基于 doo-sabin的细分
简介
没有 cc 细分好。
参考链接
http://graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs468-10-fall/LectureSlides/10_Subdivision.pdf 非常好对于细分的介绍
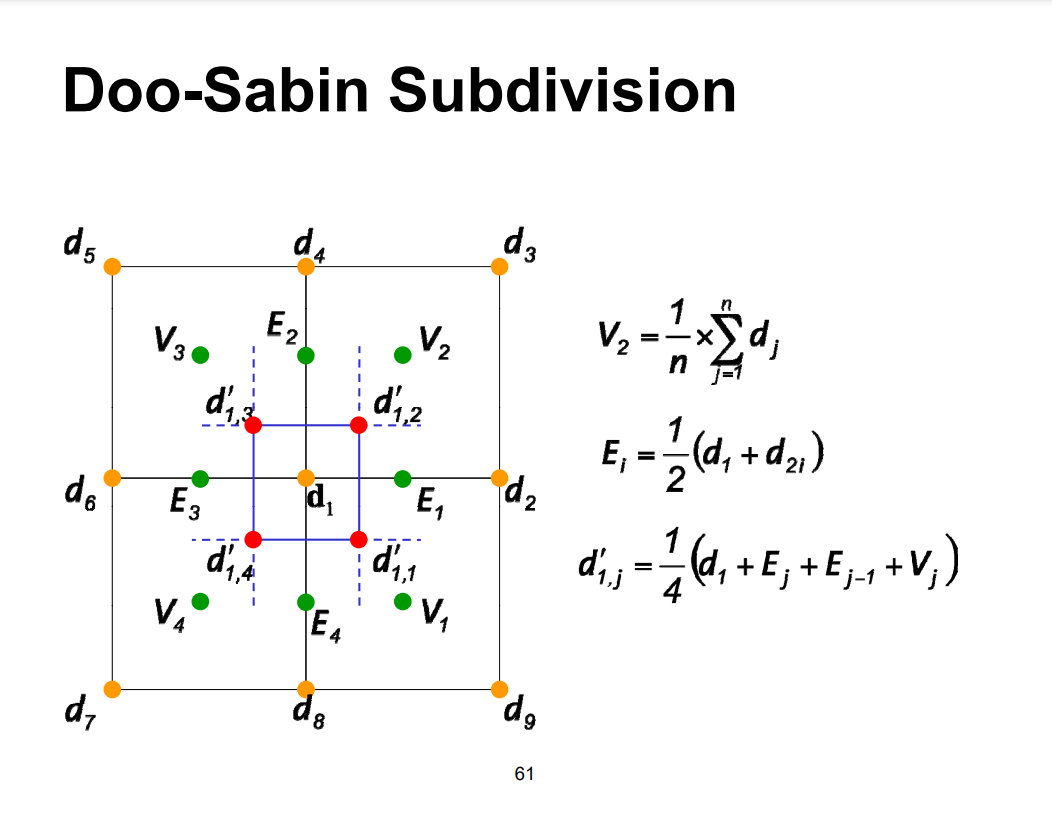
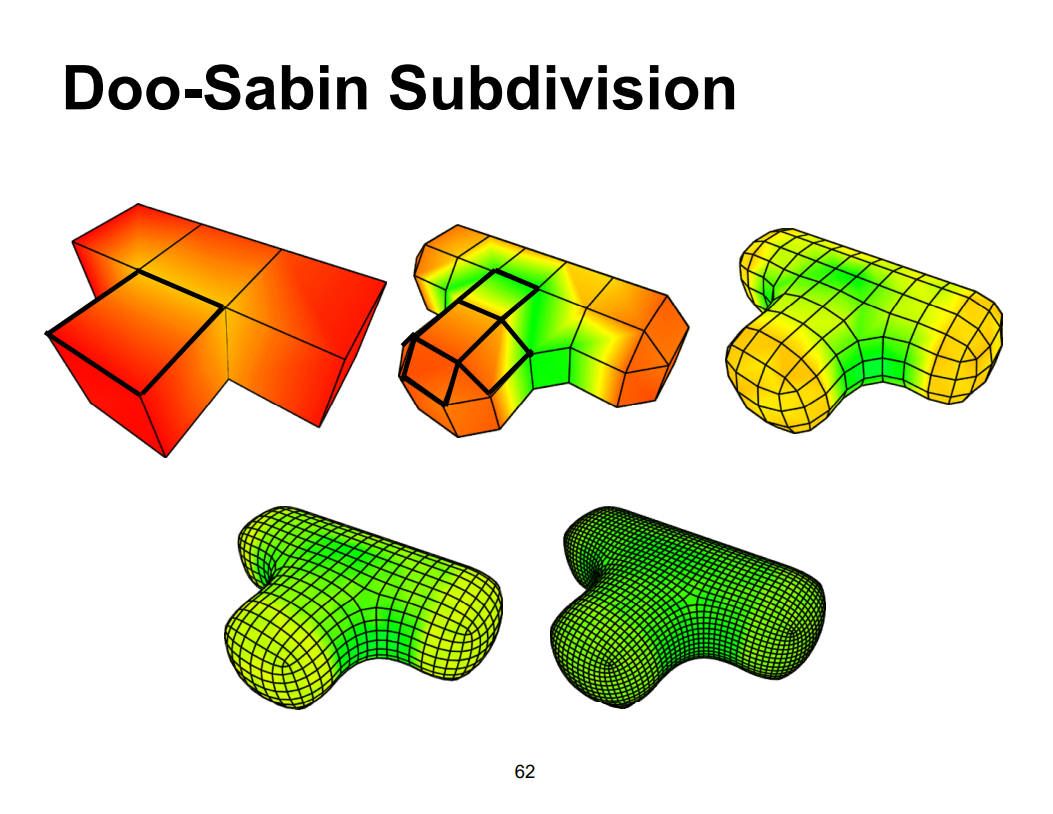
细分示意图
codeTip
代码实现过程,比较潦草。主要看第一张示意图,由于openmesh在加面的时候需要判断面的法向,做的比较粗糙,但是对于立方体的细分是支持的。
code
#include "doo_sabin_surface_subdivision.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <QInputDialog>
/**
* @description: 构造函数
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
DS::DS(Data* data_) : Strategy(data_) {
times = 1;
genCube();
}
/**
* @description: 析构函数
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
DS::~DS() {}
/*!
* Computes the weight factor for the ith vertex of a face with k
* vertices. The formula of Doo and Sabin is used.
*
* @param i Index of vertex in face (0, 1, ..., k-1)
* @param k Number of vertices
*
* @return Weight
*/
inline double DS::weights_doo_sabin(size_t k, size_t i)
{
if (i == 0)
return(0.25 + 5.0 / (4.0 * k));
else
return((3.0 + 2.0 * cos(2 * M_PI * i / k)) / (4.0 * k));
}
/**
* @description: 一整套流程
* @param {type}
* @return {int} 管线运行是否成功
*/
bool DS::Run() {
times = QInputDialog::getInt(this, "Surface Mesh", "Please input times",
1, 1, 1000, 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= times; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
char a[20];
sprintf(a, "output%d.off", i);
genMesh(a);
}
else {
genFacePoint();
genEdgePoint();
genVertexPoint();
connectPoints();
char a[20];
sprintf(a, "output%d.off", i);
genMesh(a);
}
// 清空变量
std::cout << "[DEBUG] 迭代了第 " << i << " 次。" << std::endl;
}
getResult();
return true;
}
/**
* @description: 生成一个立方体(四边形网格)
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::genCube()
{
MyMesh::VertexHandle vhandle[9];
vhandle[0] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, -1, 1));
vhandle[1] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, -1, 1));
vhandle[2] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 1, 1));
vhandle[3] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, 1, 1));
vhandle[4] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, -1, -1));
vhandle[5] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, -1, -1));
vhandle[6] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 1, -1));
vhandle[7] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, 1, -1));
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> face_vhandles;
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[7]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[6]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[5]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[4]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[4]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[5]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[5]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[6]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[6]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[7]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[7]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[4]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
}
/**
* @description: 生成所有面点
* @param {type} TODO
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::genFacePoint()
{
facePoints.clear();
for (const auto& fh : mesh.faces())
{
OpenMesh::Vec3d facePoint(0, 0, 0);
int facePointsNumber = 0;
for (const auto& fvh : mesh.fv_range(fh))
{
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point point = mesh.point(fvh);
facePoint += point;
facePointsNumber++;
}
facePoint /= facePointsNumber;
facePoints[fh.idx()] = facePoint;
}
}
/**
* @description: 生成所有的边点暂时不考虑hole 就是全是日子结构的
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::genEdgePoint()
{
edgePoints.clear();
for (auto e_it = mesh.edges_begin(); e_it != mesh.edges_end(); ++e_it)
{
// 得到边所代表的半边
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh1 = mesh.halfedge_handle(*e_it, 0); // 默认一个方向的半边
OpenMesh::Vec3d edgePoint(0, 0, 0);
int edgePointsNumber = 0;
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointV = mesh.point(mesh.from_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的起点
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointW = mesh.point(mesh.to_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的终点
edgePoints[heh1.idx()] = (pointV + pointW) / 2.0;
}
}
/**
* @description: 生成新的顶点
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::genVertexPoint()
{
vertexPoints.clear();
vertexPoints_.clear();
// 原始点接触的面的所有的面点的均值
for (auto v_it = mesh.vertices_begin(); v_it != mesh.vertices_end(); v_it++)
{
OpenMesh::Vec3d originPoint = (OpenMesh::Vec3d)mesh.point(*v_it);
OpenMesh::Vec3d facePoint(0, 0, 0);
int faceNumber = 0;
std::vector<OpenMesh::Vec3d> facePoints_;
std::vector<OpenMesh::Vec3d> edgePoints_;
for (auto vf_it = mesh.vf_iter(*v_it); vf_it.is_valid(); ++vf_it)
{ //这个顶点所带有的面迭代器
facePoints_.push_back(facePoints[(*vf_it).idx()]);
}
// 原始点接触的边的中间点的值的均值 * 2
OpenMesh::Vec3d edgePoint(0, 0, 0);
int edgeNumber = 0;
for (auto vv_it = mesh.vv_begin(*v_it); vv_it != mesh.vv_end(*v_it); vv_it++) { // 为啥还有孤立点?
OpenMesh::Vec3d point = (OpenMesh::Vec3d)mesh.point(*vv_it);
edgePoints_.push_back((point + originPoint) / 2.0);
}
int index = 0;
for (auto vf_it = mesh.vf_iter(*v_it); vf_it.is_valid(); ++vf_it)
{ //这个顶点所带有的面迭代器
vertexPoints_[(*v_it).idx()].push_back(1.0/4.0*(originPoint + edgePoints_[index] +
edgePoints_[(index - 1 + edgePoints_.size())% edgePoints_.size()] + facePoints_[index]));
index++;
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 连接面点和边点 (要严格的封闭的四边形)
* @param {type}
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::connectPoints() {
if (!mesh.has_vertex_status()) mesh.request_vertex_status();
if (!mesh.has_face_status()) mesh.request_face_status();
if (!mesh.has_edge_status()) mesh.request_edge_status();
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> vertexDelHandle;// 存储将要删除的顶点
for (const auto& v : mesh.vertices()) {
vertexDelHandle.push_back(v);
}
// 加入所有新增节点
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> facePointsHandle;
std::vector<std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle>> faceHandles;
std::map<OpenMesh::Vec3d, MyMesh::VertexHandle> out;
for (const auto& v : vertexPoints_) {
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> facePointHandle;
for (const auto& vv : v.second) {
facePointHandle.push_back(mesh.add_vertex((OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point)vv));
out[vv] = facePointHandle[facePointHandle.size() - 1];
}
faceHandles.push_back(facePointHandle);
}
std::vector<std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle>> faceEdgeHandles;
std::vector<std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle>> faceFaceHandles;
// 距离边最近的四个顶点构成一个面
int iindex = 0;
for (auto e_it = mesh.edges_begin(); e_it != mesh.edges_end(); ++e_it)
{
// 得到边所代表的半边
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh1 = mesh.halfedge_handle(*e_it, 0); // 默认一个方向的半边
OpenMesh::Vec3d edgePoint(0, 0, 0);
int edgePointsNumber = 0;
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointV = mesh.point(mesh.from_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的起点
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointW = mesh.point(mesh.to_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的终点
std::vector<OpenMesh::Vec3d> vs;
for (const auto& vt : vertexPoints_[mesh.from_vertex_handle(heh1).idx()]) {
vs.push_back(vt);
}
for (const auto& vt : vertexPoints_[mesh.to_vertex_handle(heh1).idx()]) {
vs.push_back(vt);
}
sort(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [=](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return (a - edgePoints[heh1.idx()]).norm() < (b - edgePoints[heh1.idx()]).norm();
});
// 再对这些顶点进行排序, 按照
sort(vs.begin(), vs.begin()+4, [=](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return (a - vs[0]).norm() < (b - vs[0]).norm();
});
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> vvs;
faceEdgeHandles.push_back(vvs);
faceEdgeHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[0]]);
faceEdgeHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[2]]);
faceEdgeHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[3]]);
faceEdgeHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[1]]);
iindex++;
}
iindex = 0;
for (const auto& fh : mesh.faces())
{
OpenMesh::Vec3d facePoint(0, 0, 0);
int facePointsNumber = 0;
std::vector<OpenMesh::Vec3d> vs;
int ix = 0;
for (const auto& fvh : mesh.fv_range(fh))
{
ix++;
for (const auto& vt : vertexPoints_[(fvh).idx()]) {
vs.push_back(vt);
}
}
// 选取最近的四个顶点
sort(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [=](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return (a - facePoints[fh.idx()]).norm() < (b - facePoints[fh.idx()]).norm();
});
// 再对这些顶点进行排序, 按照
sort(vs.begin(), vs.begin() + 4, [=](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return (a - vs[0]).norm() < (b - vs[0]).norm();
});
std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle> vvs;
faceFaceHandles.push_back(vvs);
if (ix == 3) {
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[0]]);
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[1]]);
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[2]]);
}
else {
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[0]]);
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[2]]);
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[3]]);
faceFaceHandles[iindex].push_back(out[vs[1]]);
}
iindex++;
}
std::vector<std::vector<MyMesh::VertexHandle>> v;
int i = 0;
std::vector<MyMesh::FaceHandle> faceDelHandle;// 存储将要删除的面
for (const auto& fh : mesh.faces()) {
faceDelHandle.push_back(fh);
}
// 开始新增顶点的面
for (const auto& fvh : faceHandles) {
mesh.add_face(fvh);
}
// 开始新增边的面
int indexx = 0;
for (const auto& fvh : faceEdgeHandles) {
if (mesh.add_face(fvh)==OpenMesh::FaceHandle(-1)) {
auto tmp = faceEdgeHandles[indexx][1];
faceEdgeHandles[indexx][1] = faceEdgeHandles[indexx][3];
faceEdgeHandles[indexx][3] = tmp;
mesh.add_face(fvh);
}
indexx++;
}
// 开始新增面的面
indexx = 0;
for (const auto& fvh : faceFaceHandles) {
if (mesh.add_face(fvh) == OpenMesh::FaceHandle(-1)) {
if (faceFaceHandles[indexx].size() == 4) {
auto tmp = faceFaceHandles[indexx][1];
faceFaceHandles[indexx][1] = faceFaceHandles[indexx][3];
faceFaceHandles[indexx][3] = tmp;
}
else if(faceFaceHandles[indexx].size() == 3){
auto tmp = faceFaceHandles[indexx][1];
faceFaceHandles[indexx][1] = faceFaceHandles[indexx][2];
faceFaceHandles[indexx][2] = tmp;
}
mesh.add_face(fvh);
}
indexx++;
}
//// 开始删除面
for (int i = 0; i < faceDelHandle.size(); i++) {
mesh.delete_face(faceDelHandle[i], true);
}
//开始删除顶点
for (int i = 0; i < vertexDelHandle.size(); i++) {
mesh.delete_vertex(vertexDelHandle[i], true);
}
mesh.garbage_collection();
if (mesh.has_vertex_status()) mesh.release_vertex_status();
if (mesh.has_face_status()) mesh.release_face_status();
if (mesh.has_edge_status()) mesh.release_edge_status();
}
/**
* @description: 输出新网格
* @param {string} name 文件名称 默认 output.obj
* @return {type}
*/
void DS::genMesh(std::string name) {
if (name == "") {
name = "output.off";
}
try {
if (!OpenMesh::IO::write_mesh(mesh, name)) {
std::cerr << "Cannot write mesh to file 'output.off'" << std::endl;
return;
}
}
catch (std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return;
}
}
void DS::getResult() {
//if (getData()->edges.size() == 0) {
// getData()->edges.push_back(std::vector<V3f>());
//}
getData()->edges.push_back(std::vector<V3f>());
for (auto e_it = mesh.edges_begin(); e_it != mesh.edges_end(); ++e_it)
{
// 得到边所代表的半边
OpenMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh1 = mesh.halfedge_handle(*e_it, 0); // 默认一个方向的半边
OpenMesh::Vec3d edgePoint(0, 0, 0);
int edgePointsNumber = 0;
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointV = mesh.point(mesh.from_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的起点
OpenMesh::DefaultTraits::Point pointW = mesh.point(mesh.to_vertex_handle(heh1)); // 这条(半)边的终点
getData()->edges[0].push_back({ pointV[0], pointV[1], pointV[2] });
getData()->edges[0].push_back({ pointW[0], pointW[1], pointW[2] });
}
}
#pragma once
#include "strategy.h"
#include "qwidget.h"
#include <OpenMesh/Core/Mesh/PolyMesh_ArrayKernelT.hh>
#include <OpenMesh/Core/IO/MeshIO.hh>
#include <map>
//typedef struct FFACE {
// int faceId;
// int edgeId1;
// int vertexId;
// int edgeId2;
//}FFACE;
class DS :public Strategy, public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
private:
typedef OpenMesh::PolyMesh_ArrayKernelT<> MyMesh;
MyMesh mesh;
std::map<int, OpenMesh::Vec3d> facePoints;
std::map<int, OpenMesh::Vec3d> edgePoints;
std::map<int, OpenMesh::Vec3d> vertexPoints;
std::map<int, std::vector<OpenMesh::Vec3d>> vertexPoints_;
int times;
public:
DS(Data* data_);
~DS();
double weights_doo_sabin(size_t k, size_t i);
void genCube();
void genFacePoint();
void genEdgePoint();
void genVertexPoint();
void connectPoints();
void genMesh(std::string name);
bool Run();
void getResult();
};
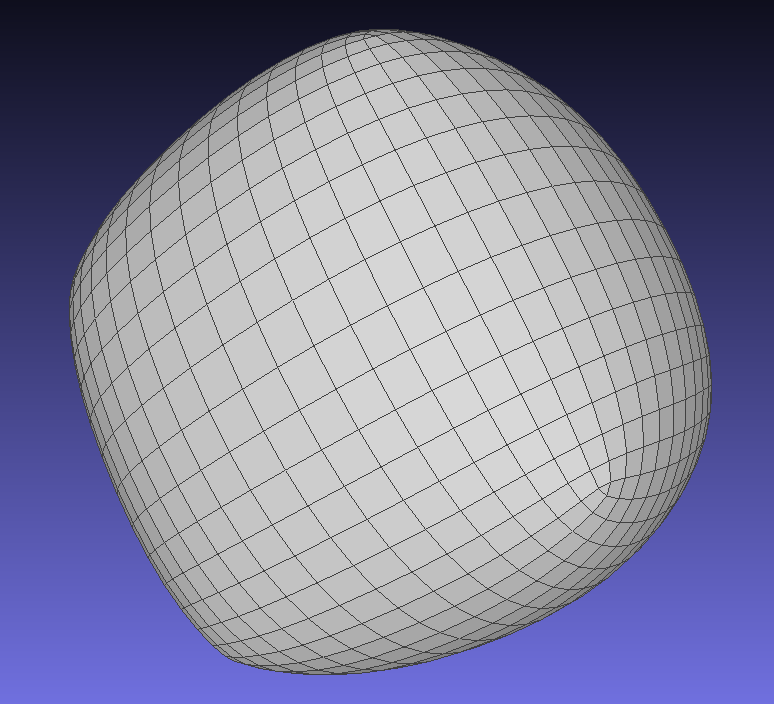
image
基于 doo-sabin的细分的更多相关文章
- Unity3d 使用DX11的曲面细分
Unity3d surface Shaderswith DX11 Tessellation Unity3d surface shader 在DX11上的曲面细分 I write this articl ...
- Google Analytics之增强型电子商务报告
虽然Google Analytics很多年以前就提供了电子商务报告的功能,但对于电子商务网站来说,这个报告缺失的东西还太多.而Google Analytics即将推出的增强型电子商务报告有望弥补这一短 ...
- Vulkan Tutorial 10 图形管线
操作系统:Windows8.1 显卡:Nivida GTX965M 开发工具:Visual Studio 2017 Introduction 通过接下来的章节,我们将会开启有关图形管线的话题,通过对图 ...
- Flexconnect部署
该记录主要用于针对于无线网络中Flexconnect的部署,可能涉及到的有Flexconnect中的组件,如何部署.(注意:在7.2版本以前,Flexconnect叫做HREAP),目前都称作为Fle ...
- 【译】Gartner CWPP市场指南
https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-1YSHGBQ8&ct=200416&st=sb?utm_source=marketo&ut ...
- 2020国防科大综述:3D点云深度学习——综述(3D点云分割部分)
目录 摘要 1.引言: 2.背景 2.1 数据集 2.2评价指标 3.3D点云分割 3.1 3D语义分割 3.1.1 基于投影的方法 多视图表示 球形表示 3.1.2 基于离散的方法 稠密离散表示 稀 ...
- 【Machine Learning】决策树案例:基于python的商品购买能力预测系统
决策树在商品购买能力预测案例中的算法实现 作者:白宁超 2016年12月24日22:05:42 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本 ...
- 基于token的多平台身份认证架构设计
基于token的多平台身份认证架构设计 1 概述 在存在账号体系的信息系统中,对身份的鉴定是非常重要的事情. 随着移动互联网时代到来,客户端的类型越来越多, 逐渐出现了 一个服务器,N个客户端的格 ...
- 记一次企业级爬虫系统升级改造(二):基于AngleSharp实现的抓取服务
爬虫系统升级改造正式启动: 在第一篇文章,博主主要介绍了本次改造的爬虫系统的业务背景与全局规划构思: 未来Support云系统,不仅仅是爬虫系统,是集爬取数据.数据建模处理统计分析.支持全文检索资源库 ...
- 码途有道----基于系统观的核心能力构建-by-韩宏老师
原文链接:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7d5a09f90102v341.html 有感于同学们在大学中如何学习计算机技术有些感概,将我书(老码识途)中的序言整理了一下 ...
随机推荐
- 一文搞懂Docker Compose
什么是Docker Compose Docker Compose 是 Docker 的一个编排管理工具,它允许你使用一个 YAML 文件来配置应用程序的服务.通过这个文件,你可以定义多个容器如何通过网 ...
- [笔记]通过命令行连接MySQL数据库服务器的几种方式总结如下
通过命令行连接MySQL数据库服务器的几种方式总结如下: 1.连接本地数据库,用户名为"root",密码"123456"(注意:"-p"和& ...
- 凯亚物联网平台如何通过MQTT网络组件接入设备
一.概述 有人提议我用kestrel代替Dotnetty ,那是不可能的, 物联网平台MQTT,rtmp,rtsp,httpflv,tcp,udp,rpc 都是基于dotnetty实现,压测没有问题, ...
- Fortify工具安装以及使用
工具简介: Fortify是一款强大的静态代码扫描分析工具,其发现代码漏洞缺陷的能力十分强悍,主要是将代码经过编译,依托于其强大的内置规则库来发现漏洞的.Fortify 是一个静态的.白盒的软件源代 ...
- Laravel RCE(CVE-2021-3129)漏洞复现
Laravel框架简介 Laravel是一套简洁.优雅的PHP Web开发框架(PHP Web Framework).它可以让你从面条一样杂乱的代码中解脱出来:它可以帮你构建一个完美的网络APP,而且 ...
- Java IO--实现文件的加密解密
我们知道文件存储的方式在计算机当中是以字节的方式进行存储的,可以通过对文件字节的操作来实现文件的加密. 下面的例子是通过读取文件的字节,然后使字节中的每一位取反(1变0,0变1),再进行倒置,来实现加 ...
- Navicat Premiun已经停止工作
与网易有道词典冲突.退出词典即可.
- 时间工具之“js初始化当前时间数据”
⑨前端:初始化当前时间数据 方案一(峰哥认可) // 2023-02this.$moment().format('yyyy-MM'),// 2023-02-02this.$moment().form ...
- HarmonyOS NEXT开发实战教程—淘宝搜索页
今天忙里偷闲,分享一个淘宝搜索页实现过程,先上效果图: 界面部分比较简单,大体分为导航栏.历史搜索.猜你想搜和热搜榜几个部分,历史搜索采用用户首选项进行存储数据. 导航栏部分相关代码如下: Flex( ...
- SQL 日常练习 (十七)
五一了, 2020过去近乎一半了, 疫情原因, 哪都没去, 其实与其出去玩, 不如呆着学习, 终身学习, 学无止境, 气有浩然, 这是我从上大学开始一直刻在脑海的训诫. 都说今年很艰难, 回头一想, ...
