【Codeforces715C&716E】Digit Tree 数学 + 点分治
C. Digit Tree
ZS the Coder has a large tree. It can be represented as an undirected connected graph of n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1edges between them. There is a single nonzero digit written on each edge.
One day, ZS the Coder was bored and decided to investigate some properties of the tree. He chose a positive integer M, which iscoprime to 10, i.e. 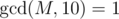 .
.
ZS consider an ordered pair of distinct vertices (u, v) interesting when if he would follow the shortest path from vertex u to vertex v and write down all the digits he encounters on his path in the same order, he will get a decimal representaion of an integer divisible by M.
Formally, ZS consider an ordered pair of distinct vertices (u, v) interesting if the following states true:
- Let a1 = u, a2, ..., ak = v be the sequence of vertices on the shortest path from u to v in the order of encountering them;
- Let di (1 ≤ i < k) be the digit written on the edge between vertices ai and ai + 1;
- The integer
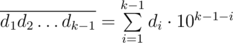 is divisible by M.
is divisible by M.
Help ZS the Coder find the number of interesting pairs!
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers, n and M (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 109, 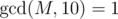 ) — the number of vertices and the number ZS has chosen respectively.
) — the number of vertices and the number ZS has chosen respectively.
The next n - 1 lines contain three integers each. i-th of them contains ui, vi and wi, denoting an edge between vertices ui and vi with digit wi written on it (0 ≤ ui, vi < n, 1 ≤ wi ≤ 9).
Output
Print a single integer — the number of interesting (by ZS the Coder's consideration) pairs.
Examples
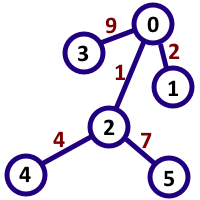
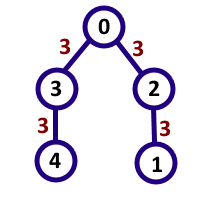
6 7
0 1 2
4 2 4
2 0 1
3 0 9
2 5 7
7
5 11
1 2 3
2 0 3
3 0 3
4 3 3
8
Note
In the first sample case, the interesting pairs are (0, 4), (1, 2), (1, 5), (3, 2), (2, 5), (5, 2), (3, 5). The numbers that are formed by these pairs are 14, 21, 217, 91, 7, 7, 917 respectively, which are all multiples of 7. Note that (2, 5) and (5, 2) are considered different.
In the second sample case, the interesting pairs are (4, 0), (0, 4), (3, 2), (2, 3), (0, 1), (1, 0), (4, 1), (1, 4), and 6 of these pairs give the number 33 while 2 of them give the number 3333, which are all multiples of 11.
Solution
一道比较好想好写的点分治
点分治显然,考虑如何计算复合的路径条数。
对于每个点我们维护两个值$Dig[x],Dig'[x]$,表示重心到这个点的路径组成的数,以及这个点到重心组成的数
这样对于一个点对$<u,v>$我们可以知道他们的$Dig[u],Dig[v],Dig'[u],Dig'[v]$,那么他们所组成的数就是$Dig'[u]*10^{k}+Dig[v]$
这个$k$我们发现,就相当于是$deep[u]$,知道这些就有思路搞了
题目的要求就是$Dig<u,v>mod M=0$也就可以转化成$Dig'[u]*10^{deep[u]}+Dig[v]\equiv 0(modM)$
然后整理一下就可以得到$Dig'[u]\equiv -Dig[v]*\frac{1}{10^{deep[u]}}$
然后用map存一下式子右边,对于一个点,它对答案的贡献就是hash表里的$Dig'[u]$的数量
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
inline int read()
{
int x=,f=; char ch=getchar();
while (ch<'' || ch>'') {if (ch=='-') f=-; ch=getchar();}
while (ch>='' && ch<='') {x=x*+ch-''; ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
#define MAXN 100010
int N,M;
map<LL,LL>hash;
LL ans;
namespace Math
{
LL power[MAXN],Inv[MAXN];
inline LL Gcd(LL a,LL b) {if (!b) return a; else return Gcd(b,a%b);}
inline void ExGcd(LL a,LL b,LL &x,LL &y) {if (!b) {x=,y=; return;} ExGcd(b,a%b,y,x); y-=(a/b)*x;}
inline LL inv(LL X) {LL x,y; ExGcd(X,M,x,y); return (x%M+M)%M;}
inline LL Pow(LL x,LL y) {LL re=; for (LL i=y; i; i>>=,x=x*x%M) if (i&) re=re*x%M; return re;}
}
using namespace Math;
namespace TreeDivide
{
struct EdgeNode{int next,to,val;}edge[MAXN<<];
int head[MAXN],cnt=;
inline void AddEdge(int u,int v,int w) {cnt++; edge[cnt].to=v; edge[cnt].next=head[u]; head[u]=cnt; edge[cnt].val=w;}
inline void InsertEdge(int u,int v,int w) {AddEdge(u,v,w); AddEdge(v,u,w);}
int size[MAXN],f[MAXN],visit[MAXN],root,deep[MAXN],Sz;
LL Dig[MAXN];
inline void Getroot(int x,int last)
{
size[x]=,f[x]=;
for (int i=head[x]; i; i=edge[i].next)
if (!visit[edge[i].to] && edge[i].to!=last)
{
Getroot(edge[i].to,x);
size[x]+=size[edge[i].to];
f[x]=max(f[x],size[edge[i].to]);
}
f[x]=max(f[x],Sz-f[x]);
if (f[x]<f[root]) root=x;
}
inline void DFS(int now,int last)
{
LL D=(((M-Dig[now])+M)%M*Inv[deep[now]])%M; hash[D]++;
for (int i=head[now]; i; i=edge[i].next)
if (edge[i].to!=last && !visit[edge[i].to])
deep[edge[i].to]=deep[now]+,
Dig[edge[i].to]=(Dig[now]*%M+edge[i].val)%M,
DFS(edge[i].to,now);
}
inline LL Get(int now,int last)
{
LL re=hash[Dig[now]];
for (int i=head[now]; i; i=edge[i].next)
if (edge[i].to!=last && !visit[edge[i].to])
Dig[edge[i].to]=(edge[i].val*power[deep[now]]%M+Dig[now])%M,
deep[edge[i].to]=deep[now]+,
re+=Get(edge[i].to,now);
return re;
}
inline void Divide(int now)
{
visit[now]=;
hash.clear(); hash[]--;
Dig[now]=0LL,deep[now]=;
DFS(now,);
ans+=Get(now,);
for (int i=head[now]; i; i=edge[i].next)
if (!visit[edge[i].to])
hash.clear(),hash[]--,
Dig[edge[i].to]=edge[i].val%M,deep[edge[i].to]=,
DFS(edge[i].to,now),
ans-=Get(edge[i].to,now);
for (int i=head[now]; i; i=edge[i].next)
if (!visit[edge[i].to])
Sz=size[edge[i].to],f[root=]=N,
Getroot(edge[i].to,now),Divide(root);
}
}
using namespace TreeDivide;
int main()
{
N=read(),M=read();
for (int x,y,z,i=; i<=N-; i++) x=read()+,y=read()+,z=read(),InsertEdge(x,y,z);
for (int i=; i<=N; i++) power[i]=Pow(,i),Inv[i]=inv(power[i]);
Sz=N; f[root=]=N+;
Getroot(,); Divide(root);
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return ;
}
【Codeforces715C&716E】Digit Tree 数学 + 点分治的更多相关文章
- 【Codeforces 715C】Digit Tree(点分治)
Description 程序员 ZS 有一棵树,它可以表示为 \(n\) 个顶点的无向连通图,顶点编号从 \(0\) 到 \(n-1\),它们之间有 \(n-1\) 条边.每条边上都有一个非零的数字. ...
- CF 716E. Digit Tree [点分治]
题意:一棵树,边上有一个个位数字,走一条路径会得到一个数字,求有多少路径得到的数字可以整除\(P\) 路径统计一般就是点分治了 \[ a*10^{deep} + b \ \equiv \pmod P\ ...
- 【题解】Digit Tree
[题解]Digit Tree CodeForces - 716E 呵呵以为是数据结构题然后是淀粉质还行... 题目就是给你一颗有边权的树,问你有多少路径,把路径上的数字顺次写出来,是\(m\)的倍数. ...
- Codeforces 716 E Digit Tree
E. Digit Tree time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- hdu 4670 Cube number on a tree(点分治)
Cube number on a tree Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/ ...
- 『sumdiv 数学推导 分治』
sumdiv(POJ 1845) Description 给定两个自然数A和B,S为A^B的所有正整数约数和,编程输出S mod 9901的结果. Input Format 只有一行,两个用空格隔开的 ...
- 【POJ1741】Tree(点分治)
[POJ1741]Tree(点分治) 题面 Vjudge 题目大意: 求树中距离小于\(K\)的点对的数量 题解 完全不觉得点分治了.. 简直\(GG\),更别说动态点分治了... 于是来复习一下. ...
- CF716E Digit Tree 点分治
题意: 给出一个树,每条边上写了一个数字,给出一个P,求有多少条路径按顺序读出的数字可以被P整除.保证P与10互质. 分析: 统计满足限制的路径,我们首先就想到了点分治. 随后我们就需要考量,我们是否 ...
- [poj1741][tree] (树/点分治)
Description Give a tree with n vertices,each edge has a length(positive integer less than 1001). Def ...
随机推荐
- 使用用户自定义类型 CLR UDT
一些复合类型进行范式分解是没有必要的,尤其是一些统一模型的情况下 SET NOCOUNT ON DECLARE @i TimeBalance SET @i = CAST(' ...
- Ubuntu16.04LTS国内快速源
一.源文件位置 备份并替换/etc/apt/sources.list的源内容: 二.更改源文件内容 sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list deb http://mirrors.a ...
- 偏移:translate ,旋转:rotate,缩放 scale,不知道什么东东:lineCap 实例
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <head> <meta charset = "utf-8"> <title>canvas</ ...
- qt5.4.0编译错误
error1: 进程"C:\Qt\Qt5.4.0\Tools\QtCreator\bin\jom.exe"退出,退出代码 2 solution:去工具->选项->构建和 ...
- C++11 - 类型推导auto关键字
在C++11中,auto关键字被作为类型自动类型推导关键字 (1)基本用法 C++98:类型 变量名 = 初值; int i = 10; C++11:auto 变量名 = 初值; auto i ...
- 【推荐】CentOS安装vsftpd-3.0.2+安全配置
注:以下所有操作均在CentOS 6.5 x86_64位系统下完成. FTP的登录一般有三种方式,分别是: 匿名用户形式:默认安装的情况下,系统只提供匿名用户访问,只需要输入用户anonymous/f ...
- android 让一个Activity停留几秒后再跳转
有时候我们需要在某个 Activity 停留几秒种,然后再跳到下一个 Activity.那么这个怎么实现呢? 一个方法是可以使用 Thread 的 sleep 函数,这个我们在 用Handler实现线 ...
- 利用mysql-proxy进行mysql数据库的读写分离
实验系统:CentOS 6.6_x86_64 实验前提:防火墙和selinux都关闭 实验说明:本实验共有4台主机,IP分配如拓扑 实验软件:mariadb-10.0.20 mysql-proxy-0 ...
- MongoDb 创建、更新以及删除文档常用命令
mongodb由C++写就,其名字来自humongous这个单词的中间部分,从名字可见其野心所在就是海量数据的处理.关于它的一个最简洁描述为:scalable, high-performance, o ...
- 运用PCA进行降维的好处
运用PCA对高维数据进行降维,有一下几个特点: (1)数据从高维空间降到低维,因为求方差的缘故,相似的特征会被合并掉,因此数据会缩减,特征的个数会减小,这有利于防止过拟合现象的出现.但PCA并不是一种 ...
