Android 程序 LinearLayout布局 参数layout_weight 探讨
官方参考文档 对LinearLayout.LayoutParams中的android:layout_weight解释如下:
Indicates how much of the extra space in the LinearLayout will be allocated to the view associated with these LayoutParams.
Specify 0 if the view should not be stretched. Otherwise the extra pixels will be pro-rated among all views whose weight is greater than 0.
extra space: 是指各个子view占用完 长度或宽度 之后再来分配。
下面引用两篇文章,仔细看完会有一定了解。
第一篇: The use of layout_weight with Android layouts
The popular Android OS uses layouts to display Views on the screen. A View is a widget that has an appearance on the screen. Examples of widgets are radio buttons, labels, edit boxes, etc.
The appearance and sequence of Views can be ordered and one of the ways to do that is through the use of the LayoutParamlayout_weight. This is an often overlooked, extremely powerful, but also tricky feature of layouts.
The Android developers website (developer.android.com) defines layout_weight as follows:
Indicates how much of the extra space in the [ViewGroup] will be allocated to the view associated with these LayoutParams.
This definition does not help us very much, especially because it is only true under specific circumstances as we see below. Let’s have a look at some examples. In the first example we want to split the display in half vertically with the following layout:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:background="#0000FF"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent" />
<LinearLayout
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>

Not using layout_weight (不写layout_weight的话,第一个子元素的match_parent会占满整个父元素,第二个就没有空间了)
------------------------------------------
Of course the split does not work because the layout_height of the first LinearLayout is set to match_parent causing it to take up all available space and leaving no room for the secondLinearLayout. Changing the layout_height to wrap_content will not help because the LinearLayouts have 0 heights making them invisible.
At this point we can show what layout_weight can do. Have a look at this, changed, piece of code and the resulting screenshot below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:background="#0000FF"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<LinearLayout
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
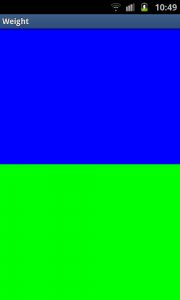
Using layout_weight
----------------------------------------------
By setting a layout_weight for the two inner LinearLayouts we can tell the parent layout to divide the available space between its children. In this example, we have set the two layout_weightvalues of the child layouts to the same value, and they will be given an equal part of the available space.
Setting a layout_weight means that the default value of this attribute is changed from 0. Assigning a value higher than zero will split up the rest of the available space in the parent View, according to the value of each View‘s layout_weight and its ratio to the overall layout_weight specified in the current layout for this and other View elements.
To give an example: in the above example we have twoLinearLayouts. If the layout_weight of each of the twoLinearLayouts is set to 1, the remaining width in the parent layout will be split equally between them (as we have seen above). If the first one has a layout_weight of 1 and the second has a layout_weight of 2, then the total weight is three and one third of the remaining space will be given to the first, and two thirds to the second, see the screenshot below.
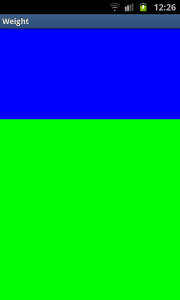
Unequal division of weight
----------------------------------
The divide is one third and two third but, still not exactly what we want. Take a close look at the code. We want the firstLinearLayout to occupy two third of the screen. Its layout_weightis set to 2. What we see is that it only occupies one third of the screen. This is the tricky bit of using layout_weight.
The problems are the circumstances it is used in. In this case it is used with layout_height set to match_parent. In some (!) cases this keeps Android from interpreting the layout_weights correctly. In this case, a vertical layout of view elements, the solution is setting layout_heights to 0dp. With a horizontal layout of view elements layout_width should be set to 0dp.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:background="#0000FF"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<LinearLayout
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>

Correct division of weight (如果希望按比例分配空间的话, 把android:layout_height(纵向) 或者 android:layout_width(横向) 设置成0dp。)
-------------------------------------
In the above examples the total weight of a View element is calculated by adding all the weights of its children. This can be overridden by adding a weightSum to the parent layout. This provides us with even more control over things. The childrenLinearLayouts can be specified to take their respective screen parts (two fourth and one fourth) and the parent LinearLayoutwill take the rest (the remaining one fourth):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:weightSum="4"
android:padding="5dp"> <!-- to show what the parent is -->
<LinearLayout
android:background="#0000FF"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<LinearLayout
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>

Example with weightSum (不占满父元素,那就在父元素上使用 android:weightSum)
----------------------------------------
As a conclusion let’s have another look at a potential gotcha when using layout_weights. First switch to a horizontalLinearLayout. This contains two TextViews, each with alayout_width set to 1, but with text of very different lengths in each:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="small"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A very very long text that needs to wrap."
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>

Texts not shown as wanted
---------------------------------------
As with the vertical layout the result is not what we expect. This time because of the specified layout_width. When calculating the layout, Android calculates the width of the two text controls first and the remaining space is then divided between them equally. Because the second TextView is wider, due to its longer text, it appears to be taking up most of the space. As seen earlier the solution is simple, using 0dp forlayout_width:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="small"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="A very very long text that needs to wrap."
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>

=============================================
第二篇文章: android中layout_weight的理解 文章从代码角度解释了一下分配原则, 具体内容点击链接就能看。
Android 程序 LinearLayout布局 参数layout_weight 探讨的更多相关文章
- Android:LinearLayout布局中Layout_weight的深刻理解
首先看一下LinearLayout布局中Layout_weight属性的作用:它是用来分配属于空间的一个属性,你可以设置他的权重.很多人不知道剩余空间是个什么概念,下面我先来说说剩余空间. 看下面代码 ...
- Android学习——LinearLayout布局实现居中、左对齐、右对齐
android:orientation="vertical"表示该布局下的元素垂直排列: 在整体垂直排列的基础上想要实现内部水平排列,则在整体LinearLayout布局下再创建一 ...
- 15.Android中LinearLayout布局一些小记录
在App中,我们经常看到布局中会有分割线,直接上代码: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <Lin ...
- Android之LinearLayout布局下怎么让按钮固定在底部
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=&quo ...
- app开发历程————Android程序解析服务器端的JSON格式数据,显示在界面上
上一篇文章写的是服务器端利用Servlet 返回JSON字符串,本文主要是利用android客户端访问服务器端链接,解析JSON格式数据,放到相应的位置上. 首先,android程序的布局文件main ...
- Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数)
[Android布局学习系列] 1.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解一 2.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数) 3.And ...
- 将Android Studio默认布局ConstraintLayout切换成LinearLayout
将Android Studio默认布局ConstraintLayout切换成LinearLayout 大部分人初次使用google android 扁平化布局ConstraintLayout都 ...
- 无废话Android之常见adb指令、电话拨号器、点击事件的4种写法、短信发送器、Android 中各种布局(1)
1.Android是什么 手机设备的软件栈,包括一个完整的操作系统.中间件.关键的应用程序,底层是linux内核,安全管理.内存管理.进程管理.电源管理.硬件驱动 2.Dalvik VM 和 JVM ...
- [置顶] Android系统五大布局详解Layout
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前,视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的.组件就是我们常见的Button.TextEdit等 ...
随机推荐
- 浅窥ArcGIS Data Store之两斑
关于 ArcGIS Data Store,我们备受大家喜爱的suwenjiang朋友在其博客空间suwenjiang的烂笔头中贡献了<ArcGIS Data Store初体验>一文,全面讲 ...
- MySql5.7主从配置
记录 环境:ubuntu16.04,mysql5.7 主机:192.168.1.240,192.168.1.241:241为Salve 1.安装mysql sudo apt-get install m ...
- win7下一直试用Beyond Compare 4
找到目录C:\Users\用户名\AppData\Roaming\BeyondCompare,将这个目录删除,重启compare即可.
- Android(java)学习笔记113:Activity的生命周期
1.首先来一张生命周期的总图: onCreate():创建Acitivity界面 onStart():让上面创建的界面可见 onResume():让上面创建的界面 ...
- LeetCode分类-前400题
1. Array 基础 27 Remove Element 26 Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array 80 Remove Duplicates from Sorte ...
- PropertyConfigurer.java
package util; import java.util.Properties; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import o ...
- 理解AttributeUsage类
类定义: // 摘要: // 指定另一特性类的用法. 此类不能被继承. [Serializable] [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class, Inherited ...
- Bootstrap标签页(Tab)插件事件
事件 下表列出了标签页(Tab)插件中要用到的事件.这些事件可在函数中当钩子使用. 事件 描述 实例 show.bs.tab 该事件在标签页显示时触发,但是必须在新标签页被显示之前.分别使用 even ...
- ASP.NET 验证控件报错:WebForms UnobtrusiveValidationMode 需要“jquery”ScriptResourceMapping。
在Visual Studio 2012中添加并使用验证控件时,可能会遇到如下的错误: WebForms UnobtrusiveValidationMode 需要“jquery”ScriptResour ...
- C#数组添加元素
一.向数组添加元素 在C#中,只能在动态数组ArrayList类中向数组添加元素.因为动态数组是一个可以改变数组长度和元素个数的数据类型. 示例: using System;using System. ...
