Chrome RenderText分析(1)
先从一些基础的类开始
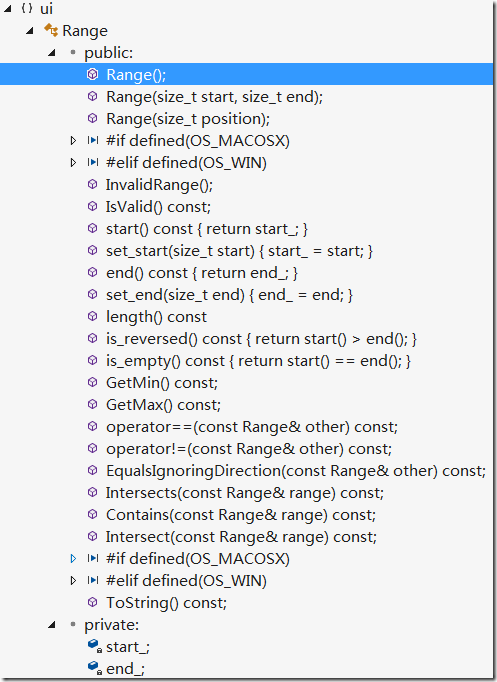
1.Range
// A Range contains two integer values that represent a numeric range, like the
// range of characters in a text selection. A range is made of a start and end
// position; when they are the same, the Range is akin to a caret. Note that
// |start_| can be greater than |end_| to respect the directionality of the
// range.
文字绘制前后有索引,比如
“hello你好”便是hello |0,4|5,6|
一段简单的测试代码
TEST(RangeTest, StartEndInit) {
ui::Range r(10, 15);
EXPECT_EQ(10U, r.start());
EXPECT_EQ(15U, r.end());
EXPECT_EQ(5U, r.length());
EXPECT_FALSE(r.is_reversed());
EXPECT_FALSE(r.is_empty());
EXPECT_TRUE(r.IsValid());
EXPECT_EQ(10U, r.GetMin());
EXPECT_EQ(15U, r.GetMax());
}
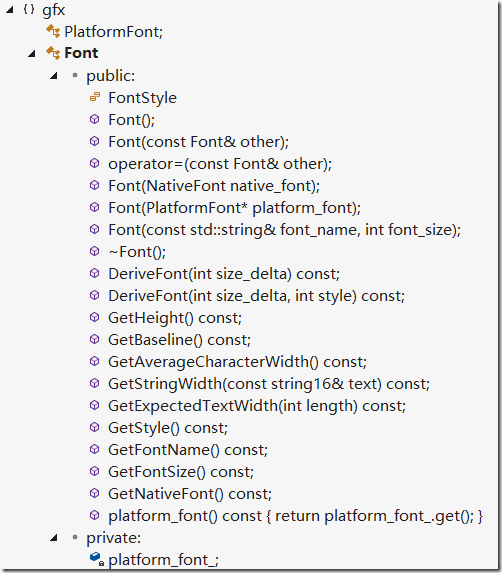
2.Font
// Font provides a wrapper around an underlying font. Copy and assignment
// operators are explicitly allowed, and cheap.
由于是跨平台的,所以其GetNativeFont返回则HFONT
3.RenderTextWin
// RenderTextWin is the Windows implementation of RenderText using Uniscribe.
Lay Out Text Using Uniscribe
Your application can use the following steps to lay out out a text paragraph with Uniscribe. This procedure assumes that the application has already divided the paragraph into runs.
- Call ScriptRecordDigitSubstitution only when starting or when receiving a WM_SETTINGCHANGE message.
- (Optional) Call ScriptIsComplex to determine if the paragraph requires complex processing.
- (Optional) If using Uniscribe to handle bidirectional text and/or digit substitution, call ScriptApplyDigitSubstitution to prepare the SCRIPT_CONTROL and SCRIPT_STATE structures as inputs to ScriptItemize. If skipping this step, but still requiring digit substitution, substitute national digits for Unicode U+0030 through U+0039 (European digits). For information about digit substitution, see Digit Shapes.
- Call ScriptItemize to divide the paragraph into items. If not using Uniscribe for digit substitution and the bidirectional order is known, for example, because of the keyboard layout used to enter the character, call ScriptItemize. In the call, provide null pointers for the SCRIPT_CONTROL and SCRIPT_STATE structures. This technique generates items by use of the shaping engine only, and the items can be reordered using the engine information.
Note Typically, applications that work only with left-to-right scripts and without any digit substitution should pass null pointers for the SCRIPT_CONTROL and SCRIPT_STATE structures.
- Merge the item information with the run information to produce ranges.
- Call ScriptShape to identify clusters and generate glyphs.
- If ScriptShape returns the code USP_E_SCRIPT_NOT_IN_FONT or S_OK with the output containing missing glyphs, select characters from a different font. Either substitute another font or disable shaping by setting the eScript member of the SCRIPT_ANALYSIS structure passed to ScriptShape to SCRIPT_UNDEFINED. For more information, see Using Font Fallback.
- Call ScriptPlace to generate advance widths and x and y positions for the glyphs in each successive range. This is the first step for which text size becomes a consideration.
- Sum the range sizes until the line overflows.
- Break the range on a word boundary by using the fSoftBreak and fWhiteSpace members in the logical attributes. To break a single character cluster off the run, use the information returned by calling ScriptBreak.
Note Decide if the first code point of a range should be a word break point because the last character of the previous range requires it. For example, if one range ends in a comma, consider the first character of the next range to be a word break point.
- Repeat steps 6 through 10 for each line in the paragraph. However, if breaking the last run on the line, call ScriptShape to reshape the remaining part of the run as the first run on the next line.
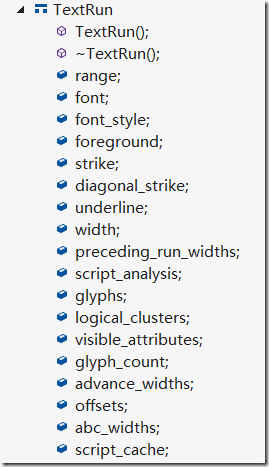
4.TextRun
用来描述每小段文字
重点来看RenderTextWin的流程
GetStringSize用于获取文字的尺寸
Size RenderTextWin::GetStringSize() {
EnsureLayout();
return string_size_;
}
首先要通过ScriptItemize方法来把文字分段,封装成TextRun数组
void RenderTextWin::ItemizeLogicalText() {
runs_.clear();
string_size_ = Size(0, GetFont().GetHeight());
common_baseline_ = 0;
// Set Uniscribe's base text direction.
script_state_.uBidiLevel =
(GetTextDirection() == base::i18n::RIGHT_TO_LEFT) ? 1 : 0;
if (text().empty())
return;
HRESULT hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY;
int script_items_count = 0;
std::vector<SCRIPT_ITEM> script_items;
const size_t text_length = GetLayoutText().length();
for (size_t n = kGuessItems; hr == E_OUTOFMEMORY && n < kMaxItems; n *= 2) {
// Derive the array of Uniscribe script items from the logical text.
// ScriptItemize always adds a terminal array item so that the length of the
// last item can be derived from the terminal SCRIPT_ITEM::iCharPos.
script_items.resize(n);
hr = ScriptItemize(GetLayoutText().c_str(),
text_length,
n - 1,
&script_control_,
&script_state_,
&script_items[0],
&script_items_count);
}
DCHECK(SUCCEEDED(hr));
if (script_items_count <= 0)
return;
// Temporarily apply composition underlines and selection colors.
ApplyCompositionAndSelectionStyles();
// Build the list of runs from the script items and ranged colors/styles.
// TODO(msw): Only break for bold/italic, not color etc. See TextRun comment.
internal::StyleIterator style(colors(), styles());
SCRIPT_ITEM* script_item = &script_items[0];
const size_t layout_text_length = GetLayoutText().length();
for (size_t run_break = 0; run_break < layout_text_length;) {
internal::TextRun* run = new internal::TextRun();
run->range.set_start(run_break);
run->font = GetFont();
run->font_style = (style.style(BOLD) ? Font::BOLD : 0) |
(style.style(ITALIC) ? Font::ITALIC : 0);
DeriveFontIfNecessary(run->font.GetFontSize(), run->font.GetHeight(),
run->font_style, &run->font);
run->foreground = style.color();
run->strike = style.style(STRIKE);
run->diagonal_strike = style.style(DIAGONAL_STRIKE);
run->underline = style.style(UNDERLINE);
run->script_analysis = script_item->a;
// Find the next break and advance the iterators as needed.
const size_t script_item_break = (script_item + 1)->iCharPos;
run_break = std::min(script_item_break,
TextIndexToLayoutIndex(style.GetRange().end()));
style.UpdatePosition(LayoutIndexToTextIndex(run_break));
if (script_item_break == run_break)
script_item++;
run->range.set_end(run_break);
runs_.push_back(run);
}
// Undo the temporarily applied composition underlines and selection colors.
UndoCompositionAndSelectionStyles();
}
注意点:
The function returns E_OUTOFMEMORY if the value of cMaxItems is insufficient. As in all error cases, no items are fully processed and no part of the output array contains defined values. If the function returns E_OUTOFMEMORY, the application can call it again with a larger pItems buffer.
1.先看斜体部分,通过ScriptItemize,得到一个SCRIPT_ITEM数组
2.再通过SCRIPT_ITEM数组封装成TextRun数组
5.TextRun的文字样式(BreakList)
看如下文字样式
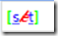
文字的样式有颜色,格式(斜体,下划线)
想要呈现”[set]”上面的文字需要把文字拆成几个分段
1.颜色分成5段[0,1,2,3,4]
2.字体分段: 每个文字可能有多个格式,比如斜体和粗体是同时出现的
为了储存以上样式信息,就出现一个BreakList的数据结构
// BreakLists manage ordered, non-overlapping, and non-repeating ranged values.
// These may be used to apply ranged colors and styles to text, for an example.
//
// Each break stores the start position and value of its associated range.
// A solitary break at position 0 applies to the entire space [0, max_).
// |max_| is initially 0 and should be set to match the available ranged space.
// The first break always has position 0, to ensure all positions have a value.
// The value of the terminal break applies to the range [break.first, max_).
// The value of other breaks apply to the range [break.first, (break+1).first).
typedef std::pair<size_t, T> Break;
std::vector<Break> breaks_;
size_t max_;
上面颜色的存储就是[0,green],[1,blue],[2,red],[3,blue],[4,green]
字体分段则是一个列表的BreakList:[[0,true],[1,true]],[[0,true],[1,true]]
看一下类成员
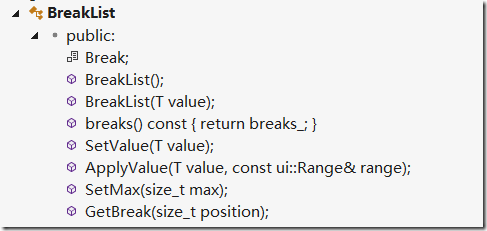
- SetValue方法设置一个默认值
- ApplyValue则设置区间的start和end值,同时清除区间的值
BreakList的设置逻辑是区间相邻不会出现重复的值.
即不会出现[0,true][1,true],[2,true]这种情况
看几个单元测试用例
1.SetValue测试
TEST_F(BreakListTest, SetValue) {
// Check the default values applied to new instances.
BreakList<bool> style_breaks(false);
EXPECT_TRUE(style_breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(false));
style_breaks.SetValue(true);
EXPECT_TRUE(style_breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(true));
// Ensure that setting values works correctly.
BreakList<SkColor> color_breaks(SK_ColorRED);
EXPECT_TRUE(color_breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(SK_ColorRED));
color_breaks.SetValue(SK_ColorBLACK);
EXPECT_TRUE(color_breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(SK_ColorBLACK));
}
重新设置SetValue回清空所有段落
2.ApplyValue
BreakList<bool> breaks(false);
const size_t max = 99;
breaks.SetMax(max);
// Apply a value to a valid range, check breaks; repeating should be no-op.
std::vector<std::pair<size_t, bool> > expected;
expected.push_back(std::pair<size_t, bool>(0, false));
expected.push_back(std::pair<size_t, bool>(2, true));
expected.push_back(std::pair<size_t, bool>(3, false));
for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
breaks.ApplyValue(true, ui::Range(2, 3));
EXPECT_TRUE(breaks.EqualsForTesting(expected));
}
ApplyValue区间的end如果不是max值则是SetValue的默认值
// Ensure applying a value over [0, |max|) is the same as setting a value.
breaks.ApplyValue(false, ui::Range(0, max));
EXPECT_TRUE(breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(false));
ApplyValue区间的end如果是max值则段区域只有1段
// Ensure applying a value that is already applied has no effect.
breaks.ApplyValue(false, ui::Range(0, 2));
breaks.ApplyValue(false, ui::Range(3, 6));
breaks.ApplyValue(false, ui::Range(7, max));
EXPECT_TRUE(breaks.EqualsValueForTesting(false));
同理,设置区域的Value都一样的话,那还是在同一个区域,也还只有1段
看完BreakList的用法之后,我们回头来看RenderTextWin中关于color和style的应用
变量
// Color and style breaks, used to color and stylize ranges of text.
// BreakList positions are stored with text indices, not layout indices.
// TODO(msw): Expand to support cursor, selection, background, etc. colors.
BreakList<SkColor> colors_;
std::vector<BreakList<bool> > styles_;
方法
void RenderText::SetColor(SkColor value) {
colors_.SetValue(value);
}
void RenderText::ApplyColor(SkColor value, const ui::Range& range) {
colors_.ApplyValue(value, range);
}
void RenderText::SetStyle(TextStyle style, bool value) {
styles_[style].SetValue(value);
}
void RenderText::ApplyStyle(TextStyle style,
bool value,
const ui::Range& range) {
styles_[style].ApplyValue(value, range);
}
回到ItemizeLogicalText方法中看StyleIterator类,其均是取BreakList的首个值
StyleIterator::StyleIterator(const BreakList<SkColor>& colors,
const std::vector<BreakList<bool> >& styles)
: colors_(colors),
styles_(styles) {
color_ = colors_.breaks().begin();
for (size_t i = 0; i < styles_.size(); ++i)
style_.push_back(styles_[i].breaks().begin());
}
Chrome RenderText分析(1)的更多相关文章
- Chrome RenderText分析(2)
接Chrome RenderText分析(1) 继续分析以下步骤 一.TextRun结构 struct TextRun { TextRun(); ~TextRun(); ui::Range r ...
- JS内存泄漏 和Chrome 内存分析工具简介(摘)
原文地址:http://web.jobbole.com/88463/ JavaScript 中 4 种常见的内存泄露陷阱 原文:Sebastián Peyrott 译文:伯乐在线专栏作者 - AR ...
- Chrome渲染分析之Timeline工具的使用
原文http://www.th7.cn/web/html-css/201406/42043.shtml Timeline工具栏提供了对于在装载你的Web应用的过程中,时间花费情况的概览,这些应用包括处 ...
- chrome性能分析
Chrome开发者工具之JavaScript内存分析 前端性能优化 —— 前端性能分析 Chrome DevTools - 性能监控
- 通过chrome浏览器分析网页加载时间
今天趁着下班的时间看了下chrome浏览器的网页加载时间分析工具和相关文档,简单写点儿东西记录一下. 以百度首页加载为例,分析下一张图片1.jgp(就是背景图)的加载时间 看右侧的Timing标签,从 ...
- Chrome性能分析工具lightHouse用法指南
本文主要讲如何使用Chrome开发者工具linghtHouse进行页面性能分析. 1.安装插件 非常简单,点击右上角的“添加至Chrome”即可. 2.使用方式 1)打开要测试的页面,点击浏览器右上角 ...
- Wappalyzer(chrome网站分析插件)
Wappalyzer是一款功能强大的.且非常实用的chrome网站技术分析插件,通过该插件能够分析目标网站所采用的平台构架. 网站环境.服务器配置环境.JavaScript框架.编程语言等参数,使用时 ...
- Chrome性能分析工具Coverage使用方法
操作路径如下: 打开控制台-->点击‘Sources’-->ctrl+shift+p-->在命令窗口输入coverage-->在下边新出现的窗口中点击左上角刷新按钮. 界面如下 ...
- 使用Chrome逆向分析JS实战---分析google网站翻译器原文存放位置
剧透:就是使用了一下Chrome DevTools的Memory功能,通过已知的JS变量的值查找JS内存中变量的引用 一:不分析一下现有的网页翻译方法么? 总所周知,(As is well known ...
随机推荐
- 04-Bootstrap的插件
1.下拉菜单 代码如下: <div class="dropdown"> <button class="btn btn-default dropdown- ...
- Linux下进程/程序网络带宽占用情况查看工具 -- NetHogs
http://www.vpser.net/manage/nethogs.html 来自. 最后略有修改 之前VPS侦探曾经介绍过流量带宽相关的工具如:iftop.vnstat,这几个都是统计和监 ...
- Windows下安装并启动mongodb
一.Windows下mongodb的安装 MongoDB 提供了可用于 32 位和 64 位系统的预编译二进制包,你可以从MongoDB官网下载安装,MongoDB 预编译二进制包下载地址:https ...
- python3 + selenium 使用 JS操作页面滚动条
js2 = "window.scrollTo(0,0);" #括号中为坐标 当不知道需要的滚动的坐标大小时: weizhi2 = driver.find_element_by_id ...
- <转>用 Java 技术创建 RESTful Web 服务
转自:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/web/wa-jaxrs/#N1017E JAX-RS:一种更为简单.可移植性更好的替代方式 Dustin Amrhe ...
- Jquery监听AJAX请求
.ajaxComplete() 当Ajax请求完成后注册一个回调函数.这是一个 AjaxEvent. .ajaxError() Ajax请求出错时注册一个回调处理函数,这是一个 Ajax Event. ...
- UOJ Round #1 题解
题解: 质量不错的一套题目啊..(题解也很不错啊) t1: 首先暴力显然有20分,把ai相同的缩在一起就有40分了 然后会发现由于原来的式子有个%很不方便处理 so计数题嘛 考虑一下容斥 最终步数=初 ...
- google gcr.io、k8s.gcr.io 国内镜像
1.首先添加docker官方的国内镜像 sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF' { "registry-mirrors": ...
- python全栈开发day23-面向对象高级:反射(getattr、hasattr、setattr、delattr)、__call__、__len__、__str__、__repr__、__hash__、__eq__、isinstance、issubclass
一.今日内容总结 1.反射 使用字符串数据类型的变量名来操作一个变量的值. #使用反射获取某个命名空间中的值, #需要 #有一个变量指向这个命名空间 #字符串数据类型的名字 #再使用getattr获取 ...
- 敌兵布阵 HDU1166
基础线段树 #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> using namespace std; int n,p,a,b,m,x,y,ans; st ...
