Android Relative Layout 安卓相对布局详解
思维导图可在幕布找到
1. 基础
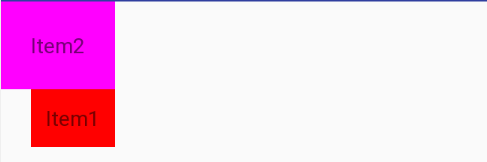
如果在相对布局里,控件没有指明相对位置,则默认都是在相对布局的左上角:
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF00FF"
android:padding="20dp"
android:text="Item2"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:text="Item1"/>

gravity
gravity属性用来设置容器内组件的对齐方式
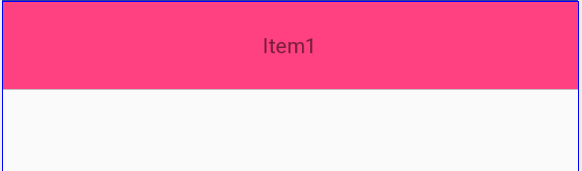
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="#FF4081"
android:text="Item1" />
效果为
2. 根据兄弟控件定位
2.1 相对兄弟组件的位置
android:layout_above:// 参考的兄弟控件上边
android:layout_below:// 参考的兄弟控件下边
android:layout_toLeftOf // 参考的兄弟控件的左边
android:layout_toRightOf // 参考的兄弟控件右边
代码示例
android:layout_below等属性通过制定控件的id来选择需要参考的兄弟组件,即@id/firstText:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/firstText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF0000 "
android:text="firstText" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/rightText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/firstText"
android:text="rightText" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/bottomText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FF00"
android:layout_below="@id/firstText"
android:text="bottomText" />
显示的效果为

2.2 对齐相对组件
对齐兄弟相对组件的有四个属性,为android:layout_align${方向}
android:layout_alignTop // 对齐参考组件的上边界
android:layout_alignBottom // 对齐参考组件的下边界
android:layout_alignLeft // 对齐参考组件的左边界
android:layout_alignRight // 对齐参考组件的右边界
android:layout_alignTop等属性同样是通过制定控件的ID来设置参考的组件的边界线:
代码示例1
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF00FF"
android:padding="20dp"
android:text="Item2"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_below="@id/item1"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/item1"
android:text="Item1"/>
效果为
代码实例2
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF00FF"
android:padding="20dp"
android:text="Item3"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:padding="10dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/item3"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/item3"
android:text="Item4"/>
效果为

3. 根据父控件定位
3.1 与父控件的四个边缘对齐
与父控件的边缘对齐的属性由android:layout_alignParent${方向}组成
android:layout_alignParentTop // 顶部对齐于父控件
android:layout_alignParentBottom // 底部对齐于父控件
android:layout_alignParentLeft // 左对齐于父控件
android:layout_alignParentRight // 右对齐于父控件
需要注意的是,这些属性是通过布尔值来设置是否对齐于父控件的某个方向的:
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="first"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
效果为:

除此之外还有layout_alignParentLeft、layout_alignParentTop
3.2 对齐至父控件的中央
对齐至父控件中央的属性可以用来设置居中的布局位置:
android:layout_centerHorizontal // 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical // 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInParent // 水平且垂直居中,处于父组件的正中央位置
代码示例
同样,这些属性也是通过设置的值也是布尔类型:
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="centerHorizontal"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="centerVertical"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="centerInParent"
android:textSize="15dp"
android:background="#0000FF"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
效果为:

4. 其他
对齐至控件的基准线
<TextView
android:id="@+id/firstText"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="100dp"
android:text="Hello" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/firstText"
android:text="World" />
如果没有使用对齐基准线,那么当Hello的字体的大于world时,world则无法和hello在同一基准线上:

通过给world的TextView添加layout_alignBaseline属性来实现对齐firstText控件的基准线:
android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/firstText"
效果为:

5. 实例
用相对布局来完成经典的梅花布局
<!--中央-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img1"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:src="@drawable/pic1"/>
<!--右边-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/img1"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:src="@drawable/pic2"/>
<!--左边-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/img1"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:src="@drawable/pic3"/>
<!--上边-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_above="@+id/img1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:src="@drawable/pic4"/>
<!--下边-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/img1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:src="@drawable/pic5"/>
效果图为

参考资料
Android Relative Layout 安卓相对布局详解的更多相关文章
- 【Android开发】交互界面布局详解
原文:http://android.eoe.cn/topic/summary Android 的系统 UI 为构建您自己的应用提供了基础的框架.主要包括主屏幕 (Home Screen).系统 UI ...
- Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数)
[Android布局学习系列] 1.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解一 2.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数) 3.And ...
- Android布局详解之一:FrameLayout
原创文章,如有转载,请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/yihui823/article/details/6702273 FrameLayout是最简单的布局了.所有放在布局里的 ...
- Android 布局详解
Android 布局详解 1.重用布局 当一个布局文件被多处使用时,最好<include>标签来重用布局. 例如:workspace_screen.xml的布局文件,在另一个布局文件中被重 ...
- Android View 的绘制流程之 Layout 和 Draw 过程详解 (二)
View 的绘制系列文章: Android View 的绘制流程之 Measure 过程详解 (一) Android View 绘制流程之 DecorView 与 ViewRootImpl 在上一篇 ...
- Android开发重点难点1:RelativeLayout(相对布局)详解
前言 啦啦啦~博主又推出了一个新的系列啦~ 之前的Android开发系列主要以完成实验的过程为主,经常会综合许多知识来写,所以难免会有知识点的交杂,给人一种混乱的感觉. 所以博主推出“重点难点”系列, ...
- Android安卓书籍推荐《Android驱动开发与移植实战详解》下载
百度云下载地址:点我 Android凭借其开源性.优异的用户体验和极为方便的开发方式,赢得了广大用户和开发者的青睐,目前已经发展成为市场占有率很高的智能手机操作系统. <Android驱动开发与 ...
- [置顶]
xamarin android toolbar(踩坑完全入门详解)
网上关于toolbar的教程有很多,很多新手,在使用toolbar的时候踩坑实在太多了,不好好总结一下,实在浪费.如果你想学习toolbar,你肯定会去去搜索androd toolbar,既然你能看到 ...
- 安卓集成发布详解(二)gradle
转自:http://frank-zhu.github.io/android/2015/06/15/android-release_app_build_gradle/ 安卓集成发布详解(二) 15 Ju ...
随机推荐
- java ant 编译打包build.xml完整配置范例
java ant 编译打包build.xml完整配置范例 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <p ...
- Azure Redis 缓存使用注意事项与排查问题文档整理
StackExchange.Redis 使用名为 synctimeout 的配置设置进行同步操作,该设置的默认值为 1000 毫秒. 如果同步调用未在规定时间内完成,StackExchange.Red ...
- Apache本地配置虚拟域名
转载+修改 例:虚拟域名为 aaa.com 端口为默认80 index.html所在目录 D:/wamp/www/web 不用解析域名,使用虚假的域名也可以 apache安装完默认是不开启虚拟服务器 ...
- linux 文件句柄数查看命令
当你的服务器在大并发达到极限时,就会报出“too many open files”. 查看线程占句柄数ulimit -a 输出如下:core file size (blocks, -c) 0data ...
- 使用Unicode字符实现换行
要让inline元素换行可以使用Unicode字符实现: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> < ...
- git第六节---git 远程仓库
远程分支类似于本地分支,是指向远程仓库中的文件的指针. 1.远程分支抓取 @git fetch origin dev :拉取远程dev内容 fetch不会对本地仓库内容进行更新,只更新远端commit ...
- 浅析 JavaScript 链式调用
对$函数你已经很熟悉了.它通常返回一个html元素或一个html元素的集合,如下: function$(){ var elements = []; for(vari=0,len=arguments.l ...
- 微信公众号支付回调页面处理asp.net
1.在商家微信商户通中配置回调url 2.在提交订单时传入的回调页面中获取支付成功后或支付失败后的参数,对订单进行处理 public partial class gzpayCallback : Sys ...
- [转]DevOps解决方案-腾讯云
本文转自:https://cloud.tencent.com/solution/devops 什么是 DevOps? DevOps 集文化理念.实践和工具于一身,可以提高企业高速交付应用程序和服务 ...
- C# 两个独立exe程序直接通信
从别的地方转载过来,转载地址不详细,需要知道的话,可以自动去搜索,我不是原作者. 我之前主要是用工序内存做过两个进程的通信. 两个独立的exe程序之间如何完成通信呢?首先想到的办法是利用生成文件的方法 ...
