理逻辑方法syncReplicaSet。
syncReplicaSet
每次调用rsc.manageReplicas方法前,都会调用rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations来判断是否可以进行replicaset期望副本的调谐操作(pod的创建删除操作),返回true时才会调用rsc.manageReplicas方法。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) syncReplicaSet(key string) error {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing %v %q (%v)", rsc.Kind, key, time.Since(startTime))
}()
...
rsNeedsSync := rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations(key)
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(rs.Spec.Selector)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("error converting pod selector to selector: %v", err))
return nil
}
...
var manageReplicasErr error
if rsNeedsSync && rs.DeletionTimestamp == nil {
manageReplicasErr = rsc.manageReplicas(filteredPods, rs)
}
...
}
rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations
接下来看到rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法,主要是用于判断是否需要在syncReplicaSet核心处理方法中调用rsc.manageReplicas方法来进行pod的创建删除操作。
(1)第一次进来(首次创建replicaset)时r.GetExpectations找不到该rs对象对应的expectations,exists的值为false,所以rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法返回true,也就是说syncReplicaSet方法中会调用rsc.manageReplicas方法来进行pod的创建操作,并在rsc.manageReplicas方法中设置expectations为期望创建500个pod;
(2)在第一次创建500个pod的操作没有完成之前,以及第一次创建500个pod的操作开始后的5分钟之内,exp.Fulfilled与exp.isExpired都返回false,所以rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法返回false,也就是说syncReplicaSet方法中不会调用rsc.manageReplicas方法来进行pod的创建操作;
(3)在第一次创建500个pod的操作完成之后,或者第一次创建500个pod操作进行了5分钟有余,则exp.Fulfilled或exp.isExpired会返回true,所以rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations方法返回true,也就是说syncReplicaSet方法中会调用rsc.manageReplicas方法来进行第二次500个pod的创建操作,并在rsc.manageReplicas方法中再次设置expectations为期望创建500个pod。
// pkg/controller/controller_utils.go
// SatisfiedExpectations returns true if the required adds/dels for the given controller have been observed.
// Add/del counts are established by the controller at sync time, and updated as controllees are observed by the controller
// manager.
func (r *ControllerExpectations) SatisfiedExpectations(controllerKey string) bool {
if exp, exists, err := r.GetExpectations(controllerKey); exists {
if exp.Fulfilled() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Controller expectations fulfilled %#v", exp)
return true
} else if exp.isExpired() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Controller expectations expired %#v", exp)
return true
} else {
klog.V(4).Infof("Controller still waiting on expectations %#v", exp)
return false
}
} else if err != nil {
klog.V(2).Infof("Error encountered while checking expectations %#v, forcing sync", err)
} else {
// When a new controller is created, it doesn't have expectations.
// When it doesn't see expected watch events for > TTL, the expectations expire.
// - In this case it wakes up, creates/deletes controllees, and sets expectations again.
// When it has satisfied expectations and no controllees need to be created/destroyed > TTL, the expectations expire.
// - In this case it continues without setting expectations till it needs to create/delete controllees.
klog.V(4).Infof("Controller %v either never recorded expectations, or the ttl expired.", controllerKey)
}
// Trigger a sync if we either encountered and error (which shouldn't happen since we're
// getting from local store) or this controller hasn't established expectations.
return true
}
exp.Fulfilled
判断replicaset对象的expectations里的期望创建pod数量以及期望删除pod数量,都小于等于0时返回true。
// Fulfilled returns true if this expectation has been fulfilled.
func (e *ControlleeExpectations) Fulfilled() bool {
// TODO: think about why this line being atomic doesn't matter
return atomic.LoadInt64(&e.add) <= 0 && atomic.LoadInt64(&e.del) <= 0
}
exp.isExpired
判断replicaset对象上次设置expectations时的时间距离现在的时间是否已经超过5分钟,是则返回true。
func (exp *ControlleeExpectations) isExpired() bool {
return clock.RealClock{}.Since(exp.timestamp) > ExpectationsTimeout
}
rsc.manageReplicas
核心处理方法,主要是根据replicaset所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量做比较,然后根据比较结果创建/删除pod,最终使得replicaset对象所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量相等。
(1)创建pod之前,会调用rsc.expectations.ExpectCreations来设置Expectations:(key,add:500,del:0);
(2)调用slowStartBatch来执行pod的创建;
(3)创建完pod之后,判断是否有创建失败的pod,并根据创建失败的pod数量,调用rsc.expectations.CreationObserved减去Expectations中相应的add的值。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) manageReplicas(filteredPods []*v1.Pod, rs *apps.ReplicaSet) error {
diff := len(filteredPods) - int(*(rs.Spec.Replicas))
...
if diff > rsc.burstReplicas {
diff = rsc.burstReplicas
}
rsc.expectations.ExpectCreations(rsKey, diff)
klog.V(2).Infof("Too few replicas for %v %s/%s, need %d, creating %d", rsc.Kind, rs.Namespace, rs.Name, *(rs.Spec.Replicas), diff)
successfulCreations, err := slowStartBatch(diff, controller.SlowStartInitialBatchSize, func() error {
...
})
if skippedPods := diff - successfulCreations; skippedPods > 0 {
klog.V(2).Infof("Slow-start failure. Skipping creation of %d pods, decrementing expectations for %v %v/%v", skippedPods, rsc.Kind, rs.Namespace, rs.Name)
for i := 0; i < skippedPods; i++ {
// Decrement the expected number of creates because the informer won't observe this pod
rsc.expectations.CreationObserved(rsKey)
}
}
...
rsc.expectations.ExpectCreations
设置replicaset对象的expectations。
// pkg/controller/controller_utils.go
func (r *ControllerExpectations) ExpectCreations(controllerKey string, adds int) error {
return r.SetExpectations(controllerKey, adds, 0)
}
// SetExpectations registers new expectations for the given controller. Forgets existing expectations.
func (r *ControllerExpectations) SetExpectations(controllerKey string, add, del int) error {
exp := &ControlleeExpectations{add: int64(add), del: int64(del), key: controllerKey, timestamp: clock.RealClock{}.Now()}
klog.V(4).Infof("Setting expectations %#v", exp)
return r.Add(exp)
}
rsc.expectations.CreationObserved
将replicaset对象expectations中期望创建的pod数量减1.
// pkg/controller/controller_utils.go
// CreationObserved atomically decrements the `add` expectation count of the given controller.
func (r *ControllerExpectations) CreationObserved(controllerKey string) {
r.LowerExpectations(controllerKey, 1, 0)
}
// Decrements the expectation counts of the given controller.
func (r *ControllerExpectations) LowerExpectations(controllerKey string, add, del int) {
if exp, exists, err := r.GetExpectations(controllerKey); err == nil && exists {
exp.Add(int64(-add), int64(-del))
// The expectations might've been modified since the update on the previous line.
klog.V(4).Infof("Lowered expectations %#v", exp)
}
}
那正常情况下(即没有pod创建异常)Expectations在什么时候会更新为(key,add:0,del:0)呢,继续看下面的分析。
pod add event handlerFunc-addPod
replicaset controller会监听pod的新增事件,每成功创建出一个pod,会调用addPod方法。在addPod方法中,同样会调用一次rsc.expectations.CreationObserved,将Expectations中期望创建的pod数量减1。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
// When a pod is created, enqueue the replica set that manages it and update its expectations.
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) addPod(obj interface{}) {
pod := obj.(*v1.Pod)
...
// If it has a ControllerRef, that's all that matters.
if controllerRef := metav1.GetControllerOf(pod); controllerRef != nil {
rs := rsc.resolveControllerRef(pod.Namespace, controllerRef)
if rs == nil {
return
}
rsKey, err := controller.KeyFunc(rs)
if err != nil {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Pod %s created: %#v.", pod.Name, pod)
rsc.expectations.CreationObserved(rsKey)
rsc.queue.Add(rsKey)
return
}
...
}
replicaset controller第一次创建了500个pod之后,通过replicaset controller对pod新增事件的watch,然后调用rsc.expectations.CreationObserved方法将Expectations中期望创建的pod数量减1,以及rsc.manageReplicas方法中对创建失败的pod数量,调用相应次数的rsc.expectations.CreationObserved方法将Expectations中期望创建的pod数量相应减少,最终使该replicaset对象的Expectations的值将变为:(key,add:0,del:0),这样在下次对该replicaset对象的调谐操作中,即可进行下一批次的500个pod的创建。
关于replicaset controller删除pod时的expectations机制,与上述创建pod时分析的expectations机制差不多,可以自己去分析下,这里不再展开分析。
总结
上面以replicaset controller创建pod为例分析了expectations的作用,删除pod的逻辑中expectations起到了类似的作用,此处不再分析。下面来总结一下replicaset controller中expectations机制的作用。
expectations机制作用总结
expectations的过期时间机制解决了某一批次创建/删除pod因某些原因一直卡住不能完成而导致的replicaset期望副本数永远达不到预期的问题。
expectations.SatisfiedExpectations返回true,则进入核心处理方法rsc.manageReplicas,根据replicaset所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量做比较,判断是否需要进行下一批次的创建/删除pod的任务。
综上可以看出,expectations主要用于控制让多个创建/删除pod批次串行执行,不让其并行执行,防止了并发执行所可能产生的重复删除pod、创建出replicaset所期望的pod数量以外的多余的pod等问题(当replicaset对象的某一创建/删除pod的批次还在进行中,这时再次进行pod的创建删除操作,如果没有expectations的判断控制,就会再次进行pod的批量创建/删除时,从而导致该问题的发生)。
k8s replicaset controller 分析(3)-expectations 机制分析的更多相关文章
- k8s replicaset controller分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析
replicaset controller分析 replicaset controller简介 replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制 ...
- k8s replicaset controller分析(1)-初始化与启动分析
replicaset controller分析 replicaset controller简介 replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制 ...
- k8s daemonset controller源码分析
daemonset controller分析 daemonset controller简介 daemonset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的 ...
- k8s endpoints controller分析
k8s endpoints controller分析 endpoints controller简介 endpoints controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控 ...
- MongoDB Sharding 机制分析
MongoDB Sharding 机制分析 MongoDB 是一种流行的非关系型数据库.作为一种文档型数据库,除了有无 schema 的灵活的数据结构,支持复杂.丰富的查询功能外,MongoDB 还自 ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析 前面一篇文章对k8s informer做了概要分析,本篇文章将对informer的初始化与启动进行分析. info ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(3)-Reflector源码分析
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(3)-Reflector源码分析 1.Reflector概述 Reflector从kube-apiserver中list&watc ...
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(4)-DeltaFIFO源码分析
client-go之DeltaFIFO源码分析 1.DeltaFIFO概述 先从名字上来看,DeltaFIFO,首先它是一个FIFO,也就是一个先进先出的队列,而Delta代表变化的资源对象,其包含资 ...
- Linux mips64r2 PCI中断路由机制分析
Linux mips64r2 PCI中断路由机制分析 本文主要分析mips64r2 PCI设备中断路由原理和irq号分配实现方法,并尝试回答如下问题: PCI设备驱动中断注册(request_irq) ...
随机推荐
- Mysql常用sql语句(6)- limit 限制查询结果的条数
测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句系列 https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html 前言 实际工作中,我们的数据表数据肯定都是万级别的,如 ...
- openswan框架和编译时说明
刚开始学习openswan项目代码时,自己尝试了在虚拟机上编译.安装.运行openswan代码,由于当时刚开始学习openswan代码,因此对于其构成并不清楚,在编译.运行过程中有了问题,基本是通过百 ...
- IKEv2协议协商流程: (IKE-SA-INIT 交换)第二包
IKEv2协议协商流程: (IKE-SA-INIT 交换)第二包 文章目录 IKEv2协议协商流程: (IKE-SA-INIT 交换)第二包 1. IKEv2 协商总体框架 2. 第二包流程图 3. ...
- IDEA weblogic远程调试
weblogic远程调试 这里我们使用vulhub的镜像作为初始构建镜像搭建漏洞环境 1. 搭建docker环境 新建一个目录,创建两个文件 DockerFile FROM vulhub/weblog ...
- Java-SpringBoot整合SpringCloud
SpringBoot整合SpringCloud 1. SpringCloud特点 SpringCloud专注于为典型的用例和扩展机制提供良好的开箱即用体验,以涵盖其他情况: 分布式/版本化配置 服务注 ...
- 洛谷P1309——瑞士轮(归并排序)
https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=1309#sub 题目背景 在双人对决的竞技性比赛,如乒乓球.羽毛球.国际象棋中,最常见的赛制是淘汰赛和循环赛.前者的特点 ...
- POJ1741——Tree(树的点分治)
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013-11-17 1 ...
- Eclipse中快速生成Javabean的方法
总结一下: 先写出属性 无参构造器:Alt+/ 再按回车 全参构造器:Alt+Shift+S 再按字母O键 再按回车 toString方法:Alt+Shift+S 再按字母S键 再按回车 get/se ...
- js设计模式之发布订阅模式
1. 定义 发布-订阅模式其实是一种对象间一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发送改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都将得到状态改变的通知. 订阅者(Subscriber)把自己想订阅的事件注册(Subscri ...
- LeetCode2-链表两数和
目录 LeetCode2-链表两数和 题目描述 示例提示 经验教训 参考正解 题目描述 示例提示 经验教训 链表题的判空条件不是万能的,有时候示例会极其复杂,根本难以通过判空来区分不同情况. /** ...
