POJ - 2528Mayor's posters (离散化+线段树区间覆盖)
- Every candidate can place exactly one poster on the wall.
- All posters are of the same height equal to the height of the wall; the width of a poster can be any integer number of bytes (byte is the unit of length in Bytetown).
- The wall is divided into segments and the width of each segment is one byte.
- Each poster must completely cover a contiguous number of wall segments.
They have built a wall 10000000 bytes long (such that there is enough place for all candidates). When the electoral campaign was restarted, the candidates were placing their posters on the wall and their posters differed widely in width. Moreover, the candidates started placing their posters on wall segments already occupied by other posters. Everyone in Bytetown was curious whose posters will be visible (entirely or in part) on the last day before elections.
Your task is to find the number of visible posters when all the posters are placed given the information about posters' size, their place and order of placement on the electoral wall.
Input
i and ri which are the number of the wall segment occupied by the left end and the right end of the i-th poster, respectively. We know that for each 1 <= i <= n, 1 <= l
i <= ri <= 10000000. After the i-th poster is placed, it entirely covers all wall segments numbered l
i, l
i+1 ,... , ri.
Output
The picture below illustrates the case of the sample input.
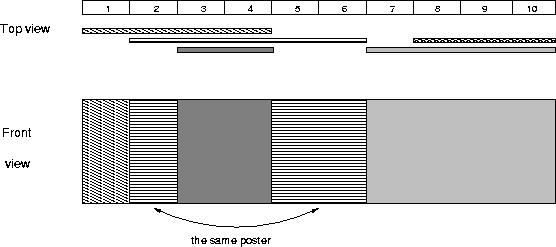
Sample Input
1
5
1 4
2 6
8 10
3 4
7 10
Sample Output
4
这道题我是参考大佬博客的,一开始我对这道题完全不知道怎么下手,百度了一下,发现是用离散化+线段树,其实我一开始还不知离散化是什么,又去学习了离散化再来写这道题; 下面是博主的分析:
题意:贴海报,海报可以覆盖,会给出你每张海报的长款,然后问你最后还能看到几张海报。
我做这道题遇到的坑点,第一点离散化,第二点线段树用的不熟练
解法:离散化,如下面的例子(题目的样例),因为单位1是一个单位长度,将下面的
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 10
— — — — — — — —
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
离散化 X[1] = 1; X[2] = 2; X[3] = 3; X[4] = 4; X[5] = 6; X[6] = 7; X[7] = 8,X[8] = 10;
于是将一个很大的区间映射到一个较小的区间之中了,然后再对每一张海报依次更新在宽度为1~8的墙上(用线段树),
最后统计不同颜色的段数。但是只是这样简单的离散化是错误的,
如三张海报为:1~10 1~4 6~10离散化时 X[ 1 ] = 1, X[ 2 ] = 4, X[ 3 ] = 6, X[ 4 ] = 10
第一张海报时:墙的1~4被染为1;
第二张海报时:墙的1~2被染为2,3~4仍为1
;第三张海报时:墙的3~4被染为3,1~2仍为2。
最终,第一张海报就显示被完全覆盖了,于是输出2,但实际上明显不是这样,正确输出为3。
新的离散方法为:在相差大于1的数间加一个数,例如在上面1 4 6 10中间加5(算法中实际上1,4之间,6,10之间都新增了数的)
X[ 1 ] = 1, X[ 2 ] = 4, X[ 3 ] = 5, X[ 4 ] = 6, X[ 5 ] = 10
这样之后,第一次是1~5被染成1;第二次1~2被染成2;第三次4~5被染成3最终,1~2为2,3为1,4~5为3,于是输出正确结果3。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std; const int MAXN = ;
int T;
int N;
int x[MAXN] , y[MAXN];
int lisan[MAXN*];
bool vis[MAXN*];
int tree[MAXN*]; //离散化要开16倍空间
int size ;
int num = ;
int tmp;
int ans ;
void pushdown(int rt )
{
tree[rt*] = tree[rt];
tree[rt*+] = tree[rt];
tree[rt] = ;
}
void Update(int tpx ,int tpy ,int value, int l ,int r ,int rt)
{
if(l>=tpx&&r<=tpy)
{
tree[rt] = value;
return;
}
if(tree[rt]!=)
pushdown(rt);
int m = (l+r)/; if(tpx<=m)
{
Update(tpx,tpy,value,l,m,rt*);
}
if(tpy>m)
{
Update(tpx,tpy,value,m+,r,rt*+);
} }
void Query(int l ,int r ,int rt)
{
if(tree[rt]!=)
{
if(!vis[tree[rt]])
{
ans++;
vis[tree[rt]] = ;
}
return ;
}
if(l==r)
return;
if(tree[rt]!=)
{
pushdown(rt);
}
int m = (l+r)/;
Query(l,m,rt*);
Query(m+,r,rt*+);
} int main()
{
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&N);
num = ;
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
for(int i = ; i <= N ;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x[i],&y[i]);
lisan[num++] = x[i];
lisan[num++] = y[i];
}
sort(lisan,lisan+num); //排序后离散化
size = unique(lisan,lisan+num)-lisan; //获得离散化后的长度
tmp = size;
for(int i = ; i < tmp ;i++)
{
if(lisan[i]-lisan[i-]>) //这样离散化才正确;见上面分析;
{
lisan[size++] = lisan[i-] + ;
}
}
sort(lisan,lisan+size); //再排序一次
for(int i = ; i <= N ;i++ )
{
int tpx = lower_bound(lisan,lisan+size,x[i])-lisan;//获取位置
int tpy = lower_bound(lisan,lisan+size,y[i])-lisan;
Update(tpx,tpy,i,,size-,);
}
ans = ;
Query(,size-,);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
POJ - 2528Mayor's posters (离散化+线段树区间覆盖)的更多相关文章
- Mayor's posters POJ - 2528 线段树区间覆盖
//线段树区间覆盖 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algori ...
- HDU 4509 湫湫系列故事——减肥记II(线段树-区间覆盖 或者 暴力技巧)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4509 题目大意: 中文意义,应该能懂. 解题思路: 因为题目给的时间是一天24小时,而且还有分钟.为了解题方便, ...
- [NOI2015] 软件包管理器【树链剖分+线段树区间覆盖】
Online Judge:Luogu-P2146 Label:树链剖分,线段树区间覆盖 题目大意 \(n\)个软件包(编号0~n-1),他们之间的依赖关系用一棵含\(n-1\)条边的树来描述.一共两种 ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters 【区间离散化+线段树区间更新&&查询变形】
任意门:http://poj.org/problem?id=2528 Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total S ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters (线段树+区间覆盖+离散化)
题意: 一共有n张海报, 按次序贴在墙上, 后贴的海报可以覆盖先贴的海报, 问一共有多少种海报出现过. 题解: 因为长度最大可以达到1e7, 但是最多只有2e4的区间个数,并且最后只是统计能看见的不同 ...
- POJ-2528 Mayor's posters(线段树区间更新+离散化)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2528 https://www.luogu.org/problem/UVA10587 Description The citizens of By ...
- POJ 2528 ——Mayor's posters(线段树+区间操作)
Time limit 1000 ms Memory limit 65536 kB Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand t ...
- POJ-2528 Mayor's posters (线段树区间更新+离散化)
题目分析:线段树区间更新+离散化 代码如下: # include<iostream> # include<cstdio> # include<queue> # in ...
- 【POJ】2528 Mayor's posters ——离散化+线段树
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Description The citizens of Bytetown, A ...
随机推荐
- POJ3249(DAG上的dfs)
Test for Job Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10567 Accepted: 2482 Des ...
- NB-LOT 科普
最全科普!你一定要了解的NB-IoT 2017-06-19 21:04物联网/操作系统/科普 工信部下发通知推动150万NB-IoT基站落地.NB-IoT汹涌而来.很多网友要求雇佣军科普一篇NB-Io ...
- 修改rbd指定位置的数据
标签(空格分隔): ceph,ceph实验 --- 我们通过查看index为0x01的小4M文件,得知了file2.txt这个文件内容在这个4M内保存的位置为0x9000,因为0x01前面还有一个4M ...
- git教程(远程仓库和管理分支)
在github上新建了一个仓库,然后相与本地的仓库联系起来 $ Git remote add origin https://github.com/liona329/learngit.git fatal ...
- Git命令之创建版本
安装 安装好Git后,将会在桌面生成 这样一个图标 运行后将会是类似控制台程序的黑色窗口,其中mingw64(参考百度百科).这样的话就可以在输入命令 例如 :git 见到下图有详细的用法表示成功否则 ...
- 使用cython把python编译so
1.需求 为了保证线上代码安全和效率,使用python编写代码,pyc可直接反编译,于是把重要代码编译so文件 2.工作 2.1 安装相关库: pip install cython yum insta ...
- 第三章 Java程序优化(待续)
字符串优化处理 String对象及其特点 String对象是java语言中重要的数据类型,但它并不是Java的基本数据类型.在C语言中,对字符串的处理最通常的做法是使用char数组,但这种方式的弊端是 ...
- 玩school 学习sql server 查询的网站
http://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/sql_like.asp
- UML设计九种图例
一.作为一种建模语言,UML的定义包括UML语义和UML表示法两个部分. UML语义:描述基于UML的精确元模型定义. UML表示法:定义UML符号的表示法,为开发者或开发工具使用这些图形符号和文本语 ...
- Excel向数据库插入数据和数据库向Excel导出数据
为了熟悉java里工作簿的相关知识点,所以找了“Excel向数据库插入数据和数据库向Excel导出数据”的功能来实现. 注意事项:1,mysql数据库: 2,需要导入的jar包有 jxl.jar,my ...
