babylon.js 学习笔记(5)
前面我们画的小房子,基本上都是用内置的标准形状组合而成,但并非所有对象都这么简单,今天我们来画一个小汽车,汽车由多个零件组成,控制这些零件的缩放、位置、旋转,如果每个都单独用代码来修改position/roration/scaling,未免太复杂,幸好babylon.js中,对象有所谓的child/parent 关系。简单来说,如果A是B的parent,则对A的任何位置/缩放/旋转,其child也会同步受影响,但child可以在parent的基础上,再独立叠加新变化。有没有发现,这很符合遗传学,孩子必然长得象父母,但是又有些自己的特征。
一、理解 parent / child 关系
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2.2, Math.PI / 2.5, 15, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
//方块6个面的颜色
const faceColors = [];
faceColors[0] = BABYLON.Color3.Blue();
faceColors[1] = BABYLON.Color3.Teal()
faceColors[2] = BABYLON.Color3.Red();
faceColors[3] = BABYLON.Color3.Purple();
faceColors[4] = BABYLON.Color3.Green();
faceColors[5] = BABYLON.Color3.Yellow();
const boxParent = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("Box", { faceColors: faceColors });
const boxChild = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("Box", { size: 0.5, faceColors: faceColors });
//小方块是大方块的child
boxChild.setParent(boxParent);
//child的独立特征
boxChild.position.x = 0;
boxChild.position.y = 2;
boxChild.position.z = 0;
boxChild.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
boxChild.rotation.y = Math.PI / 4;
boxChild.rotation.z = Math.PI / 4;
//parent的位置变化,将影响child
boxParent.position.x = 2;
boxParent.position.y = 0;
boxParent.position.z = 0;
boxParent.rotation.x = 0;
boxParent.rotation.y = 0;
boxParent.rotation.z = -Math.PI / 4;
//辅助坐标轴,方便理解
const boxChildAxes = localAxes(1.5, scene);
boxChildAxes.parent = boxChild;
showAxis(5, scene);
return scene;
}
//坐标轴
const showAxis = (size, scene) => {
const makeTextPlane = (text, color, size) => {
const dynamicTexture = new BABYLON.DynamicTexture("DynamicTexture", 50, scene, true);
dynamicTexture.hasAlpha = true;
dynamicTexture.drawText(text, 5, 40, "bold 36px Arial", color, "transparent", true);
const plane = new BABYLON.Mesh.CreatePlane("TextPlane", size, scene, true);
plane.material = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("TextPlaneMaterial", scene);
plane.material.backFaceCulling = false;
plane.material.specularColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0);
plane.material.diffuseTexture = dynamicTexture;
return plane;
};
const axisX = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisX", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, 0.05 * size, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, -0.05 * size, 0)
]);
axisX.color = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 0, 0);
const xChar = makeTextPlane("X", "white", size / 8);
xChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.9 * size, -0.05 * size, 0);
const axisY = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisY", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0)
]);
axisY.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const yChar = makeTextPlane("Y", "white", size / 8);
yChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.9 * size, -0.05 * size);
const axisZ = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisZ", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, -0.05 * size, size * 0.95),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, size * 0.95)
]);
axisZ.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 1);
const zChar = makeTextPlane("Z", "white", size / 8);
zChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, 0.9 * size);
};
//小方块的坐标轴
localAxes = (size, scene) => {
const local_axisX = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisX", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, 0.05 * size, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, -0.05 * size, 0)
], scene);
local_axisX.color = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 0, 0);
local_axisY = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisY", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0)
], scene);
local_axisY.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const local_axisZ = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisZ", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, -0.05 * size, size * 0.95),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, size * 0.95)
], scene);
local_axisZ.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 1);
const local_origin = new BABYLON.TransformNode("local_origin");
local_axisX.parent = local_origin;
local_axisY.parent = local_origin;
local_axisZ.parent = local_origin;
return local_origin;
}
代码有点长,坐标轴的部分可以先不管,只看createScene即可。
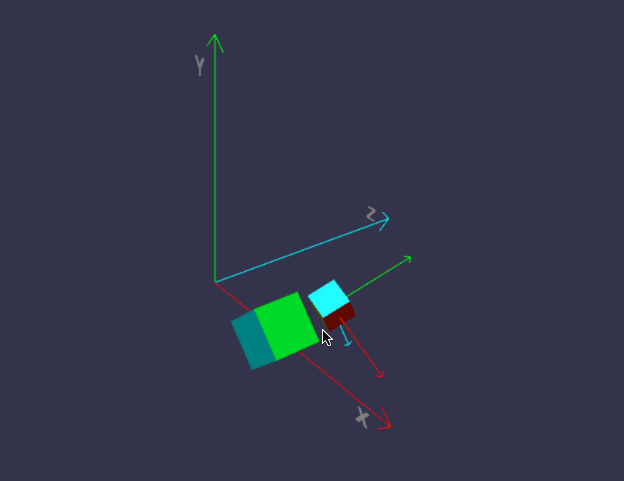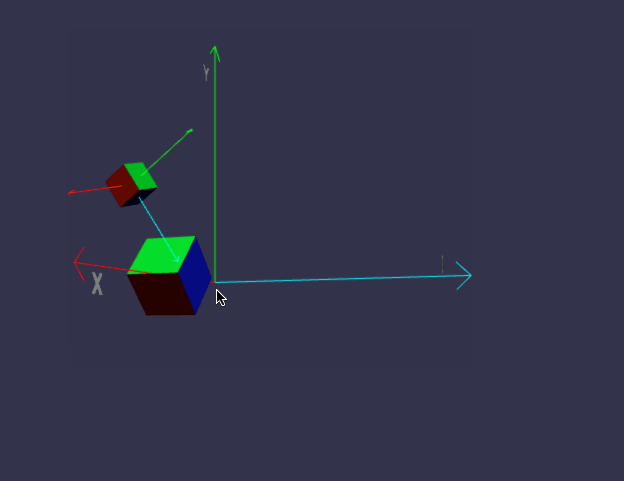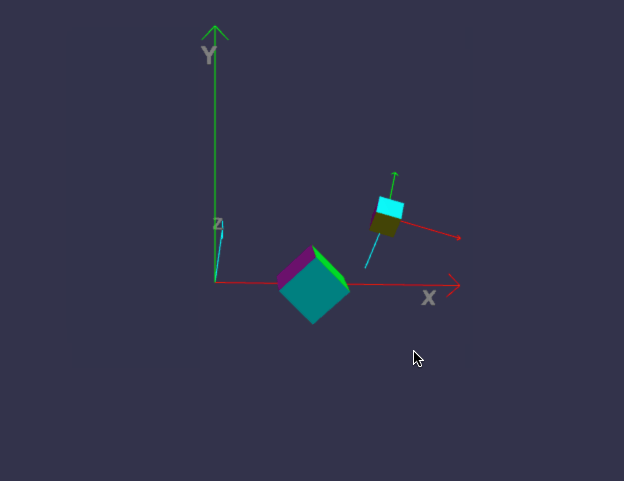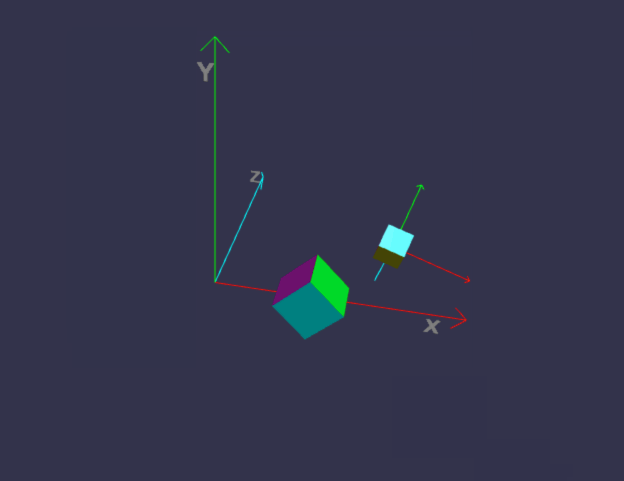
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/01.html
二、理解 ExtrudePolygon
ExtrudePolygon方法可以画出一些不规则形状,比如下面:
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2 });
return car;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/02.html
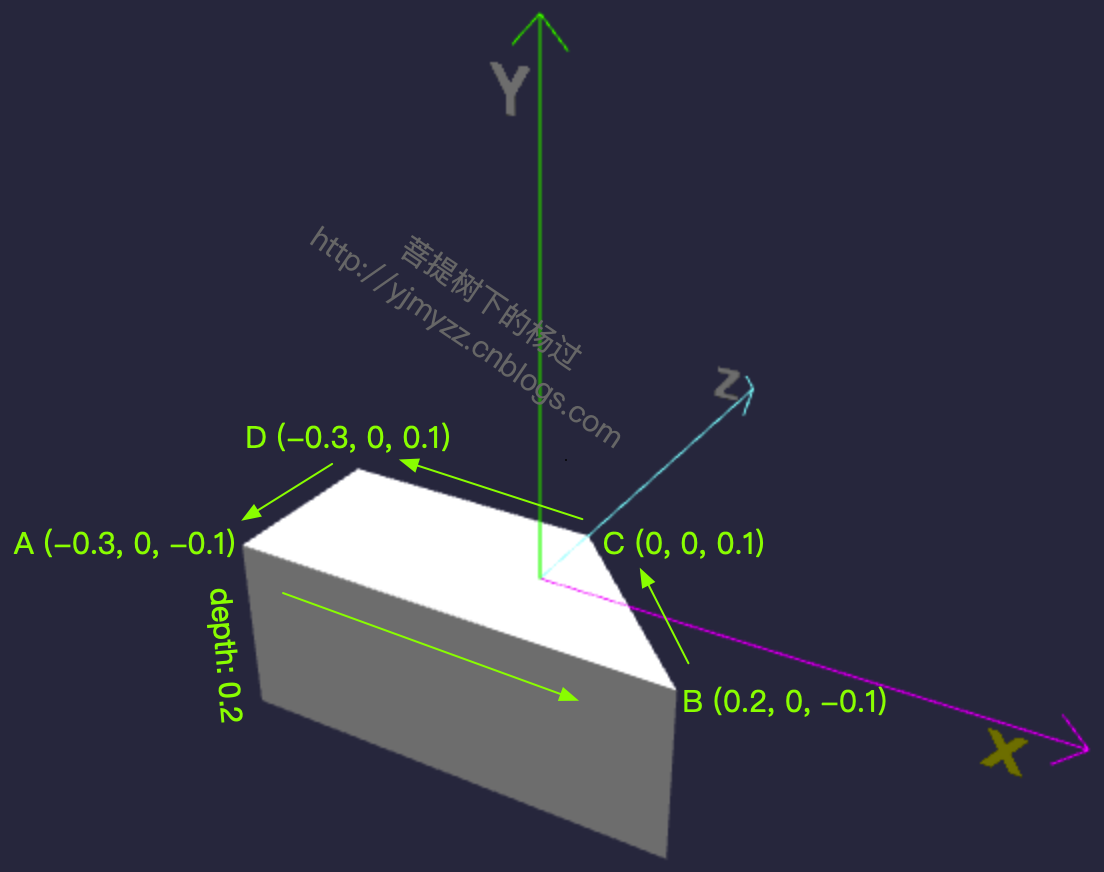
具体画的过程,可以结合下面的图理解:简单来说,A->B->C->D 先画出1个梯形,然后向下拉长,就得到了这个模型。
再完善一下,把车头及轮子加上
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
//造车身
const car = buildCar();
//安装轮子
buildWheel(car);
showAxis(0.8, scene);
return scene;
}
//车身
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2 });
return car;
}
//轮子
const buildWheel = (car) => {
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05 })
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/03.html
最后再加上贴图:

const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, -0.20, 1.5));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
const car = buildCar();
car.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//car face UVs
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0.38, 1);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 0.5);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.38, 1, 0, 0.5);
//car material
const carMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("carMat");
carMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/car.png");
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
car.material = carMat;
//wheel face UVs
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
//car material
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
return car;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/04.html
三、轮子动画
既然是汽车,轮子肯定得转起来,可以借助Animation对象来实现
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
const wheel = buildWheel();
wheelAnimation(scene, wheel);
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
//造轮子
const buildWheel = () => {
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
return wheelRB;
}
//轮子转动
const wheelAnimation = (scene, wheel) => {
//定义一个动画,每秒30帧,绕y轴转动
const animWheel = new BABYLON.Animation("wheelAnimation", "rotation.y",
30, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_FLOAT, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONLOOPMODE_CYCLE);
//动画关键帧
const wheelKeys = [];
//起始帧
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 0,
value: 0
});
//截止帧(即:第30帧,转到360度)
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 30,
value: 2 * Math.PI
});
//设置关键帧
animWheel.setKeys(wheelKeys);
//将wheel与动画关联
wheel.animations = [];
wheel.animations.push(animWheel);
//开始动画,最后的true表示循环播放
scene.beginAnimation(wheel, 0, 30, true);
}
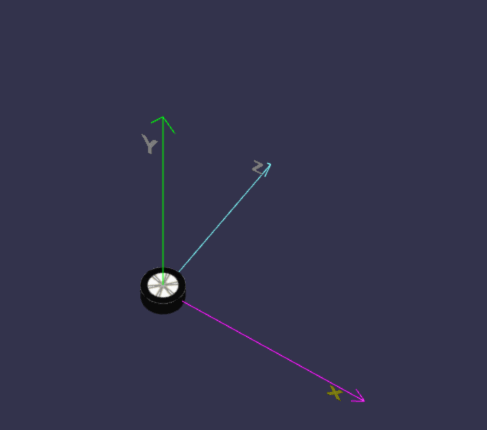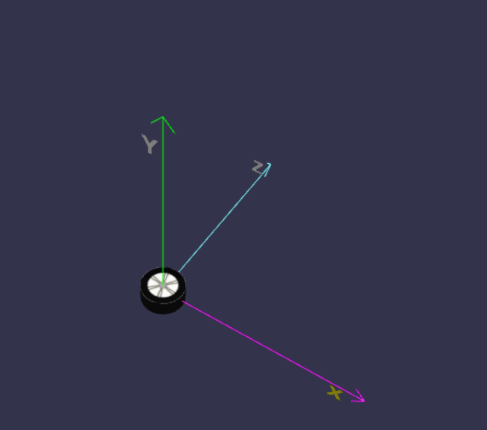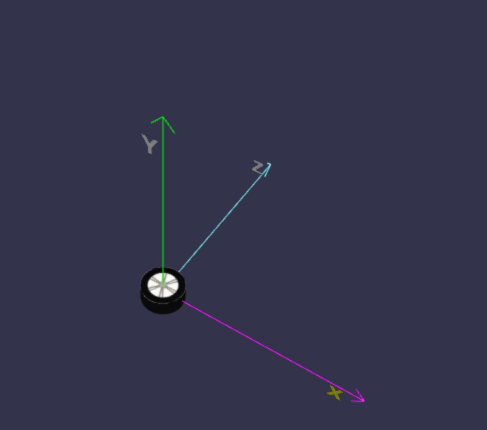
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/05.html
把4个轮子都加上动画:
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 2, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 1, 0));
const car = buildCar();
const wheels = buildWheels(car);
car.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
wheelAnimation(scene, wheels);
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//car face UVs
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0.38, 1);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 0.5);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.38, 1, 0, 0.5);
//car material
const carMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("carMat");
carMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/car.png");
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
car.material = carMat;
return car;
}
const buildWheels = (car) => {
//wheel face UVs
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
//car material
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheels = [];
wheels.push(wheelRB);
wheels.push(wheelRF);
wheels.push(wheelLB);
wheels.push(wheelLF);
return wheels;
}
//轮子转动
const wheelAnimation = (scene, wheels) => {
//定义一个动画,每秒30帧,绕y轴转动
const animWheel = new BABYLON.Animation("wheelAnimation", "rotation.y",
30, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_FLOAT, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONLOOPMODE_CYCLE);
//动画关键帧
const wheelKeys = [];
//起始帧
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 0,
value: 0
});
//截止帧(即:第30帧,转到360度)
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 30,
value: 2 * Math.PI
});
//设置关键帧
animWheel.setKeys(wheelKeys);
for (let i = 0; i < wheels.length; i++) {
//将wheel与动画关联
wheels[i].animations = [];
wheels[i].animations.push(animWheel);
//开始动画,最后的true表示循环播放
scene.beginAnimation(wheels[i], 0, 30, true);
}
}
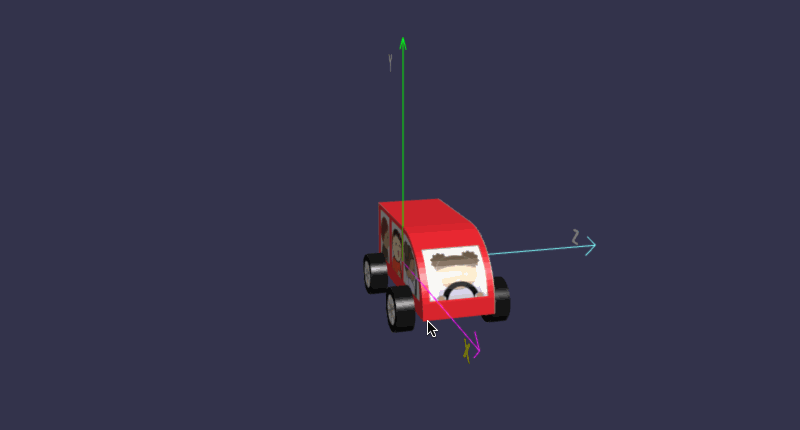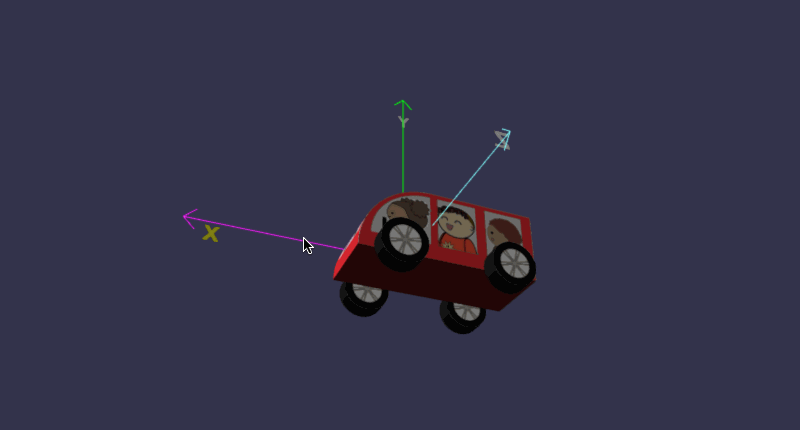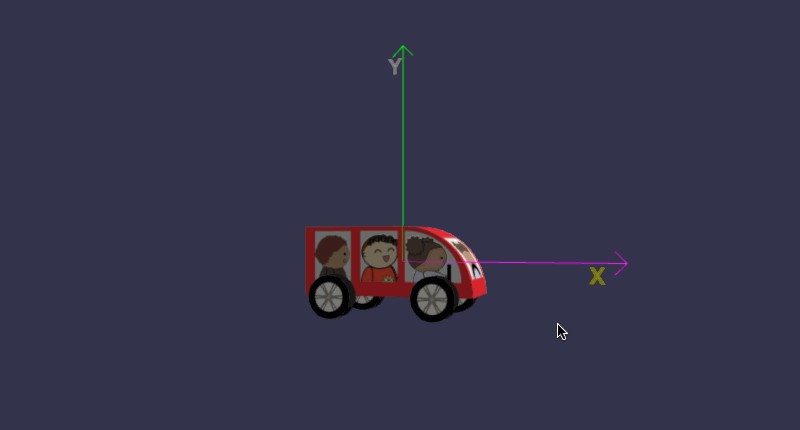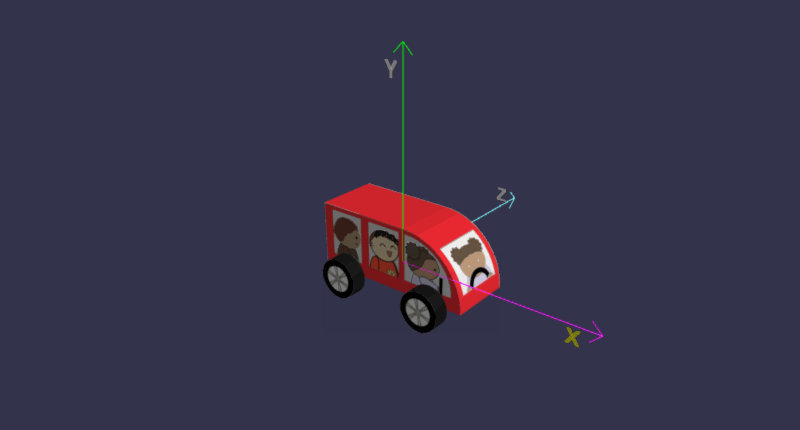
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/06.html
参考文档:https://doc.babylonjs.com/features/introductionToFeatures/chap3/carmat
babylon.js 学习笔记(5)的更多相关文章
- js学习笔记:webpack基础入门(一)
之前听说过webpack,今天想正式的接触一下,先跟着webpack的官方用户指南走: 在这里有: 如何安装webpack 如何使用webpack 如何使用loader 如何使用webpack的开发者 ...
- Vue.js学习笔记(2)vue-router
vue中vue-router的使用:
- JS 学习笔记--9---变量-作用域-内存相关
JS 中变量和其它语言中变量最大的区别就是,JS 是松散型语言,决定了它只是在某一个特定时间保存某一特定的值的一个名字而已.由于在定义变量的时候不需要显示规定必须保存某种类型的值,故变量的值以及保存的 ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 使用粒子系统模拟时空隧道(虫洞)
WebGL three.js学习笔记 使用粒子系统模拟时空隧道 本例的运行结果如图: 时空隧道demo演示 Demo地址:https://nsytsqdtn.github.io/demo/sprite ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 法向量网格材质MeshNormalMaterial的介绍和创建360度全景天空盒的方法
WebGL学习----Three.js学习笔记(5) 点击查看demo演示 Demo地址:https://nsytsqdtn.github.io/demo/360/360 简单网格材质 MeshNor ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 创建three.js代码的基本框架
WebGL学习----Three.js学习笔记(1) webgl介绍 WebGL是一种3D绘图协议,它把JavaScript和OpenGL ES 2.0结合在一起,通过增加OpenGL ES 2.0的 ...
- vue.js 学习笔记3——TypeScript
目录 vue.js 学习笔记3--TypeScript 工具 基础类型 数组 元组 枚举 字面量 接口 类类型 类类型要素 函数 函数参数 this对象和类型 重载 迭代器 Symbol.iterat ...
- 2019-4-29 js学习笔记
js学习笔记一:js数据类型 1:基本数据类型 number类型(整数,小数) String类型 boolean类型 NaN类型其实是一个nu ...
- 一点感悟:《Node.js学习笔记》star数突破1000+
写作背景 笔者前年开始撰写的<Node.js学习笔记> github star 数突破了1000,算是个里程碑吧. 从第一次提交(2016.11.03)到现在,1年半过去了.突然有些感慨, ...
- JS学习笔记5_DOM
1.DOM节点的常用属性(所有节点都支持) nodeType:元素1,属性2,文本3 nodeName:元素标签名的大写形式 nodeValue:元素节点为null,文本节点为文本内容,属性节点为属性 ...
随机推荐
- 【深度学习】MLE视角下的VAE与DDPM损失函数推导
正文 最大似然估计的由来 VAE和DDPM都是likelihood-based生成模型,都是通过学习分布->采样实现图像生成的: 这类模型最大的特点就是希望实现 \[\theta = \arg\ ...
- FirstUI:Deepseek能帮我们做很多事情,而这款开源框架专为开发者设计的开源UI框架,让你的项目加速起飞
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 开发者们总是在寻找能够提高工作效率.简化开发流程的工具.今天,我们要介绍的是一个名为Firs ...
- heapdump敏感信息提取工具-JDumpSpider(一) ,附下载链接
介绍 HeapDump敏感信息提取工具 在日常得渗透测试工作中,经常遇到spring actuator未授权漏洞,而且在实际过程中也常常会下载到heapdump这个文件.了解过这个文件的人知道,H ...
- HarmonyOS Next实战教程:实现中间凹陷的异形tabbar
今天要和大家分享的实战案例是实现中间凹陷的tabar 前些天在做墨迹天气的时候看到了这种异形的tabbar,看起来比较有挑战性,因为鸿蒙版的墨迹天气app还没有这个东西,我决定尝试做一下. 系统的Ta ...
- 思科安全大模型SOC作业应用分析
思科与Meta联合推出的 Foundation-sec-8B 大模型及 AI Defenders工具包,标志着AI技术在网络安全领域的深度融合与创新突破.两者的协同不仅重构了传统安全运营模式,更开创了 ...
- 2024网鼎杯青龙组Misc详解
MISC01 某单位网络遭到非法的攻击,安全人员对流量调查取证之后保存了关键证据,发现人员的定位信息存在泄露,请对其进行分析.flag为用户位置信息进行32位md5哈希值 位置信息,所有我们开始试ip ...
- 保姆教程系列:生成 SSH Key 并配置连接远程仓库
@ 目录 前言 第 1 步:检查是否已有 SSH Key 第 2 步:生成新的 SSH Key 第 3 步:启动 SSH Agent 并添加密钥 第 4 步:复制 SSH 公钥 第 5 步:添加 SS ...
- 第一次阶段性OOP题目集总结性Blog
前言: 基础题目训练说明 第一次基础题目有四道,题量适中,考察知识点主要是正则表达式的基本用法,以及简单分类讨论逻辑与java基础语法,考察学生能都否从讨论判断转变到便捷的正则表达式的使用,逻辑上的难 ...
- LocalDateTime获取 年月日时分秒和判断日期大小
环境:java version "13.0.1". 创建一个DateUtils类,提供三个常用方法: String 转换 LocalDateTime的方法. 获取LocalDate ...
- 企业级MediaWiki知识库系统搭建部署指南(CentOS 8)
## 一.高级环境准备 ### 1. 系统优化与安全加固 ```bash # 系统更新与内核优化 sudo dnf update -y --security sudo dnf install kern ...
