机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测的案例 1.datetime.datetime.datetime(将字符串转为为日期格式) 2.pd.get_dummies(将文本标签转换为one-hot编码) 3.rf.feature_importances_(研究样本特征的重要性) 4.fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) 对标签进行翻转
在这个案例中:
1. datetime.datetime.strptime(data, '%Y-%m-%d') # 由字符串格式转换为日期格式
2. pd.get_dummies(features) # 将数据中的文字标签转换为one-hot编码形式,增加了特征的列数
3. rf.feature_importances 探究了随机森林样本特征的重要性,对其进行排序后条形图
4.fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) # 对图中的X轴标签进行60的翻转
代码:
第一步:数据读取,通过.describe() 查看数据是否存在缺失值的情况
第二步:对年月日特征进行字符串串接,使用datetime.datetime.strptime(), 获得日期格式作为X轴的标签
第三步:对里面的几个温度特征做条形图,fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60)设置日期标签的旋转角度,plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight') 设置画风
第四步:使用pd.get_dummies(features) 将特征中文字类的标签转换为one-hot编码形式,增加了特征的维度
第五步:提取数据的特征和样本标签,转换为np.array格式
第六步:使用train_test_split 将特征和标签分为训练集和测试集
第七步:构建随机森林模型进行模型的训练和预测
第八步:进行随机森林的可视化
第九步:使用rf.feature_importances_计算出各个特征的重要性,进行排序,然后做条形图
第十步:根据第九步求得的特征重要性的排序结果,我们选用前两个特征建立模型和预测
第十一步:对模型的预测结果画直线图plot和散点图scatter,对于plot我们需要根据时间进行排序
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime # 第一步提取数据
features = pd.read_csv('data/temps.csv')
print(features.shape)
print(features.columns)
# 使用feature.describe() # 观察数据是否存在缺失值
print(features.describe()) # 第二步:我们将year,month,day特征组合成一个dates特征,作为画图的标签值比如2016-02-01 years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day'] # datetime.datetime.strptime() 将字符串转换为日期类型
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
print(dates[0:5]) # 第三步进行画图操作
# 设置画图风格
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight') # 使用plt.subplots画出多副图
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, figsize=(12, 12))
# 使得标签进行角度翻转
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) ax1.plot(dates, features['temp_2'], linewidth=4)
ax1.set_xlabel(''), ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'), ax1.set_title('pred two temperature') ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'], linewidth=4)
ax2.set_xlabel(''), ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'), ax1.set_title('pred temperature') ax3.plot(dates, features['actual'], linewidth=4)
ax3.set_xlabel(''), ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'), ax1.set_title('today temperature') ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'], linewidth=4)
ax4.set_xlabel(''), ax1.set_ylabel('temperature'), ax1.set_title('friend temperature') plt.show()
# 第四步:pd.get_dummies() 来对特征中不是数字的特征进行one-hot编码
features = pd.get_dummies(features) # 第五步:把数据分为特征和标签 y = np.array(features['actual'])
X = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
feature_names = list(X.columns)
X = np.array(X) # 第六步: 使用train_test_split 对数据进行拆分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42) # 第七步:建立随机森林的模型进行预测
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000)
rf.fit(train_X, train_y)
pred_y = rf.predict(test_X) # MSE指标通过真实值-预测值的绝对值求平均值
MSE = round(abs(pred_y - test_y).mean(), 2) # MAPE指标通过 1 - abs(误差)/真实值来表示
error = abs(pred_y - test_y) MAPE = round(np.mean((1 - error / test_y) * 100), 2) print(MSE, MAPE) # 第八步进行随机森林的可视化展示 # from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
# import pydot #pip install pydot
#
# # Pull out one tree from the forest
# tree = model.estimators_[5]
#
# # Export the image to a dot file
# export_graphviz(tree, out_file = 'tree.dot', feature_names = feature_names, rounded = True, precision = 1)
#
# # Use dot file to create a graph
# (graph, ) = pydot.graph_from_dot_file('tree.dot')
# graph.write_png('tree.png');
# print('The depth of this tree is:', tree.tree_.max_depth)
#
# # 限制树的深度重新画图
# rf_small = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=10, max_depth = 3, random_state=42)
# rf_small.fit(train_x,train_y)
#
# # Extract the small tree
# tree_small = rf_small.estimators_[5]
#
# # Save the tree as a png image
# export_graphviz(tree_small, out_file = 'small_tree.dot', feature_names = feature_names, rounded = True, precision = 1)
#
# (graph, ) = pydot.graph_from_dot_file('small_tree.dot')
#
# graph.write_png('small_tree.png') #第九步:探讨随机森林特征的重要性
features_importances = rf.feature_importances_
features_importance_pairs = [(feature_name, features_importance) for feature_name, features_importance in
zip(feature_names, features_importances)]
# 对里面的特征进行排序操作
features_importance_pairs = sorted(features_importance_pairs, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
features_importance_name = [name[0] for name in features_importance_pairs]
features_importance_val = [name[1] for name in features_importance_pairs] figure = plt.figure()
plt.bar(range(len(features_importance_name)), features_importance_val, orientation='vertical')
plt.xticks(range(len(features_importance_name)), features_importance_name, rotation='vertical')
plt.show()
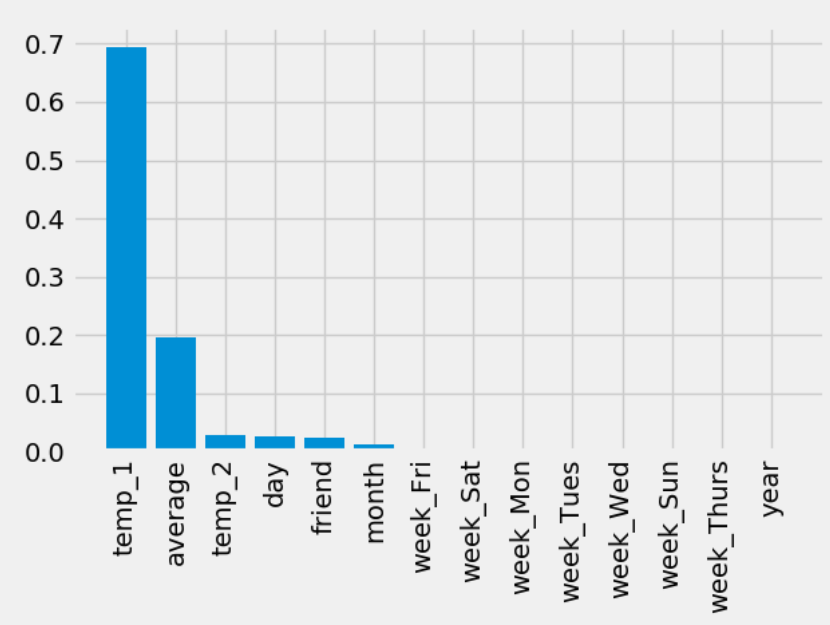
# 第十步:通过上述的作图,我们可以发现前两个特征很重要,因此我们只选用前两个特征作为训练数据
X = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
y = np.array(features['actual'])
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
train_x_two = train_x[['temp_1', 'average']].values
test_x_two = test_x[['temp_1', 'average']].values
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=1000)
rf.fit(train_x_two, train_y)
pred_y = rf.predict(test_x_two)
# MSE指标通过真实值-预测值的绝对值求平均值
MSE = round(abs(pred_y - test_y).mean(), 2)
# MAPE指标通过 1 - abs(误差)/真实值来表示
error = abs(pred_y - test_y)
MAPE = round(np.mean((1 - error / test_y) * 100), 2)
print(MSE, MAPE)
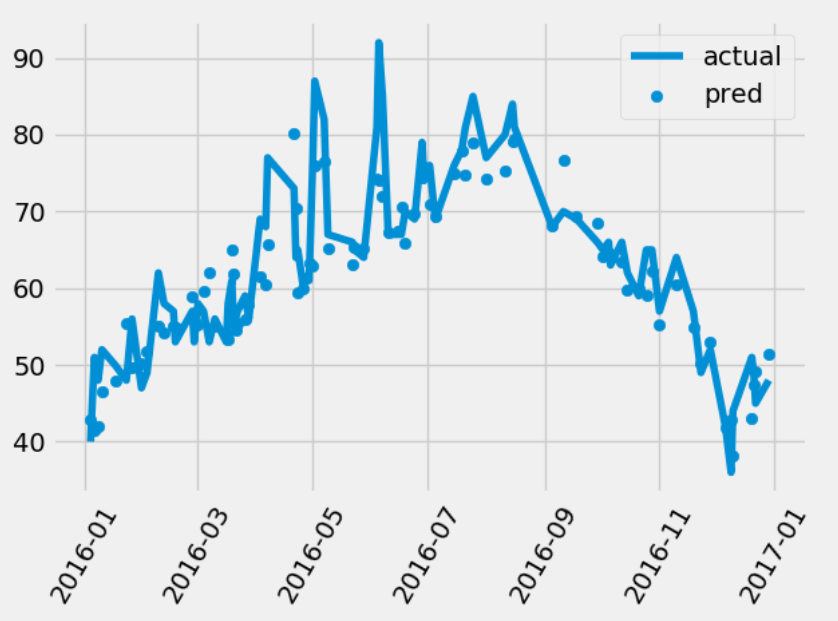
# 我们发现只使用两个特征也是具有差不多的结果,因此我们可以通过减少特征来增加反应的时间
fig = plt.figure()
years = test_x['year']
months = test_x['month']
days = test_x['day']
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
print(dates[0:5])
# 对真实的数据进行排序,因为需要画plot图
dates_test_paris = [(date, test_) for date, test_ in zip(dates, test_y)]
dates_test_paris = sorted(dates_test_paris, key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)
dates_test_data = [x[0] for x in dates_test_paris]
dates_test_val = [x[1] for x in dates_test_paris]
plt.plot(dates_test_data, dates_test_val, label='actual')
plt.scatter(dates, pred_y, label='pred')
plt.xticks(rotation='')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测的案例 1.datetime.datetime.datetime(将字符串转为为日期格式) 2.pd.get_dummies(将文本标签转换为one-hot编码) 3.rf.feature_importances_(研究样本特征的重要性) 4.fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=60) 对标签进行翻转的更多相关文章
- 机器学习入门-随机森林温度预测-增加样本数据 1.sns.pairplot(画出两个关系的散点图) 2.MAE(平均绝对误差) 3.MAPE(准确率指标)
在上一个博客中,我们构建了随机森林温度预测的基础模型,并且研究了特征重要性. 在这个博客中,我们将从两方面来研究数据对预测结果的影响 第一方面:特征不变,只增加样本的数据 第二方面:增加特征数,增加样 ...
- 机器学习入门-随机森林预测温度-不同参数对结果的影响调参 1.RandomedSearchCV(随机参数组的选择) 2.GridSearchCV(网格参数搜索) 3.pprint(顺序打印) 4.rf.get_params(获得当前的输入参数)
使用了RamdomedSearchCV迭代100次,从参数组里面选择出当前最佳的参数组合 在RamdomedSearchCV的基础上,使用GridSearchCV在上面最佳参数的周围选择一些合适的参数 ...
- 100天搞定机器学习|Day56 随机森林工作原理及调参实战(信用卡欺诈预测)
本文是对100天搞定机器学习|Day33-34 随机森林的补充 前文对随机森林的概念.工作原理.使用方法做了简单介绍,并提供了分类和回归的实例. 本期我们重点讲一下: 1.集成学习.Bagging和随 ...
- 使用基于Apache Spark的随机森林方法预测贷款风险
使用基于Apache Spark的随机森林方法预测贷款风险 原文:Predicting Loan Credit Risk using Apache Spark Machine Learning R ...
- Python机器学习笔记——随机森林算法
随机森林算法的理论知识 随机森林是一种有监督学习算法,是以决策树为基学习器的集成学习算法.随机森林非常简单,易于实现,计算开销也很小,但是它在分类和回归上表现出非常惊人的性能,因此,随机森林被誉为“代 ...
- 【机器学习】随机森林RF
随机森林(RF, RandomForest)包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定.通过自助法(boot-strap)重采样技术,不断生成训练样本和测试样本,由训练样本 ...
- 100天搞定机器学习|Day33-34 随机森林
前情回顾 机器学习100天|Day1数据预处理 100天搞定机器学习|Day2简单线性回归分析 100天搞定机器学习|Day3多元线性回归 100天搞定机器学习|Day4-6 逻辑回归 100天搞定机 ...
- paper 84:机器学习算法--随机森林
http://www.cnblogs.com/wentingtu/archive/2011/12/13/2286212.html中一些内容 基础内容: 这里只是准备简单谈谈基础的内容,主要参考一下别人 ...
- 机器学习技法-随机森林(Random Forest)
课程地址:https://class.coursera.org/ntumltwo-002/lecture 重要!重要!重要~ 一.随机森林(RF) 1.RF介绍 RF通过Bagging的方式将许多个C ...
随机推荐
- selinux操作
setenforce 0 关闭SELinux setenforce 1 临时打开SELinux getenforce 查看SELinux状态 永久关闭SELinux : # cat /etc/seli ...
- nodejs express 学习
nodejs的大名好多人应该是听过的,而作为nodejs web 开发的框架express 大家也应该比较熟悉. 记录一下关于express API 的文档: express() 创建express ...
- svn分支开发注意事项
1.切换的时候最好查看本文件的是主干上的还是分支上的, 单击右键,点击属性,可以看到以下图片,其中"URL"就可以 看到是主干还是分支 2.切换到分支 点击切换后就选择要切换到的路 ...
- 01.ubuntu14.04安装HI3518EV200 SDK的过程
转载,侵删 1.海思SDK安装编译 Hi3518EV200_SDK是基于Hi3518EV200_DMEB的软件开发包,包含了在Linux相关应用开发时使用的各种工具及其源代码,是用户开发中最基本的软件 ...
- 【转】每天一个linux命令(54):ping命令
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2013/03/06/2945407.html Linux系统的ping命令是常用的网络命令,它通常用来测试与目标主 ...
- 【转】每天一个linux命令(28):tar命令
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2012/11/30/2795656.html 通过SSH访问服务器,难免会要用到压缩,解压缩,打包,解包等,这时候 ...
- 【转】每天一个linux命令(22):find 命令的参数详解
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2012/11/16/2773289.html find一些常用参数的一些常用实例和一些具体用法和注意事项. 1.使 ...
- Mfs+drbd+keepalived实现mfs系统高可用
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_53c654720102wo1k.html Moosefs分布式文件系统是一个易用的系统,但其只有在Pro版中提供了master的高可用方 ...
- JSP中的MVC
如下图
- 使用纯生js操作cookie
前段时间做项目的时候要使用js操作cookie,jquery也有相应的插件,不过还是觉得纯生的js比较好,毕竟不依赖jq. //获得coolie 的值 function cookie(name) { ...
