Stars(树状数组+线段树)
Stars
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 6676 Accepted Submission(s): 2659
often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a
plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star
be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of
the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels
of the stars.
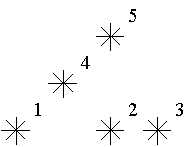
For
example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star
number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2
and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this
map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1,
one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
first line of the input file contains a number of stars N
(1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars
(two integers X and Y per line separated by a space,
0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the
plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with
equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line
contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars
of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the
level N-1.
1 1
5 1
7 1
3 3
5 5
2
1
1
0
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//#define LOCAL
const int MAXM=;
const int MAXN=;
/*struct Node{
int x,y;
};*/
int tree[MAXM+],ans[MAXN];//,die[MAXN];
//Node dt[MAXN];
/*int cmp(Node a,Node b){
if(a.y!=b.y){
return a.y<b.y;
}
else return a.x<b.x;
}*/
int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int x){
while(x<=MAXM){
tree[x]++;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int SUM(int x){
int temp=;
while(x>){
temp+=tree[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return temp;
}
/*int erfen(int l,int r,int x){
int mid;
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(die[mid]>x)r=mid-1;
else l=mid+1;
}
return l;
}*/
int main(){
/* #ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
#endif*/
int N;
int a;
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
memset(ans,,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d%*d",&a);
a++;
ans[SUM(a)]++;update(a);
// scanf("%d%d",&dt[i].x,&dt[i].y);
}
//sort(dt,dt+N,cmp);
/* for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
die[i]=SUM(dt[i].x);
update(dt[i].x);
}
sort(die,die+N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int temp=0,t=erfen(0,N-1,i);
// printf("%d**%d**%d\n",die[t-1],i,t);
temp=t;
ans[i]=temp;
// printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}*/
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
/* if(i){
printf(" ");
}*/
// printf("%d",i==0?ans[i]:ans[i]-ans[i-1]);
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
} }
return ;
}
刚开始写的也ac了:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//#define LOCAL
const int MAXM=;
const int MAXN=;
struct Node{
int x,y;
};
int tree[MAXM+],die[MAXN],ans[MAXN];
Node dt[MAXN];
/*int cmp(Node a,Node b){
if(a.y!=b.y){
return a.y<b.y;
}
else return a.x<b.x;
}*/
int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int x){
while(x<=MAXM){
tree[x]++;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int SUM(int x){
int temp=;
while(x){
temp+=tree[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return temp;
}
int main(){
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
#endif
int N;
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&dt[i].x,&dt[i].y);
dt[i].x++;
}
//sort(dt,dt+N,cmp);
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
die[i]=SUM(dt[i].x);
update(dt[i].x);
}
sort(die,die+N);
for(int i=,j=;i<N;i++){
int temp=;
while(die[j]==i){
j++;temp++;
}
ans[i]=temp;
}
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
//if(i)printf(" ");
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
// puts("");
}
return ;
}
刚开始发现超时改成二分找了,更快点的最后也ac了:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//#define LOCAL
const int MAXM=;
const int MAXN=;
struct Node{
int x,y;
};
int tree[MAXM+],die[MAXN],ans[MAXN];
Node dt[MAXN];
/*int cmp(Node a,Node b){
if(a.y!=b.y){
return a.y<b.y;
}
else return a.x<b.x;
}*/
int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int x){
while(x<=MAXM){
tree[x]++;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int SUM(int x){
int temp=;
while(x){
temp+=tree[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return temp;
}
int erfen(int l,int r,int x){
int mid;
while(l<=r){
mid=(l+r)>>;
if(die[mid]>x)r=mid-;
else l=mid+;
}
return l;
}
int main(){
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
#endif
int N;
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&dt[i].x,&dt[i].y);
dt[i].x++;
}
//sort(dt,dt+N,cmp);
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
die[i]=SUM(dt[i].x);
update(dt[i].x);
}
sort(die,die+N);
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
int temp=,t=erfen(,N-,i);
// printf("%d**%d**%d\n",die[t-1],i,t);
temp=t;
ans[i]=temp;
// printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
//if(i)printf(" ");
printf("%d\n",i==?ans[i]:ans[i]-ans[i-]);
}
// puts("");
}
return ;
}
线段树来一发:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MAXN=;
#define L tree[root].l
#define R tree[root].r
#define S tree[root].sum
#define lson root<<1,l,mid
#define rson root<<1|1,mid+1,r struct Node{
int l,r,sum;
};
Node tree[MAXN<<];
int res[MAXN>>];
int ans;
void build(int root,int l,int r){
L=l;R=r;
S=;
if(l==r)return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
build(lson);
build(rson);
}
void update(int root,int x){
if(L==x&&R==x){
S++;
return;
}
int mid=(L+R)>>;
if(mid>=x)update(root<<,x);
else update(root<<|,x);
S=tree[root<<].sum+tree[root<<|].sum;
}
void query(int root,int x){
if(L>=&&R<=x){
ans+=S;
return;
}
int mid=(L+R)>>;
if(mid>=)query(root<<,x);
if(mid<x)query(root<<|,x);
}
int main(){
int N,a;
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
build(,,MAXN-);
memset(res,,sizeof(res));
for(int i=;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d%*d",&a);
a++;
ans=;
query(,a);
res[ans]++;
update(,a);
}
for(int i=;i<N;i++)printf("%d\n",res[i]);
}
return ;
}
Stars(树状数组+线段树)的更多相关文章
- 洛谷P2414 阿狸的打字机 [NOI2011] AC自动机+树状数组/线段树
正解:AC自动机+树状数组/线段树 解题报告: 传送门! 这道题,首先想到暴力思路还是不难的,首先看到y有那么多个,菜鸡如我还不怎么会可持久化之类的,那就直接排个序什么的然后按顺序做就好,这样听说有7 ...
- 树状数组 && 线段树应用 -- 求逆序数
参考:算法学习(二)——树状数组求逆序数 .线段树或树状数组求逆序数(附例题) 应用树状数组 || 线段树求逆序数是一种很巧妙的技巧,这个技巧的关键在于如何把原来单纯的求区间和操作转换为 求小于等于a ...
- hdu1394(枚举/树状数组/线段树单点更新&区间求和)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1394 题意:给出一个循环数组,求其逆序对最少为多少: 思路:对于逆序对: 交换两个相邻数,逆序数 +1 ...
- hdu 1166:敌兵布阵(树状数组 / 线段树,入门练习题)
敌兵布阵 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- hdu 5147 Sequence II【树状数组/线段树】
Sequence IITime Limit: 5000/2500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Problem ...
- 数据结构--树状数组&&线段树--基本操作
随笔目的:方便以后对树状数组(BIT)以及基本线段树的回顾 例题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1166 例题:hdu 1166 敌兵布阵 T ...
- BZOJ_1901_&_ZJU_2112_Dynamic_Rankings_(主席树+树状数组/线段树+(Treap/Splay))
描述 http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1901 给出一个长度为n的数列A,有m次询问,询问分两种:1.修改某一位置的值;2.求区间[l, ...
- BZOJ 3333 排队计划 树状数组+线段树
题目大意:给定一个序列.每次选择一个位置,把这个位置之后全部小于等于这个数的数抽出来,排序,再插回去,求每次操作后的逆序对数 首先我们每一次操作 对于这个位置前面的数 因为排序的数与前面的数位置关系不 ...
- 第十四个目标(dp + 树状数组 + 线段树)
Problem 2236 第十四个目标 Accept: 17 Submit: 35 Time Limit: 1000 mSec Memory Limit : 32768 KB Probl ...
- Curious Robin Hood(树状数组+线段树)
1112 - Curious Robin Hood PDF (English) Statistics Forum Time Limit: 1 second(s) Memory Limit: 64 ...
随机推荐
- threadid=1: thread exiting with uncaught exception (group=0x40db8930)
异常信息如下: 07-26 17:23:49.521: W/dalvikvm(29229): threadid=1: thread exiting with uncaught exception (g ...
- python3.5之输出HTML实体字符
出 关① 徐兰 凭山俯海古边州, 旆②影风翻见戍楼. 马后桃花马前雪,出关争得不回头? [注]关,指居庸关.②旆(pèi),旌旗. 刚刚学习用python写爬虫,实战一下. 抓取出一个网页的内容 ...
- libvirt python binding 变成了一个新项目
http://libvirt.org/git/ $ git clone git://libvirt.org/libvirt-python.git 2013年的事情了. $ git show a7a12 ...
- android加载更多的图片
这是昨天改进后的,我测试了下,可以加载图片到5万张,估计5万以上也是没问题的,我只试到5万,其实也没必要这么高,现实中1000左右就差不多了,不过我的应用到100就差不多了, package com. ...
- Pie(求最小身高差,dp)
Pie Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submis ...
- 自己写的sql server触发器练练--高手请您跳过吧
set ANSI_NULLS ONset QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ONgo ALTER TRIGGER [insertReplyToic] ON [dbo].[bbsReplyTopic] ...
- 从文档流来看内联元素和块元素的css排版
veda原创[抄录]讲得很好存自己这里看 从文档流来看内联元素和块元素的css排版 CSS文档流与块级元素(block).内联元素(inline),之前翻阅不少书籍,看过不少文章, 看到所多的是零碎的 ...
- sass安装步骤
sass 基于Ruby,首先需要安装Ruby.当然也有node-sass,那是另外一种使用方式了.如果能FQ的,就不用看了,主要写给翻不了墙的人用. 1.安装Ruby,ruby下载地址: http:/ ...
- js 下拉框效果
<script type="text/javascript"> window.onload = function () { ]; ]; var aLi = oSub.g ...
- USACO Section 4.3 Street Race(图的连通性+枚举)
虽说是IOI'95,但是也是挺水的..for 第一问,n最大为50,所以可以直接枚举起点和终点之外的所有点,然后dfs判断是否连通:for 第二问,易知答案一定是第一问的子集,所以从第一问中的答案中枚 ...
