OpenStack Networking – FlatManager and FlatDHCPManager
最好的分析FlatDHCPManager的源文,有机会把这篇翻译了
===========================
Over time, networking in OpenStack has been evolving from a simple, barely usable model, to one that aims to support full customer isolation. To address different user needs, OpenStack comes with a handful of “network managers”. A network manager defines the network topology for a given OpenStack deployment. As of the current stable “Essex” release of OpenStack, one can choose from three different types of network managers: FlatManager, FlatDHCPManager, VlanManager. I’ll discuss the first two of them here.
FlatManager and FlatDHCPManager have lots in common. They both rely on the concept of bridged networking, with a single bridge device. Let’s consider her the example of a multi-host network; we’ll look at a single-host use case in a subsequent post.
For each compute node, there is a single virtual bridge created, the name of which is specified in the Nova configuration file using this option:
flat_network_bridge=br100
All the VMs spawned by OpenStack get attached to this dedicated bridge.
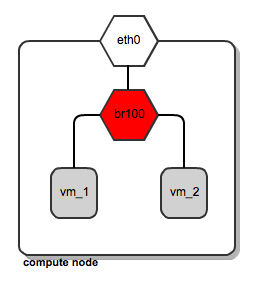
Network bridging on OpenStack compute node
This approach (single bridge per compute node) suffers from a common known limitation of bridged networking: a linux bridge can be attached only to a signle physical interface on the host machine (we could get away with VLAN interfaces here, but this is not supported by FlatDHCPManager and FlatManager). Because of this, there is no L2 isolation between hosts. They all share the same ARP broadcast domain.
The idea behind FlatManager and FlatDHCPManager is to have one “flat” IP address pool defined throughout the cluster. This address space is shared among all user instances, regardless of which tenant they belong to. Each tenant is free to grab whatever address is available in the pool.
FlatManager
FlatManager provides the most primitive set of operations. Its role boils down just to attaching the instance to the bridge on the compute node. By default, it does no IP configuration of the instance. This task is left for the systems administrator and can be done using some external DHCP server or other means.

FlatManager network topology
FlatDHCPManager
FlatDHCPManager plugs a given instance into the bridge, and on top of that provides a DHCP server to boot up from.
On each compute node:
- the network bridge is given an address from the “flat” IP pool
- a dnsmasq DHCP server process is spawned and listens on the bridge interface IP
- the bridge acts as the default gateway for all the instances running on the given compute node
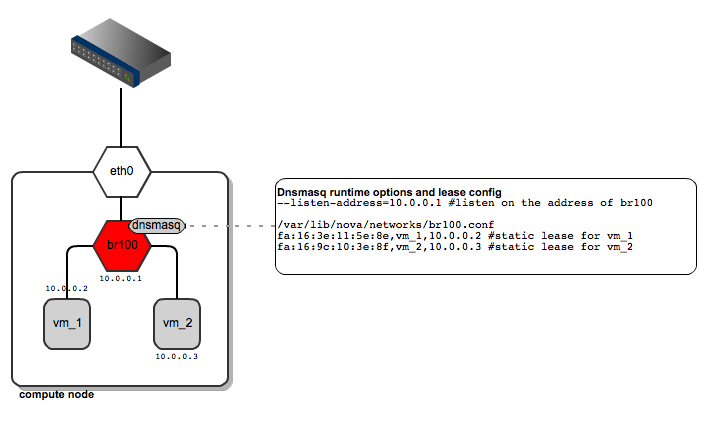
FlatDHCPManager – network topology
As for dnsmasq, FlatDHCPManager creates a static lease file per compute node to guarantee the same IP address for the instance over time. The lease file is constructed based on instance data from the Nova database, namely MAC, IP and hostname. The dnsmasq server is supposed to hand out addresses only to instances running locally on the compute node. To achieve this, instance data to be put into DHCP lease file are filtered by the ‘host’ field from the ‘instances’ table. Also, the default gateway option in dnsmasq is set to the bridge’s IP address. On the diagram below you san see that it will be given a different default gateway depending on which compute node the instance lands.
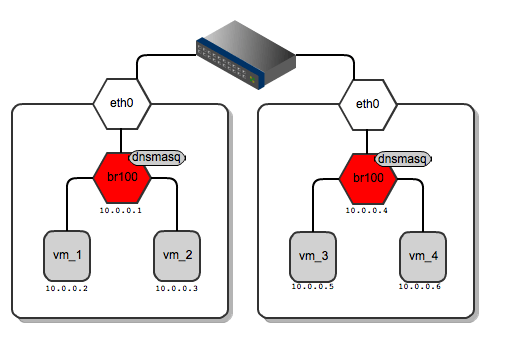
Network gateways for instances running on different compute nodes
Below I’ve shown the routing table from vm_1 and for vm_3 – each of them has a different default gateway:
root@vm_1:~# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
root@vm_3:~# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 10.0.0.4 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
By default, all the VMs in the “flat”
network can see one another regardless of which tenant they belong to.
One can enforce instance isolation by applying the following flag in nova.conf:
allow_same_net_traffic=False
This configures IPtables policies to
prevent any traffic between instances (even inside the same tenant),
unless it is unblocked in a security group.
From practical standpoint, “flat”
managers seem to be usable for homogenous, relatively small, internal
corporate clouds where there are no tenants at all, or their number is
very limited. Typically, the usage scenario will be a dynamically
scaled web server farm or an HPC cluster. For this purpose it is usually
sufficient to have a single IP address space where IP address
management is offloaded to some central DHCP server or is managed in a
simple way by OpenStack’s dnsmasq. On the other hand, flat networking
can struggle with scalability, as all the instances share the same L2
broadcast domain.
These issues (scalability +
multitenancy) are in some ways addressed by VlanManager, which will be
covered in an upcoming blog posts.
OpenStack Networking – FlatManager and FlatDHCPManager的更多相关文章
- OpenStack Networking overview
原文地址:http://docs.openstack.org/newton/install-guide-ubuntu/neutron-concepts.html Networking service ...
- OpenStack Networking
今天的数据中心网络比以往不论什么时候包括的设备都要多,比如server.网络设备.存储系统和安全设备等.这当中有非常多被近一步划分为多个虚拟机和虚拟网络.IP地址的数量.路由配置和安全规则能够迅速达到 ...
- gophercloud openstack networking 源码分析
1.network 部分 // Package networks contains functionality for working with Neutron network resources. ...
- Openstack组件部署 — Networking service_安装并配置Controller Node
目录 目录 前文列表 前提条件 网络环境 完成下面的步骤以创建数据库 创建service credentials服务凭证 创建Neutron的API Endpoints 配置自服务网络 安装网络组件 ...
- openstack组件手动部署整合
preface:当你完全且正确的配置好整个OpenStack ENV 你将能看到的和体验到的!!! 我们先来看看简单效果吧,祝君能在这条路上走的更远,更好;
- 8.OpenStack网络组件
添加网络组件 安装和配置控制器节点 创建数据库 mysql -uroot -ptoyo123 CREATE DATABASE neutron; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON neut ...
- 完整部署CentOS7.2+OpenStack+kvm 云平台环境(1)--基础环境搭建
公司在IDC机房有两台很高配置的服务器,计划在上面部署openstack云平台虚拟化环境,用于承载后期开发测试和其他的一些对内业务.以下对openstack的部署过程及其使用做一详细介绍,仅仅依据本人 ...
- CentOS RDO方式快速安装OpenStack
一.了解RDO RDO是什么? RDO是红帽Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform的社区版,类似RHEL和Fedora,RHEV和oVirt这样的关系. ...
- 发现 OpenStack: 架构、功能和交互
原文:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/cloud/library/cl-openstack-overview/index.html OpenStack 是由 ...
随机推荐
- Redis系列-php怎么通过redis扩展使用redis
From: http://blog.csdn.net/love__coder/article/details/8691679 通过前面几篇blog,我们应该对redis有个大致的认识,这里再讲解下,p ...
- linux任务计划 chkconfig工具 systemd管理服务 unit介绍 target介绍
linux任务计划 任务计划:特定时间备份数据,重启服务,shell脚本,单独的命令等等. 任务计划配置文件:cat /etc/crontab [root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/c ...
- Vue-router路由判断页面未登录跳转到登录页面
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { if (to.matched.some(record => record.meta.requireAuth) ...
- WebGL 着色器语言(GLSL ES)
1.类型转换内置函数 转换/函数/描述 转换为整形数/int(float)/将浮点数的小数部分删去,转换为整形数(比如,将3.14转换为3) 转换为整形数/intl(bool)/true被转换为1,f ...
- multiselect2side:jQuery多选列表框插件
http://blog.csdn.net/rosanu_blog/article/details/8550723 http://www.bkjia.com/jQuery/449193.html < ...
- Go语言图形界面开发:Go版GTK
https://www.cnblogs.com/tennysonsky/p/8433888.html package main import ( "os" "github ...
- git同时提交到两个仓库
有时候一个项目,希望既提交到oschina又提交到公司内网的gitlab,或者是github什么的. 使用git remote -v 查看当前git的远程仓库. 添加一个远程仓库 git remote ...
- 定时器Enable Disable控制
问题:定时器如何控制它一会可用一会不可用,根据某个业务需求,比如:一个控制台程序扫描表中某个条件的数据,处理数据,控制台分布式部署,当主机宕机后,从机扫描定时器需要可用,当主机复活后,从机的扫描定时器 ...
- SpringBoot------注解把配置文件自动映射到属性和实体类
1.映射到属性 package top.ytheng.demo.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Valu ...
- 开发还是应该使用linux
这几天在Windows系统下,安装了几个IDE,体量大,4.5个G,启动速度慢,占用系统资源多,并且最难受的是,这些IDE的限制性太强,只能按照UI给定的规则来操作,例如现在手中有一个已完成的项目,用 ...
