HDFS读写数据块--${dfs.data.dir}选择策略
最近工作需要,看了HDFS读写数据块这部分。不过可能跟网上大部分帖子不一样,本文主要写了${dfs.data.dir}的选择策略,也就是block在DataNode上的放置策略。我主要是从我们工作需要的角度来读这部分代码的。
hdfs-site.xml
<property>
<name>dfs.data.dir</name>
<value>/mnt/datadir1/data,/mnt/datadir2/data,/mnt/datadir3/data</value>
</property>
所谓${dfs.data.dir}的选择策略,就是当DataNode配置有多个${dfs.data.dir}目录时(如上面的配置),该选择哪个目录来存放block。一般多个硬盘分别挂载到不同的${dfs.data.dir}下,所以存储block是要决定block该放到哪个磁盘上。
创建文件总共有两步:
1、在写block之前,需要与NameNode通信来生成文件(INodeFile、INodeFileUnderConstruction)。首先在DFSClient端的create()方法中发起写请求,然后通过RPC由NameNode最终调用FSNameSystem的startFileInternal()方法来创建文件。
private void startFileInternal(String src,
PermissionStatus permissions,
String holder,
String clientMachine,
boolean overwrite,
boolean append,
boolean createParent,
short replication,
long blockSize
) throws IOException {
if (NameNode.stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("DIR* startFile: src=" + src
+ ", holder=" + holder
+ ", clientMachine=" + clientMachine
+ ", createParent=" + createParent
+ ", replication=" + replication
+ ", overwrite=" + overwrite
+ ", append=" + append);
} FSPermissionChecker pc = getPermissionChecker();
synchronized (this) {
if (isInSafeMode())
throw new SafeModeException("Cannot create " + src, safeMode);
if (!DFSUtil.isValidName(src)) {
throw new IOException("Invalid name: " + src);
} // Verify that the destination does not exist as a directory already.
boolean pathExists = dir.exists(src);
if (pathExists && dir.isDir(src)) {
throw new IOException("Cannot create "+ src + "; already exists as a directory");
} if (isPermissionEnabled) {
if (append || (overwrite && pathExists)) {
checkPathAccess(pc, src, FsAction.WRITE);
} else {
checkAncestorAccess(pc, src, FsAction.WRITE);
}
} if (!createParent) {
verifyParentDir(src);
} try {
INode myFile = dir.getFileINode(src); //根据路径寻找该文件
recoverLeaseInternal(myFile, src, holder, clientMachine, false); try {
verifyReplication(src, replication, clientMachine);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IOException("failed to create " + e.getMessage());
}
if (append) {//若是追加操作
if (myFile == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("failed to append to non-existent "
+ src + " on client " + clientMachine);
} else if (myFile.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException("failed to append to directory " + src
+ " on client " + clientMachine);
}
} else if (!dir.isValidToCreate(src)) {
if (overwrite) {//允许覆盖原来的文件
delete(src, true);
} else {
throw new IOException("failed to create file " + src
+ " on client " + clientMachine
+ " either because the filename is invalid or the file exists");
}
} DatanodeDescriptor clientNode = host2DataNodeMap
.getDatanodeByHost(clientMachine); if (append) {
//
// Replace current node with a INodeUnderConstruction.
// Recreate in-memory lease record.
//
INodeFile node = (INodeFile) myFile;
INodeFileUnderConstruction cons = new INodeFileUnderConstruction(
node.getLocalNameBytes(), node.getReplication(),
node.getModificationTime(), node.getPreferredBlockSize(),
node.getBlocks(), node.getPermissionStatus(), holder,
clientMachine, clientNode);
dir.replaceNode(src, node, cons);
leaseManager.addLease(cons.clientName, src); } else {
// Now we can add the name to the filesystem. This file has no
// blocks associated with it.
//
checkFsObjectLimit(); // increment global generation stamp
long genstamp = nextGenerationStamp();
INodeFileUnderConstruction newNode = dir.addFile(src, permissions,
replication, blockSize, holder, clientMachine, clientNode,
genstamp);
if (newNode == null) {
throw new IOException("DIR* startFile: Unable to add to namespace");
}
leaseManager.addLease(newNode.clientName, src);
if (NameNode.stateChangeLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("DIR* startFile: "
+"add "+src+" to namespace for "+holder);
}
}
} catch (IOException ie) {
NameNode.stateChangeLog.warn("DIR* startFile: "
+ie.getMessage());
throw ie;
}
}
}
startFileInternal()
该方法的主要内容如下:
1)首先做一些检查(安全模式、权限、该路径是否已经以文件夹形式存在等)
2)若不是追加操作:
生成generation stamp(针对每个文件生成一个);并构造INodeFileUnderConstruction对象(preferredBlockSize);将这个文件添加到filesystem;添加租约(即有时间限制的写锁);
若是追加操作:
将src下的INodeFile替换成INodeFileUnderConstruction;添加租约;
2、在NameNode端生成文件之后,client向NameNode申请block,并将其写入到DataNode。在上面的工作完成后,就启动DataStreamer线程来向DataNode中写入block。整个流程如下:
1)一些前期检查
2)向NameNode申请block(与NameNode有一次通信)
a. 根据副本放置策略,选择N个DataNode作为block的放置位置;
b. 随机生成一个不重复的blockID;
c. 把该block添加到对应的文件;
3)将目标DN组织成pipeline,并向第一个DN发送Packet
选择其中几个比较重要的方法分析下:
/**
* The client would like to obtain an additional block for the indicated
* filename (which is being written-to). Return an array that consists
* of the block, plus a set of machines. The first on this list should
* be where the client writes data. Subsequent items in the list must
* be provided in the connection to the first datanode.
*
* Make sure the previous blocks have been reported by datanodes and
* are replicated. Will return an empty 2-elt array if we want the
* client to "try again later".
*/
//向NameNode申请block
public LocatedBlock getAdditionalBlock(String src,
String clientName,
HashMap<Node, Node> excludedNodes
) throws IOException {
long fileLength, blockSize;
int replication;
DatanodeDescriptor clientNode = null;
Block newBlock = null; NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("BLOCK* getAdditionalBlock: "
+src+" for "+clientName); synchronized (this) {
if (isInSafeMode()) {//check safemode first for failing-fast
throw new SafeModeException("Cannot add block to " + src, safeMode);
}
// have we exceeded the configured limit of fs objects.
checkFsObjectLimit(); INodeFileUnderConstruction pendingFile = checkLease(src, clientName); //
// If we fail this, bad things happen!
//
if (!checkFileProgress(pendingFile, false)) {
throw new NotReplicatedYetException("Not replicated yet:" + src);
}
fileLength = pendingFile.computeContentSummary().getLength();
blockSize = pendingFile.getPreferredBlockSize();
clientNode = pendingFile.getClientNode();
replication = (int)pendingFile.getReplication();
} // choose targets for the new block to be allocated.
//选择副本存放的位置
DatanodeDescriptor targets[] = replicator.chooseTarget(src,
replication,
clientNode,
excludedNodes,
blockSize);
if (targets.length < this.minReplication) {
throw new IOException("File " + src + " could only be replicated to " +
targets.length + " nodes, instead of " +
minReplication);
} // Allocate a new block and record it in the INode.
synchronized (this) {
if (isInSafeMode()) { //make sure it is not in safemode again.
throw new SafeModeException("Cannot add block to " + src, safeMode);
}
INode[] pathINodes = dir.getExistingPathINodes(src);
int inodesLen = pathINodes.length;
checkLease(src, clientName, pathINodes[inodesLen-1]);
INodeFileUnderConstruction pendingFile = (INodeFileUnderConstruction)
pathINodes[inodesLen - 1]; if (!checkFileProgress(pendingFile, false)) {
throw new NotReplicatedYetException("Not replicated yet:" + src);
} // allocate new block record block locations in INode.
//分配block,并随机生成一个不重复的blockID,然后在INode中记录该block
newBlock = allocateBlock(src, pathINodes);
pendingFile.setTargets(targets); for (DatanodeDescriptor dn : targets) {
dn.incBlocksScheduled();
}
dir.persistBlocks(src, pendingFile);
}
if (persistBlocks) {
getEditLog().logSync();
} // Create next block
LocatedBlock b = new LocatedBlock(newBlock, targets, fileLength);
if (isAccessTokenEnabled) {
b.setBlockToken(accessTokenHandler.generateToken(b.getBlock(),
EnumSet.of(BlockTokenSecretManager.AccessMode.WRITE)));
}
return b;
}
getAdditionalBlock
上面的方法还涉及到了块的选择策略,这个留在下一篇再说。下面这个图来总结下上面方法的调用层次:

最后重点说一下block在DataNode上的存储策略。其调度层次如下:

首先说一下其中涉及到的数据结构:
class FSVolume { //卷信息,代表${dfs.data.dir}
private File currentDir; //存放block,即${dfs.data.dir}/current
private FSDir dataDir; //表示currentDir有哪些块文件
private File tmpDir; //存放一些临时文件,即${dfs.data.dir}/tmp
private File blocksBeingWritten; //放置正在写的block,即${dfs.data.dir}/ blocksBeingWritten
private File detachDir; //是否写分离,即${dfs.data.dir}/detach
private DF usage;
private DU dfsUsage;
private long reserved;
static class FSVolumeSet { //卷信息集合,代表多个${dfs.data.dir}
FSVolume[] volumes = null; //代表多个FSVolume,并将其组织成一个数组
int curVolume = 0; //指示当前正在使用哪一个FSVolume
FSVolumeSet 代表多个${dfs.data.dir}目录的集合,它将这些目录组织成一个数组volumes,然后用curVolume来指示当前正在使用的是哪个${dfs.data.dir}目录。${dfs.data.dir}的选择策略如下:
当有多个${dfs.data.dir}时,DataNode顺序地从volumes选择一个FSVolume用来存放block(先放在blocksBeingWritten目录下,写完后再转移到current目录下);
每次写完一个block, curVolume增1。以此实现多个${dfs.data.dir}目录的轮流写。该策略在FSDataSet.FSVolumeSet的getNextVolume()方法中实现。
synchronized FSVolume getNextVolume(long blockSize) throws IOException {
if(volumes.length < 1) {
throw new DiskOutOfSpaceException("No more available volumes");
}
// since volumes could've been removed because of the failure
// make sure we are not out of bounds
if(curVolume >= volumes.length) {
curVolume = 0;
}
int startVolume = curVolume;
while (true) {
FSVolume volume = volumes[curVolume];
curVolume = (curVolume + 1) % volumes.length; //增1
if (volume.getAvailable() > blockSize) { return volume; }
if (curVolume == startVolume) {
throw new DiskOutOfSpaceException("Insufficient space for an additional block");
}
}
}
接着来说一下读block的过程。在Map Task执行时,nextKeyValue()方法来从block中读取数据,主要步骤如下:
1、根据创建Map Task时指定的文件偏移量和长度,来确定应该读取哪个block,并获取这个block的详细信息。(与NameNode有一次通信)。
2、根据block所在的DataNode,选择一个最好的DN,并建立与该DN的socket连接(默认不启用本地读)。
其方法的调用层次如下:
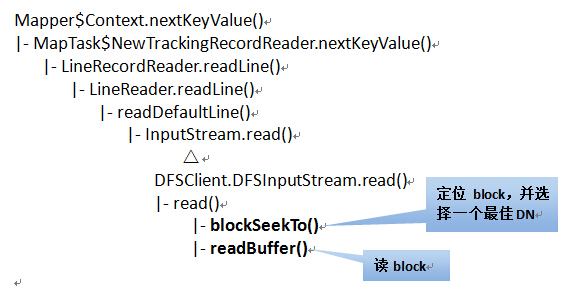
Map Task读取数据是由RecordReader类来完成的。它是个接口,有两个子类:
BlockReaderLocal:读取本地block(不通过DataNode)
RemoteBlockReader:读取远程block(通过DataNode)
Map Task在读取数据时,即使是本地数据也是使用RemoteBlockReader来读的,也就是通过socket,默认不开启本地读。通过这个链接的方法可以开启本地读(http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/ShortCircuitLocalReads.html),也就是使用BlockReaderLocal直接来从本地读block,而不通过DataNode。以下的分析都是基于BlockReaderLocal来完成的。
先说一下涉及到的数据结构:
public class BlockLocalPathInfo implements Writable { //用来描述block的位置信息
private Block block; //特定的块文件
private String localBlockPath = ""; //块文件的本地存储路径
private String localMetaPath = ""; //块校验文件的本地存储路径
//Stores the cache and proxy for a local datanode.
private static class LocalDatanodeInfo { //代表本机上的某个DataNode(一个机器上可能运行多个DataNode)
private final Map<Block, BlockLocalPathInfo> cache; //其中维护的表(block-->block位置信息)
// Multiple datanodes could be running on the local machine. Store proxies in
// a map keyed by the ipc port of the datanode.
//BlockReaderLocal中维护的表:
private static Map<Integer, LocalDatanodeInfo> localDatanodeInfoMap = new HashMap<Integer, LocalDatanodeInfo>();
// Integer:表示端口号
// LocalDatanodeInfo:表示某个DataNode
/**
* This class is used by the datanode to maintain the map from a block
* to its metadata.
*/
class DatanodeBlockInfo { //表示该DN上的所有block信息(block-->block元信息) private FSVolume volume; //block所在的FSVolume
private File file; // block file
private boolean detached; // block的写复制是否完成
//block与block元信息映射表
HashMap<Block,DatanodeBlockInfo> volumeMap = new HashMap<Block, DatanodeBlockInfo>();;
在读block时,首先根据localDatanodeInfoMap确定要访问的DataNode;然后从volumeMap中找到block对应的DatanodeBlockInfo信息(这其中就包括block对应的FSVolume,这是在存储block时确定的。本文前边有写);然后根据DatanodeBlockInfo来构造BlockLocalPathInfo对象,将block的相关信息存放到BlockLocalPathInfo对象中。最后BlockReaderLocal根据BlockLocalPathInfo对象来读取相应的block。 具体在BlockReaderLocal.newBlockReader()方法中。
本文基于hadoop1.2.1
如有错误,还请指正
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/gwgyk/p/4124038.html
HDFS读写数据块--${dfs.data.dir}选择策略的更多相关文章
- hadoop datanode启动失败(All directories in dfs.data.dir are invalid)
由于hadoop节点的磁盘满了,导致节点死掉,今天对其进行扩容.首先,将原节点的数据拷贝到目标节点下,从而避免数据的丢失,但是在执行hadoop_daemon.sh start datanode后没有 ...
- Hadoop Datanode节点无法启动(All directories in dfs.data.dir are invalid)
Hadoop Datanode节点无法启动(All directories in dfs.data.dir are invalid) java.io.IOException: All director ...
- ${mapred.local.dir}选择策略--Map Task存放中间结果
上篇说了block在DataNode配置有多个${dfs.data.dir}时的存储策略,本文主要介绍TaskTracker在配置有多个${mapred.local.dir}时的选择策略. mapre ...
- Hadoop -- HDFS 读写数据
一.HDFS读写文件过程 1.读取文件过程 1) 初始化FileSystem,然后客户端(client)用FileSystem的open()函数打开文件 2) FileSyst ...
- 大数据:Hadoop(HDFS 读写数据流程及优缺点)
一.HDFS 写数据流程 写的过程: CLIENT(客户端):用来发起读写请求,并拆分文件成多个 Block: NAMENODE:全局的协调和把控所有的请求,提供 Block 存放在 DataNode ...
- HDFS读写数据流程
HDFS的组成 1.NameNode:存储文件的元数据,如文件名,文件目录结构,文件属性(创建时间,文件权限,文件大小) 以及每个文件的块列表和块所在的DataNode等.类似于一本书的目录功能. 2 ...
- HDFS读写数据过程
一.文件的打开 1.1.客户端 HDFS打开一个文件,需要在客户端调用DistributedFileSystem.open(Path f, int bufferSize),其实现为: public F ...
- HDFS 读写数据流程
一.上传数据 二.下载数据 三.读写时的节点位置选择 1.网络节点距离(机架感知) 下图中: client 到 DN1 的距离为 4 client 到 NN 的距离为 3 DN1 到 DN2 的距离为 ...
- Hdfs读写数据出错
1.Hdfs读数据出错:若在读数据的过程中,客户端和DataNode的通信出现错误,则会尝试连接下一个 包含次文件块的DataNode.同时记录失败的DataNode,此后不再被连接. 2.Hdfs在 ...
随机推荐
- 使用js设置input标签只读 readonly 属性
先上代码: <html> <head> <title> test </title> <meta charset="utf-8" ...
- dom4j如何解析XML文件
最近在 一些对xml文件的操作,下面简单写一个dom4j解析xml文件并将其封装到一个javabean中的例子,只是具有针对性的,不是通用的,仅供参考哦~~ 首先说:dom4j是一个java的XML ...
- Canvas 与 Paint 类的 使用
使用canvas画布和paint画笔可以自定义view 案例:fastindexbar 基本用法 public class DrawView extends View{ private Rect mR ...
- Crontab中的除号(slash)到底怎么用?
crontab 是Linux中配置定时任务的工具,在各种配置中,我们经常会看到除号(Slash)的使用,那么这个除号到底标示什么意思,使用中有哪些需要注意的地方呢? 在定时任务中,我们经常有这样的 ...
- MYSQL limit,offset 区别
SELECT keyword FROM keyword_rank WHERE advertiserid' order by keyword LIMIT OFFSET ; 比如这个SQL ,limit后 ...
- dpkg: 处理归档 /var/cache/apt/archives/软件名 (--unpack)时出错:由于已经达到 MaxReports 限制,没有写入 apport 报告。
一.环境介绍: OS:ubuntu16.04 64bit 二.错误如下: 正准备解包 .../libqt4-script_4%3a4.8.7+dfsg-5ubuntu2_i386.deb ...正在 ...
- 1019: [SHOI2008]汉诺塔
1019: [SHOI2008]汉诺塔 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 1495 Solved: 916[Submit][Status] ...
- 在WebBrowser中截获弹出对话框内容并将其屏蔽
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; usin ...
- python走起之第十二话
1. ORM介绍 orm英文全称object relational mapping,就是对象映射关系程序,简单来说我们类似python这种面向对象的程序来说一切皆对象,但是我们使用的数据库却都是关系型 ...
- 【转】linux中do{...} while(0)的解释
在看ldlm的代码过程中遇到了一个很奇怪的问题,有很多宏定义使用了do while(0)这种看起来好像没啥用的代码.然后我就问问师兄,才得知,这种用法很常见,自己又查了一下资料,原来在linux内核代 ...
