格式化输出(%用法和fomat用法)
一:%用法
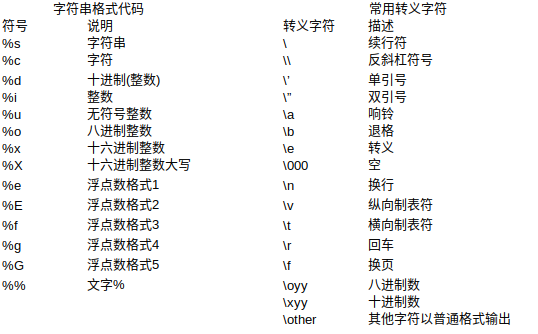
1、整数输出
%o —— oct 八进制
%d —— dec 十进制
%x —— hex 十六进制
print('%o' % 20) #
print('%d' % 20) #
print('%x' % 20) #
2、浮点数输出
%f ——保留小数点后面六位有效数字
%.3f,保留3位小数位
%e ——保留小数点后面六位有效数字,指数形式输出
%.3e,保留3位小数位,使用科学计数法
%g ——在保证六位有效数字的前提下,使用小数方式,否则使用科学计数法
%.3g,保留3位有效数字,使用小数或科学计数法
print('%f' % 1.11) # 默认保留6位小数 1.110000
print('%.1f' % 1.11) # 取1位小数 1.1
print('%e' % 1.11) # 默认6位小数,用科学计数法 1.110000e+00
print('%.3e' % 1.11) # 取3位小数,用科学计数法 1.110e+00
print('%g' % 1111.1111) # 默认6位有效数字 1111.11
print('%.7g' % 1111.1111) # 取7位有效数字 1111.111
print('%.2g' % 1111.1111) # 取2位有效数字,自动转换为科学计数法 1.1e+03
3、字符串输出
%s
%10s——右对齐,占位符10位
%-10s——左对齐,占位符10位
%.2s——截取2位字符串
%10.2s——10位占位符,截取两位字符串
print('%s' % 'hello world') # 字符串输出 hello world
print('%20s' % 'hello world') # 右对齐,取20位,不够则补位 hello world
print('%-20s' % 'hello world') # 左对齐,取20位,不够则补位 hello world
print('%.2s' % 'hello world') # 取2位 he
print('%10.2s' % 'hello world') # 右对齐,取2位 he
print('%-10.2s' % 'hello world') # 左对齐,取2位 he
4、其他
二:format用法
相对基本格式化输出采用‘%’的方法,format()功能更强大,该函数把字符串当成一个模板,通过传入的参数进行格式化,并且使用大括号‘{}’作为特殊字符代替‘%’
1、位置匹配
(1)不带编号,即“{}”
(2)带数字编号,可调换顺序,即“{1}”、“{2}”
(3)带关键字,即“{a}”、“{tom}”
print('{} {}'.format('hello','world')) # 不带字段 hello world
print('{0} {1}'.format('hello','world')) # 带数字编号 hello world
print('{0} {1} {0}'.format('hello','world')) # 打乱顺序 hello world hello
print('{1} {1} {0}'.format('hello','world')) # world world hello
print('{a} {tom} {a}'.format(tom='hello',a='world')) # 带关键字 world hello world
# 通过位置匹配
print('{0}, {1}, {2}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')) # a, b, c
print('{}, {}, {}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')) # 3.1+版本支持 a, b, c
print('{2}, {1}, {0}'.format('a', 'b', 'c')) # c, b, a
print('{2}, {1}, {0}'.format(*'abc')) # 可打乱顺序 c, b, a
print('{0}{1}{0}'.format('abra', 'cad')) # 可重复 abracadabra
# 通过类的属性匹配
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x, self.y = x, y
def __str__(self):
return 'Point({self.x}, {self.y})'.format(self=self)
print(str(Point(4, 2))) # Point(4, 2)
# 通过下标或者key匹配参数
coord = (3, 5)
print('X: {0[0]}; Y: {0[1]}'.format(coord)) # X: 3; Y: 5
a = {'a': 'test_a', 'b': 'test_b'}
print('X: {0[a]}; Y: {0[b]}'.format(a)) # X: test_a; Y: test_b
2、格式转换
'b' - 二进制。将数字以2为基数进行输出。
'c' - 字符。在打印之前将整数转换成对应的Unicode字符串。
'd' - 十进制整数。将数字以10为基数进行输出。
'o' - 八进制。将数字以8为基数进行输出。
'x' - 十六进制。将数字以16为基数进行输出,9以上的位数用小写字母。
'e' - 幂符号。用科学计数法打印数字。用'e'表示幂。
'g' - 一般格式。将数值以fixed-point格式输出。当数值特别大的时候,用幂形式打印。
'n' - 数字。当值为整数时和'd'相同,值为浮点数时和'g'相同。不同的是它会根据区域设置插入数字分隔符。
'%' - 百分数。将数值乘以100然后以fixed-point('f')格式打印,值后面会有一个百分号。
print('{0:b}'.format(3)) #
print('{:c}'.format(20)) #
print('{:d}'.format(20)) #
print('{:o}'.format(20)) #
print('{:x}'.format(20)) #
print('{:e}'.format(20)) # 2.000000e+01
print('{:g}'.format(20.1)) # 20.1
print('{:f}'.format(20)) # 20.000000
print('{:n}'.format(20)) #
print('{:%}'.format(20)) # 2000.000000%
3、format变形用法
# f"xxxx"
# 可在字符串前加f以达到格式化的目的,在{}里加入对象,此为format的另一种形式: a = "hello"
b = "world"
print(f"{a} {b}") name = 'jack'
age = 18
sex = 'man'
job = "IT"
salary = 9999.99 print(f'my name is {name.capitalize()}.') # my name is Jack.
print(f'I am {age:*^10} years old.') # I am ****18**** years old.
print(f'I am a {sex}') # I am a man
print(f'My salary is {salary:10.3f}') # My salary is 9999.990
格式化输出(%用法和fomat用法)的更多相关文章
- python基础_格式化输出(%用法和format用法)(转载)
python基础_格式化输出(%用法和format用法) 目录 %用法 format用法 %用法 1.整数的输出 %o -- oct 八进制%d -- dec 十进制%x -- hex 十六进制 &g ...
- python基础_格式化输出(%用法和format用法)
目录 %用法 format用法 %用法 1.整数的输出 %o —— oct 八进制%d —— dec 十进制%x —— hex 十六进制 1 >>> print('%o' % 2 ...
- 【Python笔记】1、格式化输出(%用法和format用法)
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/fat39/p/7159881.html 一.格式化输出1.整数的输出%o —— oct 八进制%d —— dec 十进制%x —— hex 十六 ...
- 自学Python1.8-python input/print用法 格式化输出
自学Python之路 自学Python1.8-python input/print用法 格式化输出 1.input函数 Python3.x 中 input() 函数接受一个标准输入数据,返回为 str ...
- golang格式化输出-fmt包用法详解
golang格式化输出-fmt包用法详解 注意:我在这里给出golang查询关于包的使用的地址:https://godoc.org 声明: 此片文章并非原创,大多数内容都是来自:https:// ...
- Python格式化输出——format用法示例
format OR % 提到Python中的格式化输出方法,一般来说有以下两种方式: print('hello %s' % 'world') # hello world print('hello {} ...
- python格式化输出之format用法
format用法 相对基本格式化输出采用‘%’的方法,format()功能更强大,该函数把字符串当成一个模板,通过传入的参数进行格式化,并且使用大括号‘{}’作为特殊字符代替‘%’ 使用方法由两种:b ...
- python格式化输出(% format用法)
%基本用法: 十进制输出:print('%d' % 6) 6也可以换成其它的数字变量 八进制输出:print('%o' % 6) 6也可以换成其它的数字变量 字符串输出:print('%s' ...
- Python print函数用法,print 格式化输出
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zanfeng/article/details/52164124 使用print输出各型的 字符串 整数 浮点数 出度及精度控制 strHello ...
随机推荐
- InheritableThreadLocal详解
InheritableThreadLocal详解 https://www.jianshu.com/p/94ba4a918ff5 InheritableThreadLocal——父线程传递本地变 ...
- php 逻辑题
越长大约发现,高中学的数学,都还给了数学老师,一点都没有留住. 最近遇到了一个 逻辑题,然后想了半天,后来做出来了,我就发现了,我可能是一个假的理科生.很简单的样子. 废话不说,看看这道题吧. /** ...
- Angular复习笔记7-路由(下)
Angular复习笔记7-路由(下) 这是angular路由的第二篇,也是最后一篇.继续上一章的内容 路由跳转 Web应用中的页面跳转,指的是应用响应某个事件,从一个页面跳转到另一个页面的行为.对于使 ...
- scp 基本用法(提高scp传输速度)
Outline spc 可以帮你实现: Linux Server 之间互传数据: Linux Server 和 Windows Server 之间互传数据: 参考: https://www.cnblo ...
- django中navie时间和aware时间详解
navie时间和aware时间: 什么是navie时间?什么是aware时间? navie时间:不知道自己的时间表示的是哪个时区的.也就是不知道自己几斤几两.比较幼稚. aware时间:知道自己的时间 ...
- Spring Boot 复习
简介 Spring Boot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring 应用的初始搭 建以及开发过程.该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义 ...
- 使用MHA实现MySQL主从复制高可用
一.MHA简介 MHA(Master High Availability)目前在MySQL高可用方面是一个相对成熟的解决方案,它由日本DeNA公司的youshimaton(现就职于Fac ...
- VUE组件3 数据流和.sync修饰符
单向数据流:数据通过prop从父组件传递到子组件中,当父级组件中的数据更新时,传子组件也会更新,但不能在子组件中修改.防止子组件在无意中修改,改变父级组件状态 然而,双向数据绑定在某些情况下有用.如果 ...
- ubuntu16安装php开发环境
一,安装 ubuntu 工具 sudo apt install -y git curl zsh vim 二,安装php 和 php-fpm , redis ,memcached 等 sudo apt ...
- nginx 页面加载不全的问题
在nginx的server中添加: proxy_buffer_size 2m; proxy_buffers 8 1m; proxy_busy_buffers_size 2m; 这是由于页面内容过长,默 ...
