hdu1507——Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2114 Accepted Submission(s): 867
Special Judge
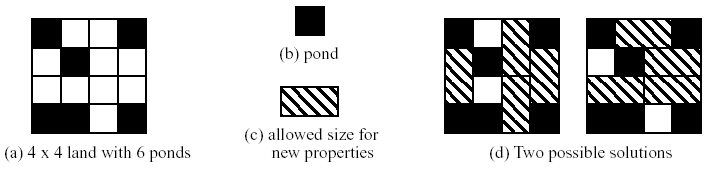
squares. He turned some of the squares into ponds, for he loved to hunt ducks and wanted to attract them to his property. (You cannot be sure, for you have not been to the place, but he may have made so many ponds that the land may now consist of several disconnected
islands.)
Your uncle Tom wants to sell the inherited land, but local rules now regulate property sales. Your uncle has been informed that, at his great-great-uncle's request, a law has been passed which establishes that property can only be sold in rectangular lots the
size of two squares of your uncle's property. Furthermore, ponds are not salable property.
Your uncle asked your help to determine the largest number of properties he could sell (the remaining squares will become recreational parks).
K indicating the number of squares that have been turned into ponds ( (N x M) - K <= 50). Each of the next K lines contains two integers X and Y describing the position of a square which was turned into a pond (1 <= X <= N and 1 <= Y <= M). The end of input
is indicated by N = M = 0.
If there are more than one solution, anyone is acceptable. there is a blank line after each test case. See sample below for clarification of the output format.
4 4
6
1 1
1 4
2 2
4 1
4 2
4 4
4 3
4
4 2
3 2
2 2
3 1
0 0
4
(1,2)--(1,3)
(2,1)--(3,1)
(2,3)--(3,3)
(2,4)--(3,4) 3
(1,1)--(2,1)
(1,2)--(1,3)
(2,3)--(3,3)
二分匹配。建边的根据是枚举全部可行的点,然后枚举周围四个方向。输出方案根据mark数组
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10010;
struct node
{
int to;
int next;
}edge[4 * maxn]; int vis[maxn];
int head[maxn];
int mark[maxn];
bool used[maxn];
bool mat[110][110];
int cnt[110][110];
int tot;
int n, m;
int index; void addedge(int from, int to)
{
edge[tot].to = to;
edge[tot].next = head[from];
head[from] = tot++;
} bool dfs(int x)
{
for (int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
if (!used[edge[i].to])
{
used[edge[i].to] = 1;
if (mark[edge[i].to] == -1 || dfs(mark[edge[i].to]))
{
mark[edge[i].to] = x;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} int hungary()
{
memset(mark, -1, sizeof(mark));
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
if (dfs(i))
ans++;
}
return ans;
} int main()
{
int k;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m))
{
if (!n && !m)
{
break;
}
scanf("%d", &k);
map<int, int>qu;
qu.clear();
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
memset(mat, false, sizeof(mat));
memset(vis, -1, sizeof(vis));
tot=0;
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
x--;
y--;
mat[x][y] = true;
}
index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (!mat[i][j])
{
cnt[i][j] = index++;
qu[index - 1] = i * m + j;
} for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (!mat[i][j])
{
if (i > 0 && !mat[i - 1][j])
addedge(cnt[i][j], cnt[i - 1][j]);
if (i < n-1 && !mat[i + 1][j])
addedge(cnt[i][j], cnt[i + 1][j]);
if (j > 0 && !mat[i][j - 1])
addedge(cnt[i][j], cnt[i][j - 1]);
if (j < m - 1 && !mat[i][j + 1])
addedge(cnt[i][j], cnt[i][j + 1]);
}
}
int res = hungary();
printf("%d\n", res / 2);
for (int i = 0; i < index; ++i)
{
if (mark[i] != -1)
{
int a = qu[i];
int b = qu[mark[i]];
int x1 = a / m + 1;
int y1 = a % m + 1;
int x2 = b / m + 1;
int y2 = b % m + 1;
if (vis[a] == -1 && vis[b] == -1)
{
printf("(%d,%d)--(%d,%d)\n", x1, y1, x2, y2);
vis[a] = b;
vis[b] = a;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
hdu1507——Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*的更多相关文章
- HDOJ 1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
直接对每一个格子进行dfs结果除以2能够得到答案可是有大量反复的结果,不好输出答案. 能够仅仅对横纵坐标相加是奇数的格子dfs.... Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* Time ...
- ZOJ 1516 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land(二分匹配 最大匹配 匈牙利啊)
题目链接:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=516 Your old uncle Tom inherited a p ...
- hdu-----(1507)Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*(二分匹配)
Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (J ...
- HDU1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* 二分图匹配 匈牙利算法 黑白染色
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/8254062.html 题目传送门 - HDU1507 题意概括 有一个n*m的棋盘,有些点是废的. 现在让你用1 ...
- hdu1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* 二分匹配
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1507 将i+j为奇数的构成x集合中 将i+j为偶数的构成y集合中 然后就是构建二部图 关键就是构图 然 ...
- HDU1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
题目是跟 zoj1516是一样的,但多了匹配后的输出 详解zoj1516可见http://www.cnblogs.com/CSU3901130321/p/4228057.html #include & ...
- HDU 1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*(二分图匹配)
Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (J ...
- Hdu 1507 Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* 分类: Brush Mode 2014-07-30 09:28 112人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (J ...
- Uncle Tom's Inherited Land*
Uncle Tom's Inherited Land* Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java ...
随机推荐
- spring注解开发-声明式事务(源码)
1. 环境搭建与测试 1)导入相关依赖 数据源.数据库驱动.Spring-jdbc模块 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework< ...
- Hadoop集群安装指南(CHD5.9.1)(分布式+图文详解)
centos7.1,CDH5.9.1,3台机器,终极指导安装 下载链接如下: 安装文件下载链接如下: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1RQYNiWn9a-T8GXcCsoDBs ...
- LInux设备驱动分析—— kmalloc和kzalloc函数
今晚在研究EVM5728开发板上面Linux系统的IIC设备驱动程序,偶然之间看到驱动程序中有一处使用了kzalloc函数,本人之前都是使用Linux内核提供的kmalloc / kfree函数来给设 ...
- API对接中经常会出现的签名获取,这只是某一种,仅供给有需要的人参考
要求: 1.对所有传入参数(含系统参数和接口参数)按照字段名的 ASCII 码从小到大排序(字典序)后,使用 URL 键值对的格式.(即 key1=value1&key2=value2…)拼接 ...
- SCI journals on Energy
SCI journals on Energy Table of Contents 1. SCI- Clarivate - Thomson Reuters 1 SCI- Clarivate - Thom ...
- idea 中的svn的使用
http://www.cnblogs.com/whc321/p/5669804.html 很详细
- exports和moudle. exports
http://zihua.li/2012/03/use-module-exports-or-exports-in-node/ https://github.com/seajs/seajs/issues ...
- [luoguP1227] [JSOI2008]完美的对称(sort)
传送门 排序! #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define N 20001 ...
- POJ1450:Gridland 【杂题】
题目大意:先给出了TSP的背景,然后给出一个n*m的单位格点的图,图中除边缘上的点与八个方向的点有边连接,距离为欧拉距离,求从左上角出发的TSP 思路:从水题列表中看到的题,但看一开始给出的backg ...
- hdu 1421经典dp
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define N 2001 #define inf 0x3fffffff int a[N],dp[N ...
