Spark Structured Streaming框架(4)之窗口管理详解
1. 结构
1.1 概述
Structured Streaming组件滑动窗口功能由三个参数决定其功能:窗口时间、滑动步长和触发时间.
- 窗口时间:是指确定数据操作的长度;
- 滑动步长:是指窗口每次向前移动的时间长度;
- 触发时间:是指Structured Streaming将数据写入外部DataStreamWriter的时间间隔。
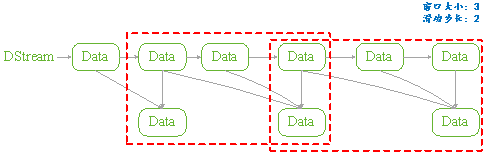
图 11
1.2 API
用户管理Structured Streaming的窗口功能,可以分为两步完成:
API是通过一个全局的window方法来设置,如下所示是其Spark实现细节:
|
def window(timeColumn:Column, windowDuratiion:String, slideDuration:String):Column ={ window(timeColumn, windowDuration, slideDuration, "0" second) } |
- timecolumn:具有时间戳的列;
- windowDuration:为窗口的时间长度;
- slideDuration:为滑动的步长;
- return:返回的数据类型是Column。
Structured Streaming在通过readStream对象的load方法加载数据后,悔返回一个DataFrame对象(Dataset[T]类型)。所以用户将上述定义的Column对象传递给DataFrame对象,从而就实现了窗口功能的设置。
由于window方法返回的数据类型是Column,所以只要DataFrame对象方法中具有columnl类型的参数就可以进行设置。如Dataset的select和groupBy方法。如下是Spark源码中select和groupBy方法的实现细节:
|
def select (cols:Column*):DataFrame = withPlan{ Project(cols.map(_.named),logicalPlan) } |
|
def groupBy(cols:Column*):RelationGroupedDataset={ RelationGroupedDataset(toDF(), cols.map(_.expr), RelationGroupedDataset.GroupByType) } |
1.3 类型
如上述介绍的Structured Streaming API,根据Dataset提供的方法,我们可以将其分为两类:
- 聚合操作:是指具有对数据进行组合操作的方法,如groupBy方法;
- 非聚合操作:是指普通的数据操作方法,如select方法
PS:
两类操作都有明确的输出形式(outputMode),不能混用。
2. 聚合操作
2.1 操作方法
聚合操作是指接收到的数据DataFrame先进行groupBy等操作,器操作的特征是返回RelationGroupedDataset类型的数据。若Structured Streaming存在的聚合操作,那么输出形式必须为"complete",否则程序会出现异常。
如下所示的聚合操作示例:
|
Import spark.implicits._ Val words = … // streaming DataFrame of schema{timestamp:timestamp, word:String} val windowedCounts = words.groupBy( window($"timestamp","10 minutes","5 minutes"), $"word" ).count() |
2.2 example
本例是Spark程序自带的example,其功能是接收socket数据,在接受socket数据,在接受完数据后将数据按空格" "进行分割;然后统计每个单词出现的次数;最后按时间戳排序输出。
如下具体程序内容:
|
package org.apache.spark.examples.sql.streaming import java.sql.Timestamp import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._ /** * Counts words in UTF8 encoded, '\n' delimited text received from the network over a * sliding window of configurable duration. Each line from the network is tagged * with a timestamp that is used to determine the windows into which it falls. * * Usage: StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed <hostname> <port> <window duration> * [<slide duration>] * <hostname> and <port> describe the TCP server that Structured Streaming * would connect to receive data. * <window duration> gives the size of window, specified as integer number of seconds * <slide duration> gives the amount of time successive windows are offset from one another, * given in the same units as above. <slide duration> should be less than or equal to * <window duration>. If the two are equal, successive windows have no overlap. If * <slide duration> is not provided, it defaults to <window duration>. * * To run this on your local machine, you need to first run a Netcat server * `$ nc -lk 9999` * and then run the example * `$ bin/run-example sql.streaming.StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed * localhost 9999 <window duration in seconds> [<slide duration in seconds>]` * * One recommended <window duration>, <slide duration> pair is 10, 5 */ object StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed { def main(args: Array[String]) { if (args.length < 3) { System.err.println("Usage: StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed <hostname> <port>" + " <window duration in seconds> [<slide duration in seconds>]") System.exit(1) } val host = args(0) val port = args(1).toInt val windowSize = args(2).toInt val slideSize = if (args.length == 3) windowSize else args(3).toInt if (slideSize > windowSize) { System.err.println("<slide duration> must be less than or equal to <window duration>") } val windowDuration = s"$windowSize seconds" val slideDuration = s"$slideSize seconds" val spark = SparkSession .builder .appName("StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed") .getOrCreate() import spark.implicits._ // Create DataFrame representing the stream of input lines from connection to host:port val lines = spark.readStream .format("socket") .option("host", host) .option("port", port) .option("includeTimestamp", true) //输出内容包括时间戳 .load() // Split the lines into words, retaining timestamps val words = lines.as[(String, Timestamp)].flatMap(line => line._1.split(" ").map(word => (word, line._2)) ).toDF("word", "timestamp") // Group the data by window and word and compute the count of each group //设置窗口大小和滑动窗口步长 val windowedCounts = words.groupBy( window($"timestamp", windowDuration, slideDuration), $"word" ).count().orderBy("window") // Start running the query that prints the windowed word counts to the console //由于采用聚合操作,所以需要指定"complete"输出形式。指定"truncate"只是为了在控制台输出时,不进行列宽度自动缩小。 val query = windowedCounts.writeStream .outputMode("complete") .format("console") .option("truncate", "false") .start() query.awaitTermination() } } |
3. 非聚合操作
3.1 操作方法
非聚合操作是指接收到的数据DataFrame进行select等操作,其操作的特征是返回Dataset类型的数据。若Structured Streaming进行非聚合操作,那么输出形式必须为"append",否则程序会出现异常。若spark 2.1.1 版本则输出形式开可以是"update"。
3.2 example
本例功能只是简单地将接收到的数据保持原样输出,不进行任何其它操作。只是为了观察Structured Streaming的窗口功能。如下所示:
|
object StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed { def main(args: Array[String]) { if (args.length < 3) { System.err.println("Usage: StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed <hostname> <port>" + " <window duration in seconds> [<slide duration in seconds>]") System.exit(1) } val host = args(0) val port = args(1).toInt val windowSize = args(2).toInt val slideSize = if (args.length == 3) windowSize else args(3).toInt val triggerTime = args(4).toInt if (slideSize > windowSize) { System.err.println("<slide duration> must be less than or equal to <window duration>") } val windowDuration = s"$windowSize seconds" val slideDuration = s"$slideSize seconds" val spark = SparkSession .builder .appName("StructuredNetworkWordCountWindowed") .getOrCreate() import spark.implicits._ // Create DataFrame representing the stream of input lines from connection to host:port val lines = spark.readStream .format("socket") .option("host", host) .option("port", port) .option("includeTimestamp", true) .load() val wordCounts:DataFrame = lines.select(window($"timestamp",windowDuration,slideDuration),$"value") // Start running the query that prints the windowed word counts to the console val query = wordCounts.writeStream .outputMode("append") .format("console") .trigger(ProcessingTime(s"$triggerTime seconds")) .option("truncate", "false") .start() query.awaitTermination() } } |
|
#nc –lk 9999 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
#spark-submit –class structuredNetWordCount ./sparkStreaming.jar localhost 9999 3 2 1 |
|
输出: Batch:0 +---------------------------------------+-----+ |window |value| |[2017-05-16 11:14:15.0,2017-05-16 11:14:19.0]|1 | |[2017-05-16 11:14:15.0,2017-05-16 11:14:19.0]|2 | +---------------------------------------+-----+ Batch:1 +---------------------------------------+-----+ |window |value| |[2017-05-16 11:14:15.0,2017-05-16 11:14:19.0]|3 | |[2017-05-16 11:14:18.0,2017-05-16 11:14:22.0]|3 | |[2017-05-16 11:14:18.0,2017-05-16 11:14:22.0]|4 | +---------------------------------------+-----+ Batch:2 +---------------------------------------+-----+ |window |value| |[2017-05-16 11:14:18.0,2017-05-16 11:14:22.0]|5 | |[2017-05-16 11:14:18.0,2017-05-16 11:14:22.0]|6 | |[2017-05-16 11:14:21.0,2017-05-16 11:14:25.0]|6 | +---------------------------------------+-----+ |
4. 参考文献
Spark Structured Streaming框架(4)之窗口管理详解的更多相关文章
- Spark Structured Streaming框架(5)之进程管理
Structured Streaming提供一些API来管理Streaming对象.用户可以通过这些API来手动管理已经启动的Streaming,保证在系统中的Streaming有序执行. 1. St ...
- Spark Structured streaming框架(1)之基本使用
Spark Struntured Streaming是Spark 2.1.0版本后新增加的流计算引擎,本博将通过几篇博文详细介绍这个框架.这篇是介绍Spark Structured Streamin ...
- Spark Structured Streaming框架(1)之基本用法
Spark Struntured Streaming是Spark 2.1.0版本后新增加的流计算引擎,本博将通过几篇博文详细介绍这个框架.这篇是介绍Spark Structured Streamin ...
- Spark Structured Streaming框架(3)之数据输出源详解
Spark Structured streaming API支持的输出源有:Console.Memory.File和Foreach.其中Console在前两篇博文中已有详述,而Memory使用非常简单 ...
- Spark Structured Streaming框架(2)之数据输入源详解
Spark Structured Streaming目前的2.1.0版本只支持输入源:File.kafka和socket. 1. Socket Socket方式是最简单的数据输入源,如Quick ex ...
- Spark Structured Streaming框架(2)之数据输入源详解
Spark Structured Streaming目前的2.1.0版本只支持输入源:File.kafka和socket. 1. Socket Socket方式是最简单的数据输入源,如Quick ex ...
- Spark2.3(三十四):Spark Structured Streaming之withWaterMark和windows窗口是否可以实现最近一小时统计
WaterMark除了可以限定来迟数据范围,是否可以实现最近一小时统计? WaterMark目的用来限定参数计算数据的范围:比如当前计算数据内max timestamp是12::00,waterMar ...
- DataFlow编程模型与Spark Structured streaming
流式(streaming)和批量( batch):流式数据,实际上更准确的说法应该是unbounded data(processing),也就是无边界的连续的数据的处理:对应的批量计算,更准确的说法是 ...
- Spark2.3(三十五)Spark Structured Streaming源代码剖析(从CSDN和Github中看到别人分析的源代码的文章值得收藏)
从CSDN中读取到关于spark structured streaming源代码分析不错的几篇文章 spark源码分析--事件总线LiveListenerBus spark事件总线的核心是LiveLi ...
随机推荐
- java中poi解析excel(兼容07版本以上及以下:.xls和.xlsx格式)
package com.genersoft.cbms.ysbz.ExcelDr.cmd; import com.genersoft.cbms.ysbz.ExcelDr.dao.ExcelDrDao; ...
- free bsd x修改UTC->SCT
#cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Taipei /etc/localtime #ntpdate asia.pool.ntp.org #adjkerntz -a #date
- flume-ng tmp
flume-ng 是一个分布式,高可用的日志收集系统.主要用来将分布在不同服务器上的业务日志汇总在一个集中的数据存储中心 一 安装与环境配置 下载地址 http://flume.apache.org/ ...
- Maven项目Update Project...后JRE System Library会自动变回1.5解决办法
<build> <finalName>pay</finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>o ...
- 如何在github上发起一个pull request,如何贡献代码,参与开源项目
点击页面右上角的 “fork” ,把你关注的项目fork到你自己的账号下了. 把项目克隆到本地 修改并push 回到你的github界面,发起请求: 在自己fork的库处新建请求:New pull r ...
- php 生成下载连接
public function showdownload(){ $file_url=$_GET['url']; $new_name='激活码'; if(!isset($file_url)||trim( ...
- onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent调用时序(转)
onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent调用时序 onInterceptTouchEvent()是ViewGroup的一个方法,目的是在系统向该ViewGroup及其各个c ...
- 对无向图的深度优先搜索(DFS)
[0]README 0.1) 本文总结于 数据结构与算法分析, 源代码均为原创, 旨在 理解 如何对无向图进行深度优先搜索 的idea 并用源代码加以实现: 0.2) 本文还引入了 背向边(定义见下文 ...
- 编程算法 - 二叉树的最低公共祖先 代码(C)
二叉树的最低公共祖先 代码(C) 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy 二叉树的最低公共祖先(lowest common ancestor), 首先先序遍 ...
- JAVA card 应用开发(六) 个人化数据的线路安全和数据安全
卡片个人化数据的线路安全和数据安全 说明:下面理论,基于GP2.2规范. 一.线路安全 1. 概念:线路安全.就是对于数据不保密.但要保证数据的完整性和防止被篡改. 2. 方法:在原有的数据基础上.加 ...
