JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(映射Map)
一:映射Map分类
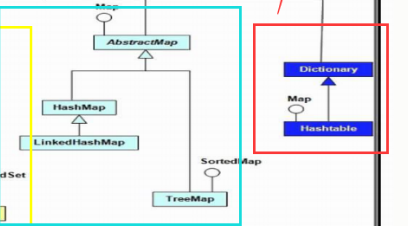
二:Hashtable(同步,慢,数据量小)
–K-V对,K和V都不允许为null
–同步,多线程安全
–无序的
–适合小数据量
–主要方法:clear, contains/containsValue, containsKey, get,
put,remove, size
(一)基本使用方法
Hashtable<Integer,String> ht=new Hashtable<Integer,String>();
//ht.put(1, null); //编译不报错 运行时报错
//ht.put(null, "das");
ht.put(, "adad");
ht.put(, "adsdad");
ht.put(, "adadge");
//进行判断是否含有数据
System.out.println(ht.contains("adad"));
System.out.println(ht.containsValue("adad")); //contains和containsValue一样
System.out.println(ht.containsKey());
//进行数据获取
System.out.println(ht.get());
//进行更新
ht.put(, ""); //按照键,更新值
//进行移除
System.out.println(ht.containsKey());
ht.remove();
System.out.println(ht.containsKey());
//获取大小
System.out.println(ht.size());
true
true
true
adadge
true
false
(二)遍历方法
public static void traverseByEntry(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("=======Entry迭代器遍历=======");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer,String>> iter=ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> ent= iter.next();
key = ent.getKey();
value=ent.getValue();
System.out.println(key+":"+value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("=======KeySet迭代器遍历=======");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter=ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
value=ht.get(key);
System.out.println(key+":"+value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
//Enumeration只在Hashtable中用到了,后面废弃不用
public static void traverseByKeyEnumeration(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("=======KeyEnumeration迭代器遍历=======");
Integer key;
String value;
Enumeration<Integer> keys=ht.keys(); //一次性获取所有的key值,
while(keys.hasMoreElements()) {
key = keys.nextElement();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
(三)性能测试:数据量越大,差距越小
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
ht.put(i, "aaa");
} //进行遍历
traverseByEntry(ht);
traverseByKeySet(ht);
traverseByKeyEnumeration(ht);
=======Entry迭代器遍历=======
13470233纳秒
=======KeySet迭代器遍历=======
8841551纳秒
=======KeyEnumeration迭代器遍历=======
4933705纳秒
三:HashMap(不支持同步,快,数据量大)
–K-V对,K和V都允许为nul
–不同步,多线程不安全
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));
–无序的
–主要方法:clear, containsValue, containsKey, get, put,remove, size
(一)基本使用方法一致
HashMap<Integer,String> hm =new HashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(, "aaa");
hm.put(, "bbb");
hm.put(, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey());
System.out.println(hm.get()); hm.put(, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get()); hm.remove();
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); hm.clear();
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
(二)遍历方法除了没有Enumeration,其他一致
public static void traverseByEntry(HashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
traverseByEntry
public static void traverseByKeySet(HashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
traverseByKeySet
四:Properties (同步,文件形式,数据量小)
–继承于Hashtable
–可以将K-V对保存在文件
–适用于数据量少的配置文件
–继承自Hashtable的方法:clear, contains/containsValue, containsKey,
get, put,remove, size
–从文件加载的load方法, 写入到文件中的store方法
–获取属性 getProperty ,设置属性setProperty
(一)使用方法
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties; //关于Properties类常用的操作
public class PropertiesTest {
//根据Key读取Value
public static String GetValueByKey(String filePath, String key) {
Properties pps = new Properties();
try {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream (new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in); //所有的K-V对都加载了
String value = pps.getProperty(key);
//System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
return value; }catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
} //读取Properties的全部信息
public static void GetAllProperties(String filePath) throws IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in); //所有的K-V对都加载了
Enumeration en = pps.propertyNames(); //得到配置文件的名字 while(en.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) en.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
//System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
} } //写入Properties信息
public static void WriteProperties (String filePath, String pKey, String pValue) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if(!file.exists())
{
file.createNewFile();
}
Properties pps = new Properties(); InputStream in = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
pps.load(in); //先加载原来的文件键值对,在其基础上进行设置,再写入
//调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。使用 getProperty 方法提供并行性。
//强制要求为属性的键和值使用字符串。返回值是 Hashtable 调用 put 的结果。
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
pps.setProperty(pKey, pValue);
//以适合使用 load 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式,
//将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流
pps.store(out, "Update " + pKey + " name");
out.close();
} public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException{
System.out.println("写入Test.properties================");
WriteProperties("Test.properties","name", ""); System.out.println("加载Test.properties================");
GetAllProperties("Test.properties"); System.out.println("从Test.properties加载================");
String value = GetValueByKey("Test.properties", "name");
System.out.println("name is " + value);
}
}
五:LinkedHashMap和TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
–基于双向链表的维持插入顺序的HashMap
TreeMap
–基于红黑树的Map,可以根据key的自然排序或者compareTo方法进行排序输出
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry; public class LinkedHashMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> hm =new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(, "aaa");
hm.put(, "bbb");
hm.put(, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey());
System.out.println(hm.get()); hm.put(, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get()); hm.remove();
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); //hm.clear();
//System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); System.out.println("遍历开始=================="); Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束=================="); LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> hm2 =new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
} public static void traverseByEntry(LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
} public static void traverseByKeySet(LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
LinkedHashMapTest
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry; public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer,String> hm =new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(, null);
//hm.put(null, "abc"); 编译没错,运行报空指针异常
hm.put(, "aaa");
hm.put(, "bbb");
hm.put(, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey());
System.out.println(hm.get()); hm.put(, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get()); //hm.remove(2);
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); //hm.clear();
//System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); System.out.println("遍历开始=================="); Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束=================="); TreeMap<Integer,String> hm2 =new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
} public static void traverseByEntry(TreeMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
} public static void traverseByKeySet(TreeMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
TreeMapTest
六:总结
–HashMap是最常用的映射结构
–如需要排序,考虑LinkedHashMap和TreeMap
–如需要将K-V存储为文件,可采用Properties类
JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(映射Map)的更多相关文章
- 《Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10》学习笔记 第5章 继承
<Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10>学习笔记 第5章 继承 目录 <Java核心技术·卷Ⅰ:基础知识(原版10>学习笔记 第5章 继承 5.1 类.超类和子类 5.1 ...
- Java核心技术 卷1 基础知识-第一天
基本数据类型 java是一种强数据类的的语言 共有8种基本数据类型 其中: 整型4种 int(4字节) short(2字节) long(8字节) byte(1字节) java中整型的范围与机器无关 长 ...
- [Java面试三]JavaWeb基础知识总结.
1.web服务器与HTTP协议 Web服务器 l WEB,在英语中web即表示网页的意思,它用于表示Internet主机上供外界访问的资源. l Internet上供外界访问的Web资源分为: • 静 ...
- Java中浮点数的基础知识
偶然查看Math.round的JDK public static int round(float a) { if (a != 0x1.fffffep-2f) // greatest float val ...
- JAVA面试题相关基础知识
1.面向对象的特征有哪些方面 ①抽象: 抽象就是忽略一个主题中与当前目标无关的那些方面,以便更充分地注意与当前目标有关的方面.抽象并不打算了解全部问题,而只是选择其中的一部分,暂时不用部分细节 ...
- Java学习之旅基础知识篇:数据类型及流程控制
经过开篇对Java运行机制及相关环境搭建,本篇主要讨论Java程序开发的基础知识点,我简单的梳理一下.在讲解数据类型之前,我顺便提及一下Java注释:单行注释.多行注释以及文档注释,这里重点强调文档注 ...
- java 程序运行的基础知识【Java bytecode】
聊聊文字,写一篇关于 java 基础知识的博文. JVM 线程栈 到 函数运行 每一个JVM线程来说启动的时候都会创建一个私有的线程栈.一个jvm线程栈用来存储栈帧,jvm线程栈和C语言中的栈很类似, ...
- Java学习1——计算机基础知识
本文包含了一些计算机基础知识:计算机组成:Windows常用快捷键:DOS常用命令:计算机语言发展史.
- Java学习之旅基础知识篇:面向对象之封装、继承及多态
Java是一种面向对象设计的高级语言,支持继承.封装和多态三大基本特征,首先我们从面向对象两大概念:类和对象(也称为实例)谈起.来看看最基本的类定义语法: /*命名规则: *类名(首字母大写,多个单词 ...
- Java Script 学习笔记 -- 基础知识
Java script 概述 java Script 的简介 JavaScript一种直译式脚本语言,是一种动态类型.弱类型.基于原型的语言,内置支持类型.它的解释器被称为JavaScript引擎,为 ...
随机推荐
- Android InputType
转载: http://blog.csdn.net/wei_zhi/article/details/50094503 在Android开发过程中,我们经常使用到EditText控件,并且会根据各种需求设 ...
- 图灵机器人API接口
调用图灵API接口实现人机交互 流程一: 注册 图灵机器人官网: http://www.tuling123.com/ 第一步: 先注册, 然后创建机器人, 拿到一个32位的key 编码方式 UTF-8 ...
- 数据库SQL SELECT查询的工作原理
一般开发员只会应用SQL的四条经典语句:select,insert,delete,update.但是我从来没有研究过它们的工作原理,这篇我想说一说select在数据库中的工作原理. B/S架构中最经典 ...
- 进程间的通讯————IPC
""" IPC 指的是进程间通讯 之所以开启子进程 肯定需要它帮我们完成任务 很多情况下 需要将数据返回给父进程 然而 进程内存是物理隔离的 解决方案: 1.将共享数据放 ...
- django.core.exceptions.AppRegistryNotReady: Apps aren't loaded yet.
报错现象 django 启动的时候报错 django.core.exceptions.AppRegistryNotReady: Apps aren't loaded yet. 报错解决 记不清是我有毛 ...
- Linux iptables设置
先举例子说明,若服务器网卡: eth0 10.10.0.100 eth0:0 10.10.0.200 eth0:1 10.10.0.201 eth0:2 10.10.0.202 只允许10.10.0. ...
- AtCoder ExaWizards2019题解
AtCoder ExaWizards2019题解 AtCoder (因为代码直接用模板写的,可能有点冗长) A.Regular Triangle 给你三根棍子的长度,问你能否用他们组成等边三角形. 什 ...
- 【转】C++命名空间 namespace的作用和使用解析
一. 为什么需要命名空间(问题提出) 命名空间是ANSIC++引入的可以由用户命名的作用域,用来处理程序中 常见的同名冲突. 在 C语言中定义了3个层次的作用域,即文件(编译单元).函数和复合语句.C ...
- NOIP2012疫情控制(二分答案+树上贪心)
H 国有n个城市,这 n个城市用n-1条双向道路相互连通构成一棵树,1号城市是首都,也是树中的根节点. H国的首都爆发了一种危害性极高的传染病.当局为了控制疫情,不让疫情扩散到边境城市(叶子节点所表示 ...
- 第四篇-以ConstraintLayout进行Android界面设计
此文章基于第三篇. 一.新建一个layout.xml文件,创建方法不再赘述,在Design界面右击LinearLayout,点击Convert LinearLayout to ConstraintLa ...
