KMP中next数组的理解与应用
理解
1、next数组一直往前走
next数组一直往前走,得到的所有前缀也是当前主串的后缀,当然了,也是当前主串的前缀。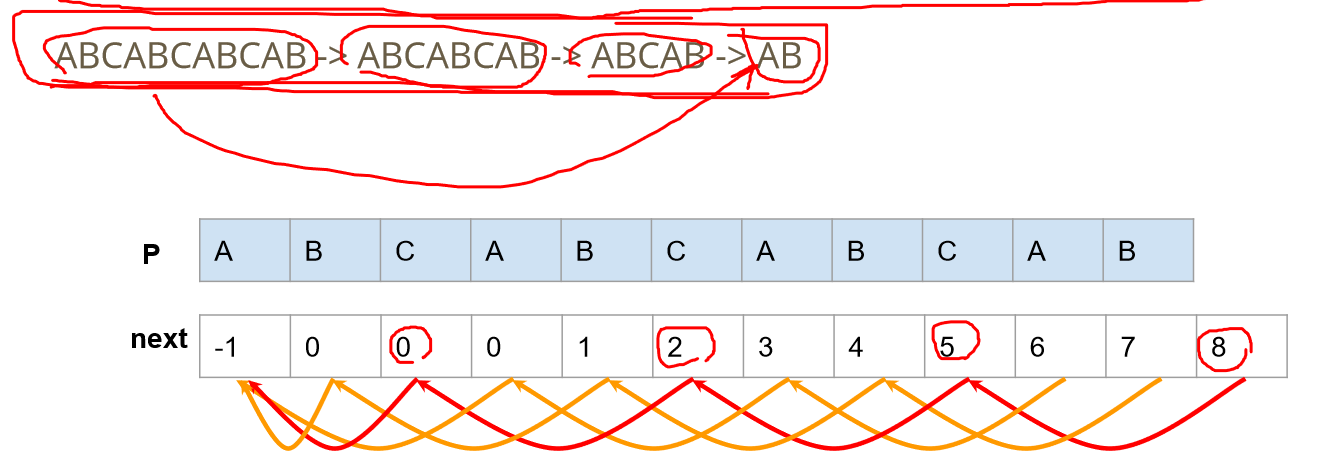
2、周期性字符串
1、周期性字符串$\Leftrightarrow n \,\% \, (n-next[n]) == 0 \ \&\& \ next[n] {\ } {\!}!{=} \ 0 $,循环节长度是$n-next[n]$。
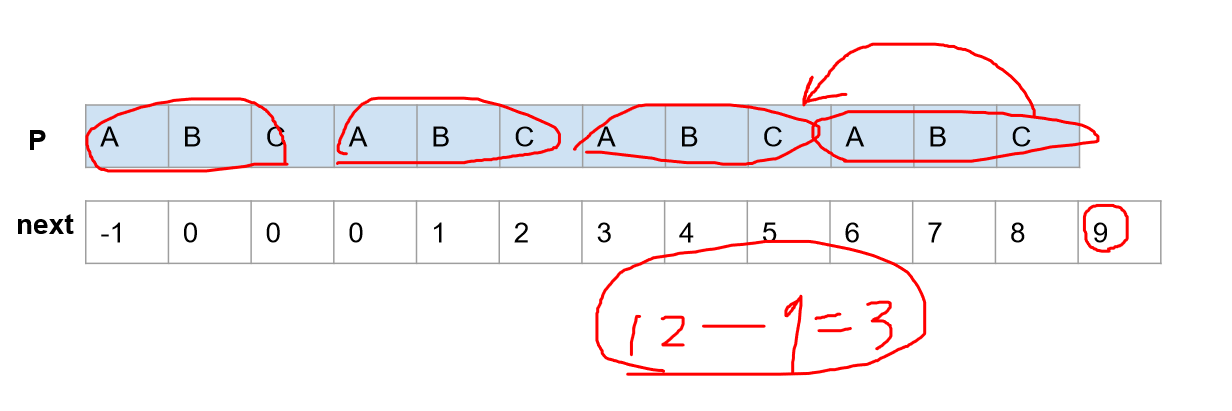
2、next数组往前跳的步长是一样的,除了最后一次。即$i-next[i]$保持恒定。

应用
- 题目一:Period
思路:先求出next数组,然后遍历一遍next数组得到所有字符结尾的字符串循环节的长度及个数
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int maxn = + ;
int nexts[maxn],n;
char s[maxn]; void pre_kmp()
{
int i = , j = nexts[] = -;
while (i < n)
{
while (j != - && s[i] != s[j]) j = nexts[j]; //当前不匹配,j回退,寻找是否存在一个长度较小的字串和开头的字串相等
nexts[++i] = ++j; //j等于已匹配的长度,如果当前位置也匹配,则nexts直接为j+1
}
} void slove()
{
pre_kmp();
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
if (i % (i - nexts[i]) == && nexts[i] != ) printf("%d %d\n", i, i / (i - nexts[i]));
} int main()
{
int T = ;
while (scanf("%d",&n) == && n)
{
scanf("%s", s);
s[n] = '#';
if (T) printf("\n");
printf("Test case #%d\n", ++T);
slove();
}
return ;
}
- 题目二:Power Strings
思路:先求next数组,再直接求循环节
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int maxn = + ;
int nexts[maxn],n;
char s[maxn]; void pre_kmp()
{
int i = , j = nexts[] = -;
//int n = strlen(s);
while (i < n)
{
while (j != - && s[i] != s[j]) j = nexts[j]; //当前不匹配,j回退,寻找是否存在一个长度较小的字串和开头的字串相等
nexts[++i] = ++j; //j等于已匹配的长度,如果当前位置也匹配,则nexts直接为j+1
}
} void slove()
{
pre_kmp();
if (n % (n - nexts[n]) != ) printf("1\n");
else printf("%d\n", n / (n - nexts[n]));
} int main()
{
int T = ;
while (scanf("%s", s) == && s[] != '.')
{
n = strlen(s);
s[n] = '#';
slove();
}
return ;
}
- 题目三:Count The String
思路:求所有前缀出现的次数和,由于next数组回退得到的前缀也是主串的后缀,所以所有next回退的次数加上本身的一次取模就是答案。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int mod = ;
const int maxn = + ;
int nexts[maxn], n;
char s[maxn]; void pre_kmp()
{
int i = , j = nexts[] = -;
//int n = strlen(s);
while (i < n)
{
while (j != - && s[i] != s[j]) j = nexts[j]; //当前不匹配,j回退,寻找是否存在一个长度较小的字串和开头的字串相等
nexts[++i] = ++j; //j等于已匹配的长度,如果当前位置也匹配,则nexts直接为j+1
}
} void slove()
{
int ans = n;
pre_kmp();
for (int i = n; i > ; i--)
{
int k = nexts[i];
while (k > )
{
ans = (ans + ) % mod;
k = nexts[k];
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
} int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%s", s);
slove();
}
return ;
}
- 题目四:Cyclic Nacklace
思路:题目大意:问至少添加多少个字符,使得这个字符串有至少两个循环节。若本身有两个循环节返回0,否则补充至两个循环节。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int mod = ;
const int maxn = + ;
int nexts[maxn], n;
char s[maxn]; void pre_kmp()
{
int i = , j = nexts[] = -;
n = strlen(s);
while (i < n)
{
while (j != - && s[i] != s[j]) j = nexts[j]; //当前不匹配,j回退,寻找是否存在一个长度较小的字串和开头的字串相等
nexts[++i] = ++j; //j等于已匹配的长度,如果当前位置也匹配,则nexts直接为j+1
}
} void slove()
{
pre_kmp();
int len = n - nexts[n];
if (n % len == && nexts[n] != ) printf("0\n");
else printf("%d\n", len - nexts[n] % len);
} int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
scanf("%s", s);
slove();
}
return ;
}
参考链接:
1、https://vjudge.net/contest/278481#overview
2、https://blog.csdn.net/hkh746392783/article/details/52015293
KMP中next数组的理解与应用的更多相关文章
- KMP中next数组的理解
next数组是KMP的核心,但对于next数组我们总是有时候感觉明白了,但有时候又感觉没明白,现在我就说下我自己对KMP中next数组的理解,首先next[i]上的数字的意义,next[i]表示的是当 ...
- POJ 2752 KMP中next数组的理解
感觉这里讲的挺好的.http://cavenkaka.iteye.com/blog/1569062 就是不断递归next数组.长度不断减小. 题意:给你一个串,如果这个串存在一个长度为n的前缀串,和长 ...
- POJ 2752 KMP中next数组的应用
题意: 让你从小到大输出给的字符串中既是前缀又是后缀的子串的长度. 思路: 先要了解这个东西: KMP中next数组表示的含义:记录着字符串匹配过程中失配情况下可以向前多跳几个字符,它描述的也是子串的 ...
- KMP算法中next数组的理解与算法的实现(java语言)
KMP 算法我们有写好的函数帮我们计算 Next 数组的值和 Nextval 数组的值,但是如果是考试,那就只能自己来手算这两个数组了,这里分享一下我的计算方法吧. 计算前缀 Next[i] 的值: ...
- poj 2406 Power Strings (kmp 中 next 数组的应用||后缀数组)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2406 Power Strings Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submiss ...
- E - Period(KMP中next数组的运用)
一个带有 n 个字符的字符串 s ,要求找出 s 的前缀中具有循环结构的字符子串,也就是要输出具有循环结构的前缀的最后一个数下标与其对应最大循环次数.(次数要求至少为2) For each prefi ...
- 对于kmp求next数组的理解
首先附上代码 1 void GetNext(char* p,int next[]) 2 { 3 int pLen = strlen(p); 4 next[0] = -1; 5 int k = -1; ...
- HDU 3746 Cyclic Nacklace(求补齐循环节最小长度 KMP中next数组的使用 好题!!!)
Cyclic Nacklace Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)T ...
- POJ1961(kmp中Next数组的性质)
对于某个位置i,i - Next[i]是循环节长度,i整除(i - Next[i])时是完整的几个循环元. ; int n, kase, Next[maxn]; char ch[maxn]; inli ...
随机推荐
- Linux设备驱动--块设备(三)之程序设计
块设备驱动注册与注销 块设备驱动中的第1个工作通常是注册它们自己到内核,完成这个任务的函数是 register_blkdev(),其原型为:int register_blkdev(unsigned i ...
- The type exists in both DLLs
2>C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\Temporary ASP.NET Files\root\c0b37647\aaceda91\Ap ...
- Map dependencies with code maps
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/modeling/map-dependencies-across-your-solutions Instal ...
- 通过查询数据库中的数据匹配在页面上:(set单条数据属性是在页面上的显示与foreach的不同) 通过ID修改提取位置表信息
ACTION OpenModifyExtractPositionById // set单条数据属性 /* * 通过ID修改提取位置表信息 */ public String OpenModifyEx ...
- Hibernate是如何延迟加载的
Hibernate是如何延迟加载的 2011-12-24 13:58 242人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 hibernatespringinterceptordao数据库integer Hibern ...
- gearcache在qemu-kvm虚拟化平台下的实现
需要用到的数据结构: 链表,基树. gearcache在qemu-kvm虚拟化平台下的实现主要有以下的步骤: 1.打开镜像文件的时候,为gearcache中的基数池(page_node_pool)和读 ...
- Vijos P1951 玄武密码 (AC自动机)
描述 在美丽的玄武湖畔,鸡鸣寺边,鸡笼山前,有一块富饶而秀美的土地,人们唤作进香河.相传一日,一缕紫气从天而至,只一瞬间便消失在了进香河中.老人们说,这是玄武神灵将天书藏匿在此. 很多年后,人们终于在 ...
- js点赞浮动特效
js自己封装的库: (function($) { $.extend({ tipsBox: function(options) { options = $.extend({ obj: null, //j ...
- .NET Core 跨平台物联网开发:上报属性(三)
系列教程目录 (一) 连接阿里云IOT (二) 设置委托事件 (三) 上报属性 (四) SDK文档 属性.方法.委托.类 http://pan.whuanle.cn/index.php?dir=up ...
- php实现rpc简单的方法
rpc是啥这不多解释,php扩展实现rpc yar是鸟哥的写的扩展,实现简单的rpc.比较很好理解 windows安装yar http://pecl.php.net/package/yar/2.0.4 ...
