HDUOJ----1301 Jungle Roads
Jungle Roads
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3968 Accepted Submission(s): 2888
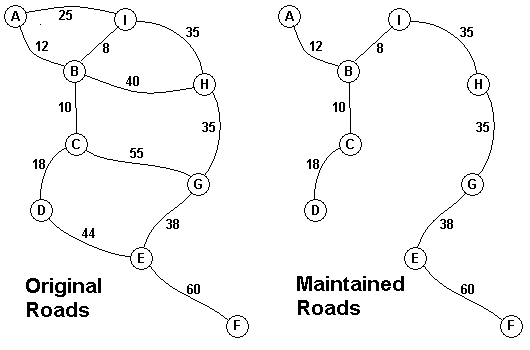
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
A 2 B 12 I 25
B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
C 2 D 18 G 55
D 1 E 44
E 2 F 60 G 38
F 0
G 1 H 35
H 1 I 35
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20
0
30
最小生成树 ,解法一 普利姆算法...
做了这么多不妨做一个总结ba 。 关于普利姆算法
普利姆一般用于连续的点...(密集型的结构图)。
通过这个p大家可能会看的比较明白....
比如 第二个样列
3
A 2 B 10 C 40
B 1 C 20 a-->(b-->c ,c) 对于这样一个图,随机从一点出发... 米前景一步变求一次最小,,,
于是 觉得用代码更有说服力。。。毕竟要说明白也很花时间,.
代码:
// test 1 prim
//< @ Gxjun coder>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f ;
int vis[],lowc[];
int prim( const int cost[][], int n)
{
int i,j,p;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
vis[]=;
int minc,res=;
for(i=; i<n ;i++)
lowc[i]=cost[][i];
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
minc=inf;
p=-;
for( j=; j<n; j++)
{
if(==vis[j] && minc>lowc[j])
{
minc = lowc[j];
p=j;
}
}
if(minc==inf) return -;
res+=minc;
vis[p]=;
for(j= ; j<n ;j++)
{
if(vis[j]== && lowc[j]>cost[p][j])
lowc[j]=cost[p][j];
} }
return res;
}
int sta[][];
int main()
{
int n,m,i,j;
char a[],b[];
int val;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
for(i= ;i<; i++)
{
for( j=; j< ;j++)
{
sta[i][j]=inf;
}
}
for(i=; i<n; i++)
{ scanf("%s %d",a,&m);
int fo=a[]-'A';
while(m--)
{
scanf("%s %d",b, &val);
int tot=b[]-'A';
sta[fo][tot]=sta[tot][fo]=val;
}
} printf("%d\n",prim(sta,n));
}
return ;
}
方法二: 克鲁斯卡尔算法(krusal)
运用并查集进行联通分量的查找,逐步口大连通分量.....
详细代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Side
{
int vs,ve; //<vs--->表示开始的位置,ve-->代表结束的位置>
int len ; // <边的长度>
}side;
side sta[]; //最多50个节点
//<用到并查集来A>
int father[];
/*初始化*/
void mset()
{
for(int i=; i< ;i++)
father[i]=i;
}
//<查找>
int setfind(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=setfind(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
// <合并>即克鲁斯卡尔算法
void krusal( int sx ,int sy)
{
int x=setfind(sx);
int y=setfind(sy);
if(x==y) return ;
if(x<y)
father[y]=x;
else
father[x]=y; }
int cmp(const void* a ,const void* b )
{
return (*(side *)a).len-(*(side*)b).len;
} int main( void )
{
int n,m,tol,val,i,ans;
char a[],b[];
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
ans=tol=;
for(i=; i<n ;i++)
{
scanf("%s%d",a,&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%s%d",b, &val);
sta[tol].vs=a[]-;
sta[tol].ve=b[]-;
sta[tol].len=val;
tol++;
}
}
mset();
qsort(sta,tol ,sizeof(sta[]),cmp);
for(i= ; i<tol ;i++)
{
int tem1=setfind(sta[i].vs);
int tem2=setfind( sta[i].ve ) ;
if(tem1 != tem2) //如果两个两桶分量不在一起,那就链接起来
{
krusal(tem1,tem2);
ans+=sta[i].len;
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
HDUOJ----1301 Jungle Roads的更多相关文章
- POJ 1251 && HDU 1301 Jungle Roads (最小生成树)
Jungle Roads 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/124434#problem/A http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vju ...
- hdu 1301 Jungle Roads 最小生成树
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1301 The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrish ...
- hdu 1301 Jungle Roads krusckal,最小生成树,并查集
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was s ...
- POJ 1251 & HDU 1301 Jungle Roads
题目: Description The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign ...
- HDOJ 1301 Jungle Roads
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1301 //HDOJ1301 #include<iostream>#include<c ...
- hdu 1301 Jungle Roads
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1301 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #inc ...
- Hdu 1301 Jungle Roads (最小生成树)
地址:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1301 很明显,这是一道“赤裸裸”的最小生成树的问题: 我这里采用了Kruskal算法,当然用Prim算法也 ...
- HDU 1301 Jungle Roads (最小生成树,基础题,模版解释)——同 poj 1251 Jungle Roads
双向边,基础题,最小生成树 题目 同题目 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include<stri ...
- POJ 1251 + HDU 1301 Jungle Roads 【最小生成树】
题解 这是一道裸的最小生成树题,拿来练手,题目就不放了 个人理解 Prim有些类似最短路和贪心,不断找距当前点最小距离的点 Kruskal类似于并查集,不断找最小的边,如果不是一棵树的节点就合并为一 ...
- 最小生成树 || HDU 1301 Jungle Roads
裸的最小生成树 输入很蓝瘦 **并查集 int find(int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); } 找到x在并查集里的根结点,如果 ...
随机推荐
- convert-a-number-to-hexadecimal
https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-a-number-to-hexadecimal/ // https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic ...
- Cesium随笔(5)CZML介绍(介个文章是转的嘿嘿)【转】
通过czml可以在cesium上实现非常棒的动态效果 (1)Cesium Language (CZML) 入门--CZML Structure(CZML的结构) 原文地址:https://github ...
- 适配 通知 Notification 通知渠道 前台服务 MD
Markdown版本笔记 我的GitHub首页 我的博客 我的微信 我的邮箱 MyAndroidBlogs baiqiantao baiqiantao bqt20094 baiqiantao@sina ...
- 对 C# 未来的期望
接触 C# 一年,总体上是一个非常完善的语言,但是某些细节特征还是不够完美.这里记下我现在对它将来的一些期望. 更强大的泛型约束 与 C++ 的模板相似,C# 的泛型使得编写适用于多种 ...
- HttpWebRequest的使用
HttpWebRequest类主要利用HTTP 协议和服务器交互,通常是通过 GET 和 POST 两种方式来对数据进行获取和提交.下面对这两种方式进行一下说明: GET 方式 GET 方式通过在网络 ...
- 使用jQuery在上传图片之前实现缩略图预览
使用jQuery在上传图片之前实现缩略图预览 jQuery代码 01 $("#uploadImage").on("change", function(){ 02 ...
- SQL-重复记录查询的几种方法
1.查找表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(peopleId)来判断 select * from people where peopleId in (select peopleId from ...
- iOS8开发~Swift(二)Playground
一.Playground介绍 Playground是Xcode6中自带的Swift代码开发环境.俗话说"功欲善其事,必先利其器".曾经在Xcode5中编写脚本代码.比如编写JS.其 ...
- HTML5游戏,五子棋
在线演示 本地下载 最近html5的游戏还真是不少,这种在线游戏既简单又有趣.收藏几个在午休时间娱乐一下.何乐而不为呢?喜欢研究的可以下载代码看看.超级推荐!
- Service 隔离
最近开发了两个App,其中一个App为另一个App提供服务(Service),但要求不允许其他的App使用此服务,一开始的想法是能在API的设计上进行过滤,后来想想此方法不是很安全,被别人反 ...
