关于KNN的python3实现
关于KNN,有幸看到这篇文章,写的很好,这里就不在赘述。直接贴上代码了,有小的改动。(原来是python2版本的,这里改为python3的,主要就是print)
环境:win7 32bit + spyder + anaconda3.5
一、初阶
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 6 16:09:00 2016 @author: Administrator
""" #Input:
# newInput:待测的数据点(1xM)
# dataSet:已知的数据(NxM)
# labels:已知数据的标签(1xM)
# k:选取的最邻近数据点的个数
#
#Output:
# 待测数据点的分类标签
# from numpy import * # creat a dataset which contain 4 samples with 2 class
def createDataSet():
# creat a matrix: each row as a sample
group = array([[1.0, 0.9], [1.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.2], [0.0, 0.1]])
labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B']
return group, labels #classify using KNN
def KNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # row number
# step1:calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps):Constract an array by repeating A reps times
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet
squreDiff = diff**2
squreDist = sum(squreDiff, axis=1) # sum if performed by row
distance = squreDist ** 0.5 #step2:sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance) classCount = {}
for i in range(k):
# choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] #step4:count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount,
# get() will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
#step5:the max vote class will return
maxCount = 0
for k, v in classCount.items():
if v > maxCount:
maxCount = v
maxIndex = k return maxIndex # test dataSet, labels = createDataSet() testX = array([1.2, 1.0])
k = 3
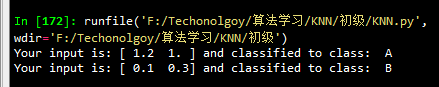
outputLabel = KNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print("Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel) testX = array([0.1, 0.3])
k = 3
outputLabel = KNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print("Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel)
运行结果:
二、进阶
用到的手写识别数据库资料在这里下载。关于资料的介绍在上面的博文也已经介绍的很清楚了。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 6 16:09:00 2016 @author: Administrator
""" #Input:
# newInput:待测的数据点(1xM)
# dataSet:已知的数据(NxM)
# labels:已知数据的标签(1xM)
# k:选取的最邻近数据点的个数
#
#Output:
# 待测数据点的分类标签
# from numpy import * #classify using KNN
def KNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # row number
# step1:calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps):Constract an array by repeating A reps times
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet
squreDiff = diff**2
squreDist = sum(squreDiff, axis=1) # sum if performed by row
distance = squreDist ** 0.5 #step2:sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance) classCount = {}
for i in range(k):
# choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] #step4:count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount,
# get() will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
#step5:the max vote class will return
maxCount = 0
for k, v in classCount.items():
if v > maxCount:
maxCount = v
maxIndex = k return maxIndex # convert image to vector
def img2vector(filename):
rows = 32
cols = 32
imgVector = zeros((1, rows * cols))
fileIn = open(filename)
for row in range(rows):
lineStr = fileIn.readline()
for col in range(cols):
imgVector[0, row * 32 + col] = int(lineStr[col]) return imgVector # load dataSet
def loadDataSet():
## step 1: Getting training set
print("---Getting training set...")
dataSetDir = 'F:\\Techonolgoy\\算法学习\\KNN\\进阶\\'
trainingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits') # load the training set
numSamples = len(trainingFileList) train_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
train_y = []
for i in range(numSamples):
filename = trainingFileList[i] # get train_x
train_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits/%s' % filename) # get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
train_y.append(label) ## step 2: Getting testing set
print("---Getting testing set...")
testingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'testDigits') # load the testing set
numSamples = len(testingFileList)
test_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
test_y = []
for i in range(numSamples):
filename = testingFileList[i] # get train_x
test_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'testDigits/%s' % filename) # get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
test_y.append(label) return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y # test hand writing class
def testHandWritingClass():
## step 1: load data
print("step 1: load data...")
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = loadDataSet() ## step 2: training...
print("step 2: training...")
pass ## step 3: testing
print("step 3: testing...")
numTestSamples = test_x.shape[0]
matchCount = 0
for i in range(numTestSamples):
predict = KNNClassify(test_x[i], train_x, train_y, 3)
if predict == test_y[i]:
matchCount += 1
accuracy = float(matchCount) / numTestSamples ## step 4: show the result
print("step 4: show the result...")
print('The classify accuracy is: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100)) testHandWritingClass()
运行结果:

关于KNN的python3实现的更多相关文章
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(一)KNN
一.KNN概述 K-(最)近邻算法KNN(k-Nearest Neighbor)是数据挖掘分类技术中最简单的方法之一.它具有精度高.对异常值不敏感的优点,适合用来处理离散的数值型数据,但是它具有 非常 ...
- Python3 k-邻近算法(KNN)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Fri Dec 29 13:13:44 2017 @author: markli " ...
- 机器学习实战python3 K近邻(KNN)算法实现
台大机器技法跟基石都看完了,但是没有编程一直,现在打算结合周志华的<机器学习>,撸一遍机器学习实战, 原书是python2 的,但是本人感觉python3更好用一些,所以打算用python ...
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(二)KNN实现简单OCR
一.前言 1.ocr概述 OCR (Optical Character Recognition,光学字符识别)是指电子设备(例如扫描仪或数码相机)检查纸上打印的字符,通过检测暗.亮的模式确定其形状,然 ...
- kNN.py源码及注释(python3.x)
import numpy as npimport operatorfrom os import listdirdef CerateDataSet(): group = np.array( ...
- KNN识别图像上的数字及python实现
领导让我每天手工录入BI系统中的数据并判断数据是否存在异常,若有异常点,则检测是系统问题还是业务问题.为了解放双手,我决定写个程序完成每天录入管理驾驶舱数据的任务.首先用按键精灵录了一套脚本把系统中的 ...
- 机器学习实战笔记(Python实现)-01-K近邻算法(KNN)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 本系列文章为<机器 ...
- 第2章KNN算法笔记_函数classify0
<机器学习实战>知识点笔记目录 K-近邻算法(KNN)思想: 1,计算未知样本与所有已知样本的距离 2,按照距离递增排序,选前K个样本(K<20) 3,针对K个样本统计各个分类的出现 ...
- 机器学习--kNN算法识别手写字母
本文主要是用kNN算法对字母图片进行特征提取,分类识别.内容如下: kNN算法及相关Python模块介绍 对字母图片进行特征提取 kNN算法实现 kNN算法分析 一.kNN算法介绍 K近邻(kNN,k ...
随机推荐
- js页面刷新之实现框架内外刷新(整体、局部)
这次总结的是框架刷新: 框架内外的按钮均可以定义网页重定向, 框架内部页面的按钮可以实现局部刷新, 框架外部页面的按钮可以实现整页刷新. 代码如下(两个html页面): <!--主界面index ...
- if,else语句的运用
1.求解一元二次方程 Console.WriteLine("求解一元二次方程:a*x*x+b*x+c=0"); Console.Write("请输入 a="); ...
- HDU 4944 FSF’s game 一道好题
FSF’s game Time Limit: 9000/4500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- [poj2777] Count Color (线段树 + 位运算) (水题)
发现自己越来越傻逼了.一道傻逼题搞了一晚上一直超时,凭啥子就我不能过??? 然后发现cin没关stdio同步... Description Chosen Problem Solving and Pro ...
- [问题2014A02] 复旦高等代数 I(14级)每周一题(第四教学周)
[问题2014A02] 求下列 \(n\) 阶行列式的值, 其中 \(a_i\neq 0\,(i=1,2,\cdots,n)\): \[ |A|=\begin{vmatrix} 0 & a_ ...
- 利用backtrace和objdump进行分析挂掉的程序
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/hanchaoman/article/details/5583457 汇编不懂,先把方法记下来. glibc为我们提供了此类能够dump栈内容的函数簇, ...
- C#类遍历
foreach语句的基本用法大家都应该知道,就是对对象进行遍历,取出相应的属性名称或属性值.Foreach(for)用法在js中使用很简单,基本如下: var objA={name:'mayday', ...
- Div中高度自适应增长方法
<html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; char ...
- 【CSU1812】三角形和矩形 【半平面交】
检验半平面交的板子. #include <stdio.h> #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define gg p ...
- golang csv问题
go语言自带的有csv文件读取模块,看起来好像不错,今天玩玩,也算是系统学习go语言的一部分--^_^ 一.写csv文件 函数: func NewWriter(w io.Writer) *Writer ...
