【BZOJ 2618】 2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 (半平面交)
2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形
Description
逆时针给出n个凸多边形的顶点坐标,求它们交的面积。例如n=2时,两个凸多边形如下图:则相交部分的面积为5.233。
Input
第一行有一个整数n,表示凸多边形的个数,以下依次描述各个多边形。第i个多边形的第一行包含一个整数mi,表示多边形的边数,以下mi行每行两个整数,逆时针给出各个顶点的坐标。
Output
输出文件仅包含一个实数,表示相交部分的面积,保留三位小数。
Sample Input
2
6
-2 0
-1 -2
1 -2
2 0
1 2
-1 2
4
0 -3
1 -1
2 2
-1 0Sample Output
5.233HINT
100%的数据满足:2<=n<=10,3<=mi<=50,每维坐标为[-1000,1000]内的整数
半平面交模板:(终于缩到100行以内了。。。之前没删调试恶心的180+)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define Maxn 1100 struct P
{
double x,y;
P() {x=y=;}
P(double x,double y):x(x),y(y){}
friend P operator - (P x,P y) {return P(x.x-y.x,x.y-y.y);}
friend P operator + (P x,P y) {return P(x.x+y.x,x.y+y.y);}
friend P operator * (P x,double y) {return P(x.x*y,x.y*y);}
friend double operator * (P x,P y) {return x.x*y.y-x.y*y.x;}
friend double operator / (P x,P y) {return x.x*y.x+x.y*y.y;}
}a[Maxn];
struct L
{
P a,b,v;double slop;
friend bool operator < (L a,L b) {return (a.slop!=b.slop)?(a.slop<b.slop):a.v*(b.b-a.a)>;}
friend P inter(L a,L b)
{
P nw=b.a-a.a;
double tt=(nw*a.v)/(a.v*b.v);
return b.a+b.v*tt;
}
friend bool jud(P x,L c) {return c.v*(x-c.a)<;}
}l[Maxn],q[Maxn];int cnt,tot; void ffind()
{
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++) l[i].v=l[i].b-l[i].a,l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].v.y,l[i].v.x);
sort(l+,l++cnt);
int L=,R=;
tot=;
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(l[i].slop!=l[i-].slop) tot++;
l[tot]=l[i];
}
cnt=tot;tot=;
q[++R]=l[];q[++R]=l[];
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[R-],q[R]),l[i])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[L+],q[L]),l[i])) L++;
q[++R]=l[i];
}
while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[R-],q[R]),q[L])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[L+],q[L]),q[R])) L++;
q[R+]=q[L];
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) a[++tot]=inter(q[i],q[i+]);
} void init()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
cnt=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);
P ft,now,nw;
scanf("%lf%lf",&ft.x,&ft.y);
now=ft;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf",&nw.x,&nw.y);
l[++cnt].b=nw,l[cnt].a=now;
now=nw;
}
l[++cnt].a=now;l[cnt].b=ft;
}
} void get_area()
{
double ans=;
for(int i=;i<tot;i++) ans+=a[i]*a[i+];
ans+=a[tot]*a[];
if(tot<) ans=;
printf("%.3lf\n",ans/);
} int main()
{
init();
ffind();
get_area();
return ;
}
【分析】
然而只是想做一道半平面交的模版题,就从星期二打到了现在。。。【下午还要考试呢真是无爱。。
这题是求凸包的交,我们可以把每一条线段转化半平面,求半平面交。
对于半平面交,最朴素的想法应该是两两线段求交点,然后判断是否在每一个平面内,然后求凸包吧(感觉奇慢无比啊)
而事实上,如果有n的半平面的话,半平面交的答案那个凸包不会超过n条边,因为每个半平面最多只贡献一条边,说明我们事实上做了很多很多无用功。
根据凸包的思想,我们觉得半平面交也是有单调性的。
那个nlogn的算法可以看zzy的论文《半平面交的新算法及其实用价值》。
半平面共用向量表示,向量的左边为有效半平面。
定义半平面的极角为表示半平面的向量的极角。
根据半平面的极角进行排序,若两个半平面极角相同,明显只需要保存最靠左的半平面,根据这个去重。
然后这样做:
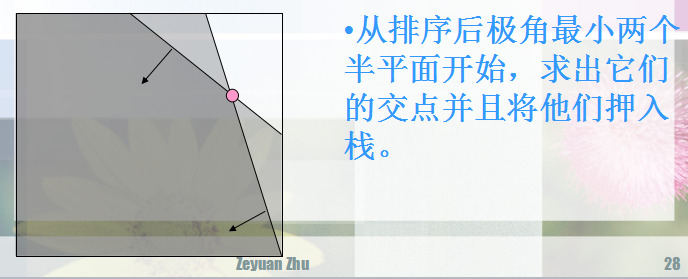
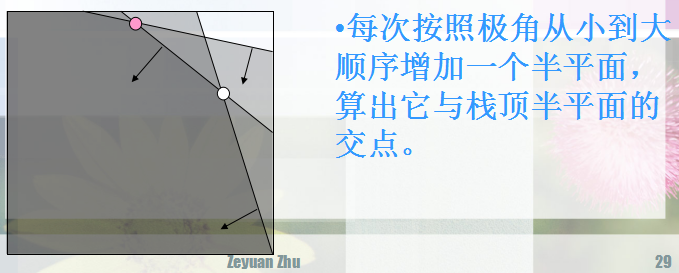

跟单调队列差不多,两边判断,删减。
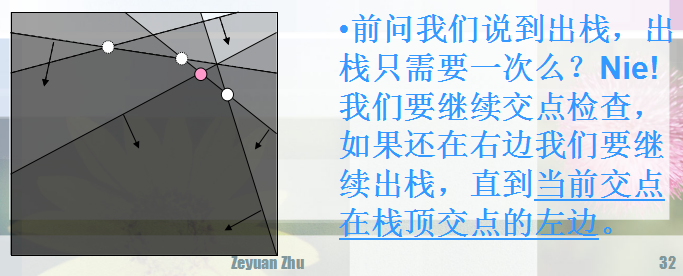
注意最后还要判断一下,去尾。像这样:


这题就是这样了。
放代码(调试很多,不删了)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define Maxn 1100 struct P {double x,y;};
struct L {P a,b;double slop;}l[Maxn];
//半平面只方向向量a->b的左部分
//slop 极角
int cnt; P operator - (P x,P y)
{
P tt;
tt.x=x.x-y.x;
tt.y=x.y-y.y;
return tt;
} P operator + (P x,P y)
{
P tt;
tt.x=x.x+y.x;
tt.y=x.y+y.y;
return tt;
} double Dot(P x,P y) {return x.x*y.x+x.y*y.y;}
double Cross(P x,P y) {return x.x*y.y-x.y*y.x;}
// bool operator < (L x,L y) {return x.slop<y.slop;} bool operator < (L a,L b)
{
if(a.slop!=b.slop)return a.slop<b.slop;
return Cross(a.b-a.a,b.b-a.a)>;
} P operator * (P X,double y)
{
P tt;
tt.x=X.x*y;
tt.y=X.y*y;
return tt;
} P a[Maxn];
L q[Maxn];
int tot; P inter(L a,L b)
{
P X=a.a-a.b,Y=b.a-b.b,nw;
double tt;
nw=b.a-a.a;
tt=Cross(nw,X)/Cross(X,Y);
P ans=b.a+Y*tt;
return ans;
} bool jud(L a,L b,L c)
{
P p=inter(a,b);
return Cross(c.b-c.a,p-c.a)<;
} void opp()
{
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
printf("%.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf = %.2lf \n",l[i].a.x,l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x,l[i].b.y,l[i].slop);
}
printf("\n");
} void output()
{
for(int i=;i<=tot;i++) printf("%2lf %.2lf\n",a[i].x,a[i].y);
printf("\n");
} void op(int L,int R)
{
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++)
printf("%lf %lf %lf %lf\n",l[i].a.x,l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x,l[i].b.y);
printf("\n");
} void ffind()
{
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].b.y-l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x-l[i].a.x);
sort(l+,l++cnt); // opp(); int L=,R=;
//去重?
tot=;
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
if(l[i].slop!=l[i-].slop) tot++;
l[tot]=l[i];
}
cnt=tot;tot=;
// opp();
q[++R]=l[];q[++R]=l[];
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
while(L<R&&jud(q[R-],q[R],l[i])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(q[L+],q[L],l[i])) L++;
q[++R]=l[i];
// op(L,R);
}
while(L<R&&jud(q[R-],q[R],q[L])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(q[L+],q[L],q[R])) L++;
q[R+]=q[L];
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++)
a[++tot]=inter(q[i],q[i+]);
// output(); // output();
} void init()
{
int n;
/*scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf\n",&l[i].a.x,&l[i].a.y,&l[i].b.x,&l[i].b.y);
}
cnt=n;*/
scanf("%d",&n);
cnt=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);
P ft,now;
scanf("%lf%lf",&ft.x,&ft.y);
now=ft;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
P nw;
scanf("%lf%lf",&nw.x,&nw.y);
l[++cnt].b=nw;
l[cnt].a=now;
now=nw;
}
l[++cnt].a=now;l[cnt].b=ft;
// opp();
} for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].b.y-l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x-l[i].a.x);
// opp(); } void get_area()
{
double ans=;
for(int i=;i<tot;i++)
{
ans+=Cross(a[i],a[i+]);
}
ans+=Cross(a[tot],a[]);
if(tot<) ans=;
printf("%.3lf\n",ans/);
} int main()
{
init();
ffind();
// output();
get_area();
return ;
}
用向量法求两直线的交点:

本质就是用面积比表示线段比。
P inter(L a,L b)
{
P X=a.a-a.b,Y=b.a-b.b,nw;
double tt;
nw=b.a-a.a;
tt=Cross(nw,X)/Cross(X,Y);
P ans=b.a+Y*tt;
return ans;
}
半平面交核心过程:
q[++R]=l[1];q[++R]=l[2];
for(int i=3;i<=cnt;i++)
{
while(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],l[i])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(q[L+1],q[L],l[i])) L++;
q[++R]=l[i];
}
if(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],q[L])) R--;
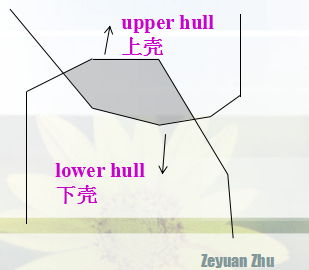
代码的具体实现其实没有分上壳和下壳,是一起做的,每次保存有用的半平面,最后相邻的求交点形成凸包。
最后也不用处理上面去尾的情况了,但是注意加一句if,判断最后加的那个半平面是有效的。
:if(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],q[L])) R--;
【倒是对几何画板越来越熟练了,捂脸= =
2016-12-24 09:48:20
【BZOJ 2618】 2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 (半平面交)的更多相关文章
- bzoj 2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 [半平面交]
2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 半平面交 注意一开始多边形边界不要太大... #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #inclu ...
- 洛谷 P4196 [CQOI2006]凸多边形 (半平面交)
题目链接:P4196 [CQOI2006]凸多边形 题意 给定 \(n\) 个凸多边形,求它们相交的面积. 思路 半平面交 半平面交的模板题. 代码 #include <bits/stdc++. ...
- BZOJ - 2618 凸多边形 (半平面交)
题意:求n个凸多边形的交面积. 半平面交模板题. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ty ...
- bzoj 2618 2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形(半平面交)
2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 656 Solved: 340[Submit][Status] ...
- 2018.07.04 BZOJ 2618 Cqoi2006凸多边形(半平面交)
2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形 Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Description 逆时针给出n个凸多边形的顶点坐标,求它们交的面积.例如n ...
- bzoj 2618 半平面交模板+学习笔记
题目大意 给你n个凸多边形,求多边形的交的面积 分析 题意\(=\)给你一堆边,让你求半平面交的面积 做法 半平面交模板 1.定义半平面为向量的左侧 2.将所有向量的起点放到一个中心,以中心参照进行逆 ...
- bzoj 2618【半平面交模板】
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> usin ...
- 【BZOJ2618】[CQOI2006]凸多边形(半平面交)
[BZOJ2618][CQOI2006]凸多边形(半平面交) 题面 BZOJ 洛谷 题解 这个东西就是要求凸多边形的边所形成的半平面交. 那么就是一个半平面交模板题了. 这里写的是平方的做法. #in ...
- [CQOI2006]凸多边形(半平面交)
很明显是一道半平面交的题. 先说一下半平面交的步骤: 1.用点向法(点+向量)表示直线 2.极角排序,若极角相同,按相对位置排序. 3.去重,极角相同的保留更优的 4.枚举边维护双端队列 5.求答案 ...
随机推荐
- 关于C/C++中的位运算技巧
本篇文章讲述在学习CSAPP位运算LAB时的一些心得. 移位运算的小技巧 C/C++对于移位运算具有不同的策略,对于无符号数,左右移位为逻辑移位,也就是直接移位:对于有符号数,采用算术移位的方式,即左 ...
- 再说 extern "C"
早知道 C++ 源文件中要调用C语言函数需要在函数申明时 指定extern "C": 要不然可以编译通过,但连接时提示找不到什么什么符号,原因是C和C++生成的函数名不一样,ext ...
- C/C++输入输出总结
*string类: 1.cin>>string时,遇到'\n'或者空格即停止,并且'\n'或空格仍留在输入里,即只读了一个单词或什么都没读,但string类自己处理好了空字符什么的.下一 ...
- 第七章 探秘Qt的核心机制-信号与槽
第七章 探秘Qt的核心机制-信号与槽 注:要想使用Qt的核心机制信号与槽,就必须在类的私有数据区声明Q_OBJECT宏,然后会有moc编译器负责读取这个宏进行代码转化,从而使Qt这个特有的机制得到使用 ...
- java计算过G文件md5 值计算
package io.bigdata; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; ...
- jdbc之分页查询
分页查询作为一项十分重要的数据库查询技术,在很多web项目中都会要用到,当然移动开发中也是会涉及的. 一.分页查询的sql语句: ps:为了方便阐述,下面统一使用student表作为查询的表:colN ...
- Linux网络通信编程(套接字模型TCP\UDP与IO多路复用模型select\poll\epoll)
Linux下测试代码: http://www.linuxhowtos.org/C_C++/socket.htm TCP模型 //TCPClient.c #include<string.h> ...
- jsp日期控件My97DatePicker的使用
My97DatePicker是一款非常灵活好用的日期控件.使用非常简单. 1.下载My97DatePicker组件包 2.将My97DatePicker包放在项目WebContent目录下 3.在页面 ...
- 在MVVMLight框架的ViewModel中实现NavigationService
网上已经有很多方法了,比如通过Messenger来实现等等.这里我只讲述一种我比较喜欢的方法,因为它很方便 首先定义一个ViewModel基类,将所有ViewModel子类继承这个基类.在基类中定义 ...
- Oracle分析函数 — sum, rollup, cube, grouping用法
本文通过例子展示sum, rollup, cube, grouping的用法. //首先建score表 create table score( class nvarchar2(20), course ...
