Hdu Binary Tree Traversals
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
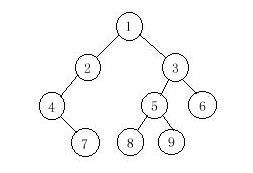
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
注: 已知二叉树的前序和中序遍历, 可以唯一确定二叉树的后序遍历, 但如果知道前序和后序,求中序遍历是不可能实现的.
算法:
由前序遍历的第一个元素可确定左、右子树的根节点,参照中序遍历又可进一步确定子树的左、
右子树元素。如此递归地参照两个遍历序列,最终构造出二叉树。
由前序和中序结果求后序遍历结果
树的遍历:给你一棵树的先序遍历结果和中序遍历的结果,让你求以后序遍历输出用递归。
每次把两个数组分成三个部分,父节点,左子树,右子树,把父节点放到数组里边,重复此步骤直到重建一棵新树
, 这时,数组里元素刚好是后序遍历的顺序
关键点:
中序遍历的特点是先遍历左子树,接着根节点,然后遍历右子树。这样根节点就把左右子树隔开了。而前序遍历的特点是先访问根节点,从而实现前序遍历结果提供根节点信息,中序遍历提供左右子树信息,从而实现二叉树的重建
【注明】
先序的排列里第一个元素是根,再比较中序的排列里根所在的位置,则能确定左子树,右子树元素个数numleft,numright且在先序排列里,先是一个根,再是numleft个左子树的元素排列,最后是numright个右子树的元素排列。
该过程就是从inorder数组中找到一个根,然后从preorder数组的位置来确定改点到底是左儿子还是右儿子。如此一直循环下去知道一棵完整的数建立完成。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> const int MAX = 1000 + 10;
int n,in[MAX],pre[MAX];
typedef struct BITree
{
int data,index;
BITree *Left,*Right;
}BiTree,*Tree; void DFS(Tree &root,int index)
{
if(root == NULL){
root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(BiTree));
root->data = in[index];
root->index = index;
root->Left = NULL;
root->Right = NULL;
}else
{
if(index < root->index)
DFS(root->Left,index);
else
DFS(root->Right,index);
}
} void CreateTree(Tree &root)
{
int i,j,index;
root = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(BiTree));
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
if(in[i] == pre[1])
{
root->data = pre[1];
root->index = i;
root->Left = NULL;
root->Right = NULL;
break;
}
index = i;
for(i = 2;i <= n;i++)
for(j = 1;j <= n;j++)
if(in[j] == pre[i])
{
if(j < index)
DFS(root->Left,j);
else
DFS(root->Right,j);
break;
}
} void PostOrder(Tree root,int x)
{
if(root == NULL) return ;
PostOrder(root->Left,x+1);
PostOrder(root->Right,x+1);
if(x == 0)
printf("%d",root->data);
else
printf("%d ",root->data);
} int main()
{
int i;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
Tree root;
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
scanf("%d",&pre[i]);
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
CreateTree(root);
PostOrder(root,0);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; const int MAX = 1000 + 10;
typedef struct BITree
{
int data;
BITree *Left,*Right;
BITree()
{
Left = NULL;
Right = NULL;
}
}*BiTree;
int pre[MAX],in[MAX]; void BuildTree(BiTree &root,int len,int pst,int ped,int inst,int ined)
{
int i,left_len = 0;
if(len<=0)return; //递归终止的条件
root = new BITree;
root->data = pre[pst];
for(i = inst;i <= ined;i++)
if(in[i] == pre[pst])
{
left_len = i - inst;
break;
}
BuildTree(root->Left,left_len,pst+1,pst+left_len,inst,i-1);
BuildTree(root->Right,len-left_len-1,pst+left_len+1,ped,i+1,ined);
} void PostTravel(BITree *root)
{
if(root)
{
PostTravel(root->Left);
PostTravel(root->Right);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}
} int main()
{
int i,n;
BiTree root;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
scanf("%d",&pre[i]);
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
BuildTree(root,n,1,n,1,n);
PostTravel(root->Left);
PostTravel(root->Right);
printf("%d\n",root->data);
}
return 0;
}
Hdu Binary Tree Traversals的更多相关文章
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals (二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals 前序遍历和中序推后序
题链;http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (J ...
- hdu 1701 (Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树前序中序推后序)
Binary Tree Traversals T ...
- hdu1710(Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU-1701 Binary Tree Traversals
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 已知先序和中序遍历,求后序遍历二叉树. 思路:先递归建树的过程,后后序遍历. Binary Tree Tr ...
- HDU 1710-Binary Tree Traversals(二进制重建)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- Binary Tree Traversals(HDU1710)二叉树的简单应用
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
随机推荐
- keil mdk中如何确保某一段程序不被优化掉
使用mdk编程,假如有一个有用的函数你定义了但是没有显式的调用,mdk在默认方式下,将会把这个函数从整个程序总删除掉,以节省ROM. 比如,你在ROM的0x00002000处定位了一个函数,假设为vo ...
- Delphi 全面控制Windows任务栏
核心提示:使用Windows95/NT/98操作系统的用户知道:Windows正常启动后,在电脑屏幕下方出现一块 任务栏. 使用Windows95/NT/98操作系统的用户知道:Windows正常启动 ...
- cdoj 秋实大哥与战争
首先,显然每个区间的最长连续子区间要么在左孩子里,要么在右孩子里,要么跨越两个孩子.于是我们可以对每个区间维护如下信息ll(left long),rl(rigth long),ml(mid long) ...
- getBoundingClientRect()来获取页面元素的位置”
getBoundingClientRect()来获取页面元素的位置” 获取的是一个对象; 延伸阅读; https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzAxODE2MjM1MA== ...
- 使用扩展名获取mimetype
在Android中很多时候我们需要计算出文件的mimetype,而我们通常的思路就是通过扩展名来获取对应的mimetype,而如果自行处理,将维护一个比较大的映射表,而实际上大可不必,Android提 ...
- Data Structure(3)——软考阶段学习小结
数据结构计算机等级考试中有,自考中有,软考中同样有,可见其内容的重要程度,今天对软考阶段视频学习内容的总结,同样是对前面学习内容的回顾,同样是对后面学习的铺垫. 中结:原本因为之前有过类似的总结,这次 ...
- 如何修改 UINavigationController、UINavigationBar 中 navigationItem 左侧 “返回” 按钮的名称
如果我们从 title 为 “首页” 的页面 A 点击进入一个子页面 B,那么在页面 B 的左上角将显示一个名为 “<首页” 的按钮.假设这个页面 A 叫 “你是我天边最美的云彩”,那在页面 B ...
- C#命名空间详解namespace
命名空间是一个域,这在个域中所有的类型名字必须是唯一的,不同的类型分组归入到层次化的命名空间, 命名空间的好处是:1.避免名字冲突,2.便于查找类型名字. 如:System.secruity.Cry ...
- Java面试题之J2EE是什么
J2EE是Sun公司提出的多层(multi-diered),分布式(distributed),基于组件(component-base)的企业级应用模型(enterpriese application ...
- 从头开始-02.C语言基础
变量的内存分析: #include <stdio.h> int main() { //内存地址由大到小 int a=10; int b=20; //&是一个地址运算符,取得变量的地 ...
