【NLP】Recurrent Neural Network and Language Models
0. Overview
What is language models?
A time series prediction problem.
It assigns a probility to a sequence of words,and the total prob of all the sequence equal one.
Many Natural Language Processing can be structured as (conditional) language modelling.
Such as Translation:
P(certain Chinese text | given English text)
Note that the Prob follows the Bayes Formula.
How to evaluate a Language Model?
Measured with cross entropy.
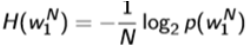
Three data sets:
1 Penn Treebank: www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
2 Billion Word Corpus: code.google.com/p/1-billion-word-language-modeling-benchmark/
3 WikiText datasets: Pointer Sentinel Mixture Models. Merity et al., arXiv 2016
|
Overview: Three approaches to build language models: Count based n-gram models: approximate the history of observed words with just the previous n words. Neural n-gram models: embed the same fixed n-gram history in a continues space and thus better capture correlations between histories. Recurrent Neural Networks: we drop the fixed n-gram history and compress the entire history in a fixed length vector, enabling long range correlations to be captured. |
1. N-Gram models:
Assumption:
Only previous history matters.
Only k-1 words are included in history
Kth order Markov model
2-gram language model:
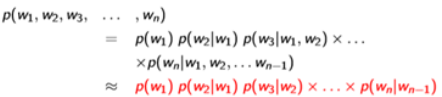
The conditioning context, wi−1, is called the history
Estimate Probabilities:
(For example: 3-gram)
 (count w1,w2,w3 appearing in the corpus)
(count w1,w2,w3 appearing in the corpus)
Interpolated Back-Off:
That is , sometimes some certain phrase don’t appear in the corpus so the Prob of them is zero. To avoid this situation, we use Interpolated Back-off. That is to say, Interpolate k-gram models(k = n-1、n-2…1) into the n-gram models.
A simpal approach:
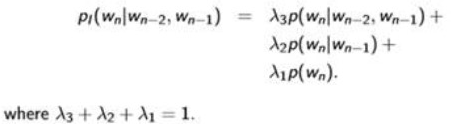
Summary for n-gram:
Good: easy to train. Fast.
Bad: Large n-grams are sparse. Hard to capture long dependencies. Cannot capture correlations between similary word distributions. Cannot resolve the word morphological problem.(running – jumping)
2. Neural N-Gram Language Models
Use A feed forward network like:
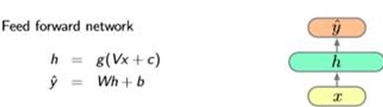
Trigram(3-gram) Neural Network Language Model for example:
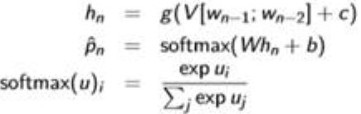
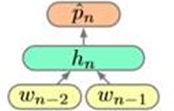
Wi are hot-vectors. Pi are distributions. And shape is |V|(words in the vocabulary)
(a sampal:detail cal graph)
Define the loss:cross entopy:
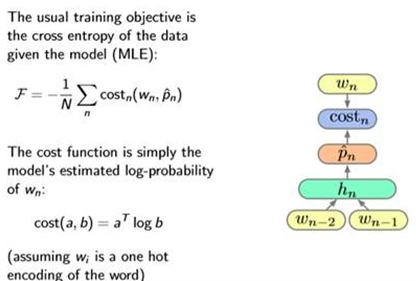
Training: use Gradient Descent

And a sampal of taining:
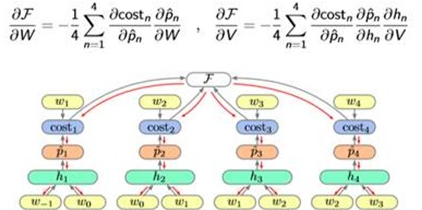
Comparsion with Count based n-gram LMs:
Good: Better performance on unseen n-grams But poorer on seen n-grams.(Sol: direct(linear) n-gram fertures). Use smaller memory than Counted based n-gram.
Bad: The number of parameters in the models scales with n-gram size. There is a limit on the longest dependencies that an be captured.
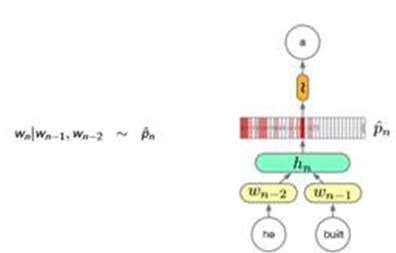
3. Recurrent Neural Network LM
That is to say, using a recurrent neural network to build our LM.
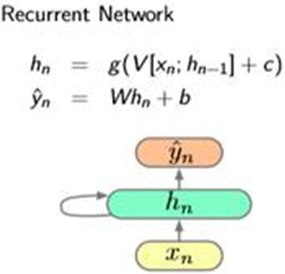

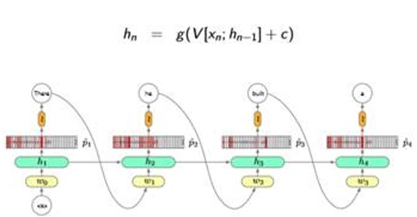
Model and Train:
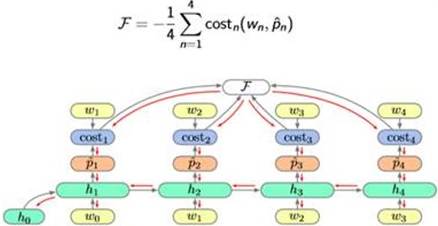
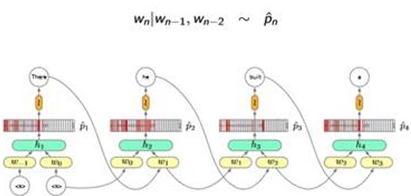
Algorithm: Back Propagation Through Time(BPTT)
Note:
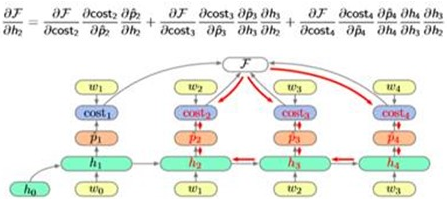
Note that, the Gradient Descent depend heavily. So the improved algorithm is:
Algorithm: Truncated Back Propagation Through Time.(TBPTT)
So the Cal graph looks like this:
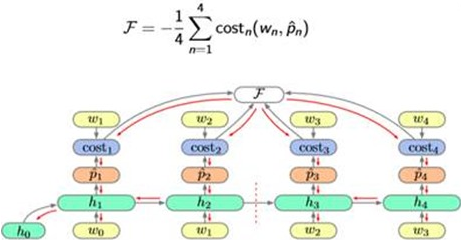
So the Training process and Gradient Descent:

Summary of the Recurrent NN LMs:
Good:
RNNs can represent unbounded dependencies, unlike models with a fixed n-gram order.
RNNs compress histories of words into a fixed size hidden vector.
The number of parameters does not grow with the length of dependencies captured, but they do grow with the amount of information stored in the hidden layer.
Bad:
RNNs are hard to learn and often will not discover long range dependencies present in the data(So we learn LSTM unit).
Increasing the size of the hidden layer, and thus memory, increases the computation and memory quadratically.
Mostly trained with Maximum Likelihood based objectives which do not encode the expected frequencies of words a priori.
Some blogs recommended:
|
Andrej Karpathy: The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/ Yoav Goldberg: The unreasonable effectiveness of Character-level Language Models nbviewer.jupyter.org/gist/yoavg/d76121dfde2618422139 Stephen Merity: Explaining and illustrating orthogonal initialization for recurrent neural networks. smerity.com/articles/2016/orthogonal_init.html |
【NLP】Recurrent Neural Network and Language Models的更多相关文章
- pytorch --Rnn语言模型(LSTM,BiLSTM) -- 《Recurrent neural network based language model》
论文通过实现RNN来完成了文本分类. 论文地址:88888888 模型结构图: 原理自行参考论文,code and comment: # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @time : ...
- Recurrent Neural Network系列1--RNN(循环神经网络)概述
作者:zhbzz2007 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhbzz2007 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 本文翻译自 RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS T ...
- 【NLP】自然语言处理:词向量和语言模型
声明: 这是转载自LICSTAR博士的牛文,原文载于此:http://licstar.net/archives/328 这篇博客是我看了半年的论文后,自己对 Deep Learning 在 NLP 领 ...
- Recurrent Neural Network Language Modeling Toolkit代码学习
Recurrent Neural Network Language Modeling Toolkit 工具使用点击打开链接 本博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/wangxingin ...
- 课程五(Sequence Models),第一 周(Recurrent Neural Networks) —— 1.Programming assignments:Building a recurrent neural network - step by step
Building your Recurrent Neural Network - Step by Step Welcome to Course 5's first assignment! In thi ...
- Recurrent Neural Network(循环神经网络)
Reference: Alex Graves的[Supervised Sequence Labelling with RecurrentNeural Networks] Alex是RNN最著名变种 ...
- Recurrent Neural Network系列2--利用Python,Theano实现RNN
作者:zhbzz2007 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhbzz2007 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 本文翻译自 RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS T ...
- Recurrent Neural Network[survey]
0.引言 我们发现传统的(如前向网络等)非循环的NN都是假设样本之间无依赖关系(至少时间和顺序上是无依赖关系),而许多学习任务却都涉及到处理序列数据,如image captioning,speech ...
- (zhuan) Recurrent Neural Network
Recurrent Neural Network 2016年07月01日 Deep learning Deep learning 字数:24235 this blog from: http:/ ...
随机推荐
- 1、FreeRTOS移植
1.FreeRTOS目录结构 FreeRTOS FreeRTOS简略目录如下: ├─FreeRTOS │ ├─Demo // 各种开发工具的完整Demo,开发者可以方便的以此搭建出自己的项目,甚至直接 ...
- Technical Development Guide---for Google
Technical Development Guide This guide provides tips and resources to help you develop your technica ...
- UVA - 12716 - 异或序列
求满足GCD(a,b) = a XOR b; 其中1<=b <=a<=n. 首先做这道题需要知道几个定理: 异或:a XOR b = c 那么 a XOR c = b; 那么我们令G ...
- 网工的Linux系统学习历程
偶遇篇作为一名通过思科CCNP认证的网络工程师,专注于网络技术.但在日常的工作中,难免不接触到服务器,对于大多数服务器来说,鉴于稳定性等因素的考虑,基本使用的都是Linux系统,包括RHEL.Cent ...
- iOS上手指点击波纹效果的实现
https://www.jianshu.com/p/35e6f53ca0fe 2016.10.19 22:00* 字数 135 阅读 2468评论 2喜欢 7 闲暇时间做了一个反馈手指点击屏幕的效果, ...
- 怎么去掉Xcode工程中的某种类型的警告 Implicit conversion loses integer precision: 'NSInteger' (aka 'long') to 'int32
unsigned long numComponents = CGColorGetNumberOfComponents([[UIColor blackColor] CGColor]); 2014年12月 ...
- Python_阻塞IO、非阻塞IO、IO多路复用
0.承上 进程: 计算机里最小的资源分配单位: 数据隔离, 利用多核,数据不安全. 线程: 计算机中最小的CPU调度单位: 数据共享,GIL锁,数据不安全. 协程: 线程的一部分,是有用户来调度的; ...
- html总结:背景图片拉伸
两种方法: ⑴推荐方法 <style>body {background-image:url(images/backimage.jpg);background-size:cover;}< ...
- java异常Exception
学习笔记: 一.程序的异常:Throwable 严重问题:Error ,我们不处理.这种问题一般很严重,不如内存溢出 问题:Exception 编译问题:不是RuntimeException异常.必须 ...
- shell脚本--CGI获取请求数据(GET / POST)
Case 1: 获取地址栏传递的参数(即通过GET方式) CGI的环境变量中有个QUERY_STRING,可以获取地址栏传递的参数,该参数可以是手动加上的,也可以是通过表单的get方式提交的,比如下面 ...
