三 概要模式 2) MR倒排索引、性能分析、搜索干扰词。
有两种不同的反向索引形式:
后者的形式提供了更多的兼容性(比如短语搜索),但是需要更多的时间和空间来创建。

以英文为例,下面是要被索引的文本:
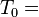
"it is what it is"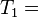
"what is it"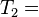
"it is a banana"
我们就能得到下面的反向文件索引:
"a": {2}
"banana": {2}
"is": {0, 1, 2}
"it": {0, 1, 2}
"what": {0, 1}
检索的条件"what", "is" 和 "it" 将对应这个集合: 。
。
对相同的文字,我们得到后面这些完全反向索引,有文档数量和当前查询的单词结果组成的的成对数据。 同样,文档数量和当前查询的单词结果都从零开始。所以,"banana": {(2, 3)} 就是说 "banana"在第三个文档里 (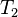 ),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
"a": {(2, 2)}
"banana": {(2, 3)}
"is": {(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 1)}
"it": {(0, 0), (0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 0)}
"what": {(0, 2), (1, 0)}
如果我们执行短语搜索"what is it" 我们得到这个短语的全部单词各自的结果所在文档为文档0和文档1。但是这个短语检索的连续的条件仅仅在文档1得到。
2.分析和设计
(1)Map过程
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容,Map过程首先必须分析输入的<key, value>对,得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档URI和词频,如图所示:

存在两个问题,第一:<key, value>对只能有两个值,在不使用Hadoop自定义数据类型的情况下,需要根据情况将其中的两个值合并成一个值,作为value或key值;
第二,通过一个Reduce过程无法同时完成词频统计和生成文档列表,所以必须增加一个Combine过程完成词频统计
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); //存储单词和URI的组合 private Text valueInfo = new Text();//存储词频 private FileSplit split; //存储Split对象 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获得<key,value>对所属的FileSplit对象 split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { //key值由单词和URI组成,如"MapReduce:1.txt" keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); // 词频初始为1 valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } }} |
(2)Combine过程
将key值相同的value值累加,得到一个单词在文档中的词频,如图
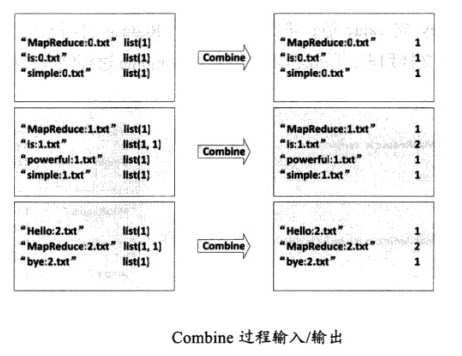
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //统计词频 int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); //重新设置value值由URI和词频组成 info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); //重新设置key值为单词 key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); }} |
(3)Reduce过程
讲过上述两个过程后,Reduce过程只需将相同key值的value值组合成倒排索引文件所需的格式即可,剩下的事情就可以直接交给MapReduce框架进行处理了

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //生成文档列表 String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); }} |
完整代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
import java.io.IOException;import java.util.StringTokenizer;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;public class InvertedIndex { public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); private Text valueInfo = new Text(); private FileSplit split; public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } } } public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); } } public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub Configuration conf = new Configuration(); String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); if(otherArgs.length != 2) { System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>"); System.exit(2); } Job job = new Job(conf, "InvertedIndex"); job.setJarByClass(InvertedIndex.class); job.setMapperClass(InvertedIndexMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setCombinerClass(InvertedIndexCombiner.class); job.setReducerClass(InvertedIndexReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); }} |

三 概要模式 2) MR倒排索引、性能分析、搜索干扰词。的更多相关文章
- 三 概要模式 3) MR计数器计数 。无 reduce 计数
计数器模式讲解: 先讲一下,就是说只用 Map 阶段 不需要 Reduce . 也就是说去掉了中间输出,而是Map 直接输出结果.大大提高了 MR 的效率且节省了 MR 中间输出读入 ...
- Trie性能分析之敏感词过滤golang
package util import ( "strings" ) type Node struct { //rune表示一个utf8字符 char rune Data inter ...
- PHP 性能分析第三篇: 性能调优实战
注意:本文是我们的 PHP 性能分析系列的第三篇,点此阅读 PHP 性能分析第一篇: XHProf & XHGui 介绍 ,或 PHP 性能分析第二篇: 深入研究 XHGui. 在本系列的 ...
- mysql性能分析工具
一.EXPALIN 在SQL语句之前加上EXPLAIN关键字就可以获取这条SQL语句执行的计划 那么返回的这些字段是什么呢? 我们先关心一下比较重要的几个字段: 1. select_type 查询类型 ...
- Android 常用的性能分析工具详解:GPU呈现模式, TraceView, Systrace, HirearchyViewer(转)
此篇将重点介绍几种常用的Android性能分析工具: 一.Logcat 日志 选取Tag=ActivityManager,可以粗略地知道界面Displaying的时间消耗.当我们打开一个Activit ...
- MySQL 索引性能分析概要
上一篇文章 MySQL 索引设计概要 介绍了影响索引设计的几大因素,包括过滤因子.索引片的宽窄与大小以及匹配列和过滤列.在文章的后半部分介绍了 数据库索引设计与优化 一书中,理想的三星索引的设计流程和 ...
- for-loop 与 json.Unmarshal 性能分析概要
原文地址:for-loop 与 json.Unmarshal 性能分析概要 前言 在项目中,常常会遇到循环交换赋值的数据处理场景,尤其是 RPC,数据交互格式要转为 Protobuf,赋值是无法避免的 ...
- SQL2005性能分析一些细节功能你是否有用到?(三)
原文:SQL2005性能分析一些细节功能你是否有用到?(三) 继上篇: SQL2005性能分析一些细节功能你是否有用到?(二) 第一: SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON 当我们比较查 ...
- c#之冒泡排序的三种实现和性能分析
冒泡排序算法是我们经常见到的尤其是子一些笔试题中. 下面和大家讨论c#中的冒泡排序,笔者提供了三种解决方案,并且会分析各自的性能优劣. 第一种估计大家都掌握的,使用数据交换来实现,这种就不多说了,园子 ...
随机推荐
- LR编写post请求
函数列表: web_submit_data(); web_custom_request(); web_get_int_property(); 1.web_submit_data(); 2.web_cu ...
- swfit的特点
swfit的特点: 1.swift句尾不需要分号,除非你想在一行中写三行代码就加分号隔开. 2.swift不要写main函数,程序默认从上往下执行 3.swift不分.h和.m文件,一个类只有.swi ...
- EFcore笔记之创建模型
排除属性:NotMapped NotMapped:排除属性在CodeFirst的时候在数据库里不创建该属性 public class Blog { public int BlogId { get; ...
- .startsWith和endsWith的使用方法与说明
a.startsWith(b) --判断字符串a,是不是以字符串b开头 a.endsWith(b) --判断字符串a,是不是以字符串b结尾
- django框架-Admin管理站点搭建
在django框架中,admin基本上算是已经写好了的,拿过来进行简单的处理即可以使用的,相对于flask来说已经是相当的便捷了. 在使用中,步骤如下: 1.管理界面本地化:即将英文标题等的变成中文, ...
- Java多线程-基础知识
一. 进程是执行中的程序,程序是静态的(我们写完以后不运行就一直放在那里),进程是执行中的程序,是动态概念的.一个进程可以有多个线程. 二. 多线程包含两个或两个以上并发运行的部分,把程序中每个这样并 ...
- 2015 Multi-University Training Contest 1 y sequence
Y sequence Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- OO问题
设计一个在线的酒店预订系统,并且可以通过城市搜索出来 解决办法: Main Class: User Room Hotel Booking Adress Enums : 房间的状态和类型 public ...
- Qt之手动布局
简述 手动布局,可以实现和水平布局.垂直布局.网格布局等相同的效果,也可实现属于自己的自定义布局,当窗体缩放时,控件可以随之变化. 其对于坐标系的建立有严格要求,纯代码思维,使用复杂,不易维护,所以一 ...
- hdu 1518 Square 深搜,,,,花样剪枝啊!!!
Square Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Su ...
