Codeforces Round#416 Div.2
A. Vladik and Courtesy
题面
At regular competition Vladik and Valera won a and b candies respectively. Vladik offered 1 his candy to Valera. After that Valera gave Vladik 2 his candies, so that no one thought that he was less generous. Vladik for same reason gave 3 candies to Valera in next turn.
More formally, the guys take turns giving each other one candy more than they received in the previous turn.
This continued until the moment when one of them couldn’t give the right amount of candy. Candies, which guys got from each other, they don’t consider as their own. You need to know, who is the first who can’t give the right amount of candy.
题意
没人轮流减去一个数字,看谁先挂。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m,cnt;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m;
cnt=1;
while (cnt )
{
if (cnt%2) n-=cnt;
else m-=cnt;
if (n<0) return 0*puts("Vladik");
if (m<0) return 0*puts("Valera");
cnt++;
}
}
B. Vladik and Complicated Book
题面
Vladik had started reading a complicated book about algorithms containing n pages. To improve understanding of what is written, his friends advised him to read pages in some order given by permutation P = [p1, p2, ..., pn], where pi denotes the number of page that should be read i-th in turn.
Sometimes Vladik’s mom sorted some subsegment of permutation P from position l to position r inclusive, because she loves the order. For every of such sorting Vladik knows number x — what index of page in permutation he should read. He is wondered if the page, which he will read after sorting, has changed. In other words, has px changed? After every sorting Vladik return permutation to initial state, so you can assume that each sorting is independent from each other.
题意
问子区间排序后第x个值的值会不会改变
找出排列后他应该在哪里,直接判断。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int a[10001];
int b[10001];
int l,r,x;
int cnt;
int cmp(int q,int w)
{
return q<w;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
cin>>l>>r>>x;
cnt=0;
for (int o=l;o<=r;o++) if (a[o] < a[x] ) cnt++;
puts( (l+cnt==x) ?"Yes":"No");
}
}
C. Vladik and Memorable Trip
题面
Vladik often travels by trains. He remembered some of his trips especially well and I would like to tell you about one of these trips:
Vladik is at initial train station, and now n people (including Vladik) want to get on the train. They are already lined up in some order, and for each of them the city code ai is known (the code of the city in which they are going to).
Train chief selects some number of disjoint segments of the original sequence of people (covering entire sequence by segments is not necessary). People who are in the same segment will be in the same train carriage. The segments are selected in such way that if at least one person travels to the city x, then all people who are going to city x should be in the same railway carriage. This means that they can’t belong to different segments. Note, that all people who travel to the city x, either go to it and in the same railway carriage, or do not go anywhere at all.
Comfort of a train trip with people on segment from position l to position r is equal to XOR of all distinct codes of cities for people on the segment from position l to position r. XOR operation also known as exclusive OR.
Total comfort of a train trip is equal to sum of comfort for each segment.
Help Vladik to know maximal possible total comfort.
题意
给一个数组,如果你选了一个数,那么就必须选上含这个数的最小区间。
我们可以预处理,得到很多线段,然后我们想办法合并这些线段。
枚举每一个线内,如果有一个区间覆盖了右边的某部分,则合并进来,如果覆盖了左边的某部分,说明之前判断过,如果完全覆盖了,说明也是之前判断过,合并过了。
然后dp,一个线段,d[线段头]转移到d[线段尾部]。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int n;
int a[5011];
int in[5011];
int ini[5011];
int last[5011];
ll d[5011];
vector< pair< int , ll > > v[5011];
map<int, pair<int,int> > m;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
last[a[i]]=i;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) if (!in[a[i]])
{
m[a[i]] = make_pair( i, last[a[i]] );
in[a[i]]=1;
}
for (auto p : m)
{
memset(ini,0,sizeof ini);
auto pi = p.second;
bool flag=0;
ll cos=0;
for (int i=p.second.first;i<=p.second.second;i++)
{
if (m[a[i]].first<p.second.first && m[a[i]].second>p.second.second)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
if (pi.first>m[a[i]].first)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
if (!ini[a[i]])
{
cos^=a[i];
ini[a[i]]=1;
}
pi.second= max(m[a[i]].second,pi.second);
}
if (flag) continue;
v[pi.first].push_back(make_pair(pi.second,cos));
}
int j=0;
for (int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
for (auto j : v[i])
d[j.first]= max(d[j.first],d[i]+j.second);
/*for (auto j : v[i])
cout<<i<<" "<<j.first<<" "<<j.second<<endl;*/
d[i+1]=max(d[i+1],d[i]);
}
cout<<d[n+1];
}
D. Vladik and Favorite Game
题面
This is an interactive problem.
Vladik has favorite game, in which he plays all his free time.
Game field could be represented as n × m matrix which consists of cells of three types:
- «.» — normal cell, player can visit it.
- «F» — finish cell, player has to finish his way there to win. There is exactly one cell of this type.
- «*» — dangerous cell, if player comes to this cell, he loses.
Initially player is located in the left top cell with coordinates (1, 1).
Player has access to 4 buttons "U", "D", "L", "R", each of them move player up, down, left and right directions respectively.
But it’s not that easy! Sometimes friends play game and change functions of buttons. Function of buttons "L" and "R" could have been swapped, also functions of buttons "U" and "D" could have been swapped. Note that functions of buttons can be changed only at the beginning of the game.
Help Vladik win the game!
题意
交互题目,感觉比C要简单很多
先bfs一个可行路径出来,然后就跟着走,如果走了以后没效果(原地不动),那就反着走
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
string d;
char a[110][110];
int vis[110][110];
string moves[]={"L","R","U","D"};
int dx[]={0,0,-1,1};
int dy[]={-1,1,0,0};
string ans;
string newans;
queue<pair<int,int> > q;
queue<string> qs;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>d;
for (int o=1;o<=m;o++) a[i][o]=d[o-1];
}
q.push(make_pair(1,1));
qs.push("");
while (!q.empty())
{
int xx=q.front().first;
int yy=q.front().second;
q.pop();
string now=qs.front();qs.pop();
for (int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
if (xx+dx[k]>n || xx+dx[k]<1) continue;
if (yy+dy[k]>m || yy+dy[k]<1) continue;
if (vis[xx+dx[k]][yy+dy[k]]) continue;
if (a[xx+dx[k]][yy+dy[k]]!='*')
{
vis[xx+dx[k]][yy+dy[k]]=1;
q.push(make_pair(xx+dx[k],yy+dy[k]));
qs.push(now+moves[k]);
if (a[xx+dx[k]][yy+dy[k]]=='F')
{
ans=now+moves[k];
}
}
if (ans!="") break;
}
if (ans!="") break;
}
if (ans=="") return 0;
//cout<<ans<<endl;
int nowx=1;
int nowy=1;
int x,y;
bool flag1=0;
bool flag2=0;
for (int i=0;i<ans.size();i++)
{
cout<<ans[i]<<endl;
fflush(stdout);
cin>>x>>y;
if (x==nowx && y==nowy && (ans[i]=='L' || ans[i]=='R') && !flag1)
{
flag1=1;
newans.clear();
for (int o=0;o<ans.size();o++)
{
if (ans[o] == 'R') newans.push_back('L');
else if (ans[o] == 'L') newans.push_back('R');
else newans.push_back(ans[o]);
}
//cout<<newans<<endl;
ans=newans;
i--;
}
else if (x==nowx && y==nowy && (ans[i]=='U' || ans[i]=='D') && !flag2)
{
flag2=1;
newans.clear();
for (int o=0;o<ans.size();o++)
{
if (ans[o] == 'U') newans.push_back('D');
else if (ans[o] == 'D') newans.push_back('U');
else newans.push_back(ans[o]);
}
//cout<<newans<<endl;
ans=newans;
i--;
}
nowx=x;
nowy=y;
}
}
E. Vladik and Entertaining Flags
题面
In his spare time Vladik estimates beauty of the flags.
Every flag could be represented as the matrix n × m which consists of positive integers.
Let's define the beauty of the flag as number of components in its matrix. We call component a set of cells with same numbers and between any pair of cells from that set there exists a path through adjacent cells from same component. Here is the example of the partitioning some flag matrix into components:
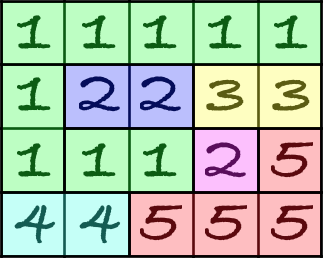
But this time he decided to change something in the process. Now he wants to estimate not the entire flag, but some segment. Segment of flag can be described as a submatrix of the flag matrix with opposite corners at (1, l) and (n, r), where conditions 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ m are satisfied.
Help Vladik to calculate the beauty for some segments of the given flag.
题意
给你一个矩形,和几个询问,问从l,r之间的列形成的矩形,的消消乐块数是多少
我很诡异的解释qwq
这题跟之前做到的atcoder题目很类似,下次一起补完
代码
//
比赛总结
这场本来感觉是要掉rating掉很多的,原因有很多方面,一个是C看错题目了,导致没写出来。
然后D搜索的时候,想着搜一条最短路,导致超时,很不应该。
E题感觉算是种套路,atcoder里面的感觉更加凶残一点。
话说我Atcoder就没做过2题以上。。
比赛链接
http://codeforces.com/contest/811
Codeforces Round#416 Div.2的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)(A,思维题,暴力,B,思维题,暴力)
A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:stand ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) C. Vladik and Memorable Trip
http://codeforces.com/contest/811/problem/C 题意: 给出一行序列,现在要选出一些区间来(不必全部选完),但是相同的数必须出现在同一个区间中,也就是说该数要么 ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/811/problem/D 题目: D. Vladik and Favorite Game time limit per test 2 ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) A+B
A. Vladik and Courtesy 2 seconds 256 megabytes At regular competition Vladik and Valera won a and ...
- Codeforces Round #416(Div. 2)-811A.。。。 811B.。。。 811C.dp。。。不会
CodeForces - 811A A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 meg ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) B. Vladik and Complicated Book
B. Vladik and Complicated Book time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)A B C 水 暴力 dp
A. Vladik and Courtesy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stand ...
- 【分类讨论】【spfa】【BFS】Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game
那个人第一步肯定要么能向下走,要么能向右走.于是一定可以判断出上下是否对调,或者左右是否对调. 然后他往这个方向再走一走就能发现一定可以再往旁边走,此时就可以判断出另一个方向是否对调. 都判断出来以后 ...
- 【动态规划】 Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) C. Vladik and Memorable Trip
划分那个序列,没必要完全覆盖原序列.对于划分出来的每个序列,对于某个值v,要么全都在该序列,要么全都不在该序列. 一个序列的价值是所有不同的值的异或和.整个的价值是所有划分出来的序列的价值之和. ...
随机推荐
- C#按制定的环境编译替换不出对应的配置项的解决措施。
1. 比如选择的 编译或者发布 环境是 QA ,但是QA里面配置的 替换节点 实际并没有被替换 解决方案: 在项目文件.csproj中最底部加入一下代码,应该成功.成功将QA的配置节点 替换掉默认的 ...
- Windows Server 2008 MetaFile设置占用内存限制
最近遇到Windows Server 2008服务器内存持续飙升,48G内存用了99%,查看任务管理器的进程,也没发现具体哪个进程用的内存比较大? 于是,在网上找了了一个查看内存的工具RamMap,具 ...
- git 分支强制删除
添加一个新功能时,你肯定不希望因为一些实验性质的代码,把主分支搞乱了,所以,每添加一个新功能,最好新建一个feature分支,在上面开发,完成后,合并,最后,删除该feature分支. 现在,你终于接 ...
- [转] initrd详解
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/leaven/archive/2010/01/07/1641324.html 在Linux操作系统中,有一项特殊的功能——初始化内存盘INITRD( ...
- 07. pt-fifo-split
iostat -dxm 1 42 1>iostat.log 2>&1 ---------------------------------------- #!/bin/bash of ...
- holiday(假期)_题解
holiday(假期) —— 一道妙题(codevs3622) Description 经过几个月辛勤的工作,FJ 决定让奶牛放假.假期可以在1…N 天内任意选择一段(需要连续),每一天都有一个享 ...
- QT学习之路(1):彩票绝对不中模拟器
//============================================//绝对不中,彩票开奖模拟器#include "mainwindow.h"#includ ...
- mysqli_query数据库有数据,查不出来
MySQLDB.class.php <?php /** * 数据库操作工具类 */ class MySQLDB { // 定义相关属性 private $host;// 主机地址 private ...
- Java界面编程—事件监听机制
组件首先要先注册事件处理器,当用户单击组件.移动鼠标或者敲击键盘时都会产生事件(Event),一旦有时间发生,应用程序就会做出对该事件的响应,这些组件就是事件源(Event source). 接受.解 ...
- 我的MVP呢?
Ladies and gentelmen, welcome the MVP of NBA 16-2017 Season:... 呃,等下,好像哪里不对.那是因为,我要说的MVP根本就不是Most Va ...
