disjoint set
MAKE-SET.x/ creates a new set whose only member (and thus representative)
is x. Since the sets are disjoint, we require that x not already be in some other
set.
UNION.x; y/ unites the dynamic sets that contain x and y, say Sx and Sy, into a
new set that is the union of these two sets. We assume that the two sets are disjoint
prior to the operation. The representative of the resulting set is any member
of Sx [ Sy, although many implementations of UNION specifically choose the
representative of either Sx or Sy as the new representative. Since we require
the sets in the collection to be disjoint, conceptually we destroy sets Sx and Sy,
removing them from the collection S. In practice, we often absorb the elements
of one of the sets into the other set.
FIND-SET.x/ returns a pointer to the representative of the (unique) set containing
x.

linklist implement
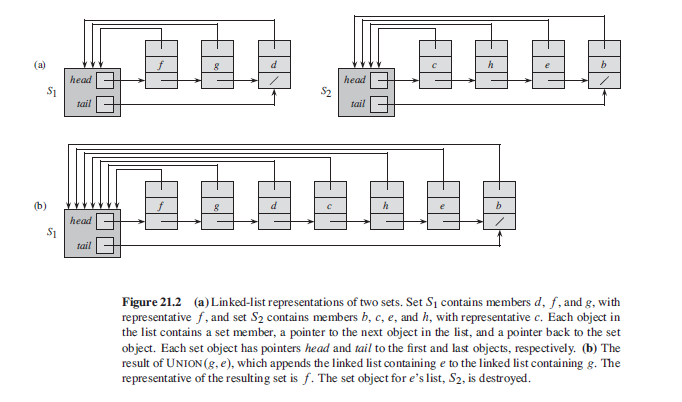
In the worst case, the above implementation of the UNION procedure requires an
average of ‚.n/ time per call because we may be appending a longer list onto
a shorter list; we must update the pointer to the set object for each member of
the longer list. Suppose instead that each list also includes the length of the list
(which we can easily maintain) and that we always append the shorter list onto the
longer, breaking ties arbitrarily. With this simple weighted-union heuristic, a single
UNION operation can still take _.n/ time if both sets have _.n/ members. As
the following theorem shows, however, a sequence of m MAKE-SET, UNION, and
FIND-SET operations, n of which are MAKE-SET operations, takes O.m C n lg n/
time.
Tree implement
Heuristics to improve the running time
So far, we have not improved on the linked-list implementation. A sequence of
n 1 UNION operations may create a tree that is just a linear chain of n nodes. By
using two heuristics, however, we can achieve a running time that is almost linear
in the total number of operations m.
The first heuristic, union by rank, is similar to the weighted-union heuristic we
used with the linked-list representation. The obvious approach would be to make
the root of the tree with fewer nodes point to the root of the tree with more nodes.
Rather than explicitly keeping track of the size of the subtree rooted at each node,
we shall use an approach that eases the analysis. For each node, we maintain a
rank, which is an upper bound on the height of the node. In union by rank, we
make the root with smaller rank point to the root with larger rank during a UNION
operation.
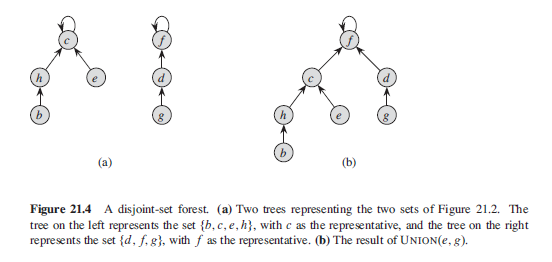
The second heuristic, path compression, is also quite simple and highly effective.
As shown in Figure 21.5, we use it during FIND-SET operations to make each
node on the find path point directly to the root. Path compression does not change
any ranks(more nodes linked to the root will cause much possibility to find it).

When we use both union by rank and path compression, the worst-case running
time is O.m ˛.n//, where ˛.n/ is a very slowly growing function, which we define
in Section 21.4. In any conceivable application of a disjoint-set data structure,
˛.n/ 4; thus, we can view the running time as linear in m in all practical situations.
Strictly speaking, however, it is superlinear. In Section 21.4, we prove this
upper bound.
package disjoint_sets;
// there have two ways,one is the linkedlist,the other is the tree,use the tree here
public class disjoint_set {
private static class Node{
private Node p;
private int rank;
private String name;
public Node(String na){
p = this; rank = 0;name = na;
}
}
public static void union(Node x,Node y){
link(findset(x),findset(y));
}
public static void link(Node x,Node y){
if(x.rank > y.rank){
y.p = x;
}
else if(y.rank > x.rank){
x.p = y;
}
else{
y.p = x;
x.rank = x.rank + 1;
}
}
public static Node findset(Node x){
if(x != x.p){
x.p = findset(x.p); //path compression
}
return x.p;
}
public static void print(Node x){ System.out.println(x.name);
if(x != x.p){
x = x.p;
print(x);
}
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node a = new Node("a");
Node b = new Node("b");
Node c = new Node("c");
Node d = new Node("d");
union(a,b);
union(b,c);
union(a,d);
print(d); } }
disjoint set的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals 分离区间的数据流
Given a data stream input of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, ..., summarize the numbers seen ...
- hdu 1232, disjoint set, linked list vs. rooted tree, a minor but substantial optimization for path c 分类: hdoj 2015-07-16 17:13 116人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
three version are provided. disjoint set, linked list version with weighted-union heuristic, rooted ...
- 数据结构与算法分析 – Disjoint Set(并查集)
什么是并查集?并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合(Disjoint Sets)的合并及查询问题. 并查集的主要操作1.合并两个不相交集合2.判断两个元素是否属于同一集合 主要操作的解释 ...
- 并查集(Disjoint Set)
在一些有N个元素的集合应用问题中,我们通常是在开始时让每个元素构成一个单元素的集合,然后按一定顺序将属于同一组的元素所在的集合合并,其间要反复查找一个元素在哪个集合中.这一类问题其特点是看似并不复杂, ...
- Leetcode: Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals && Summary of TreeMap
Given a data stream input of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, ..., summarize the numbers seen ...
- LeetCode-Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals
Given a data stream input of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, ..., summarize the numbers seen ...
- leetcode@ [352] Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals (Binary Search & TreeSet)
https://leetcode.com/problems/data-stream-as-disjoint-intervals/ Given a data stream input of non-ne ...
- 【leetcode】352. Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals
问题描述: Given a data stream input of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, ..., summarize the numbers ...
- 352. Data Stream as Disjoint Intervals
Plz take my miserable life T T. 和57 insert interval一样的,只不过insert好多. 可以直接用57的做法一个一个加,然后如果数据大的话,要用tree ...
- 数据结构 之 并查集(Disjoint Set)
一.并查集的概念: 首先,为了引出并查集,先介绍几个概念: 1.等价关系(Equivalent Relation) 自反性.对称性.传递性. 如果a和b存在等价关系,记 ...
随机推荐
- 因微信SSJD分享接口升级,分享变化
4月25日发版发现的微信分享问题,已确认是腾讯微信开发团队更新的分享的策略,而我们未能收到通知依然沿用老代码造成的.目前已经解决,解决方案如下: 微信分享的shareUrl域名必须与当前环境的安全域名 ...
- 高度自适应不能触发transition的解决方法
1. 前言 在我们不能确定一个元素的高度的时候,要使用transition过渡,是不会触发的,比如一个p标签 内容行数不固定 我们可能就要初始 height: 0 ; 过渡到 height: au ...
- Python Redis 常用操作
delete(*names) # 根据删除redis中的任意数据类型 exists(name) # 检测redis的name是否存在 keys(pattern='*') # 根据模型获取redis的n ...
- [c/c++] programming之路(15)、多维数组和二分查找法,小外挂
一.多维数组 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void main(){ ][]; int i,j; ; i < ; i++) { ...
- 使用MyBatis Generator 1.3.7自动生成代码
MyBatis Generator是一款mybatis自动代码生成工具,可以通过配置后自动生成文件. MyBatis Generator有几种方法可以生成代码,下面是其中一种. 一.官网下载 MyB ...
- FZOJ P2109 【卡德加的兔子】
题目描述 卡德加喜欢养兔子.他在达拉然的下水道里放了 $N$ 个兔笼(编号从 $1$ 到 $N$),里面养着他从德拉诺带来的兔子.它们的繁殖遵循斐波那契数列的规律:刚开始时,笼子里有一对刚出生的兔子. ...
- GPU并行的基础知识
- Android 虹软2.0人脸识别,注册失败问题 分析synchronized的作用
人脸识别需要init初始化(FaceServer中),离开时需要unInit销毁:当一个含有人脸识别的界面A跳向另一个含有人脸识别的界面B时,由于初始化和销毁都是对FaceServer类加锁(sync ...
- 雷林鹏分享:jQuery EasyUI 数据网格 - 列运算
jQuery EasyUI 数据网格 - 列运算 在本教程中,您将学习如何在可编辑的数据网格(datagrid)中包含一个运算的列.一个运算列通常包含一些从一个或多个其他列运算的值. 首先,创建一个可 ...
- java对redis的基本操作,ZZ
java对redis的基本操作 http://www.cnblogs.com/edisonfeng/p/3571870.html
