使用mahout fpgrowth算法求关联规则
使用mahout
fpgrowth
首先,这篇文章的内容大部分取自国外一篇博客Finding
association rules with Mahout Frequent Pattern Mining,写这个出于几个原因,一 原文是英文的;二该博客貌似还被墙了,反正我是用了goagent才看到的;三 我简化了其实验内容,单纯的用数字表示item了。
首先是实验环境
- jdk >= 1.6
- maven
- hadoop (>1.0.0)
- mahout >= 0.7
环境搭建就不多说了,唯一注意的是mahout按照官网的指导绝对没问题,如果安装之后报错,可能是你的hadoop版本问题,换个hadoop试试,我遇到的错就是一直
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:classpath。
我用的数据是mahout官网上提供的retail.dat,使用哪个数据没关系,mahout fpgrowth的数据格式要求如下:
[item id1], [item id2], [item id3]
0, 2, 6, ...
0, 1, 6, ...
4, 5, ...
...
间隔符可以是别的,retail.dat里用的是空格,但要注意的是使用命令行时要标志。
这里不设置MAHOUT_LOCAL,让mahout在hadoop上跑,所以先使用hadoop命令把数据放到hdfs上,在terminal输入:
hadoop fs -put output.dat retail.dat
然后输入如下指令运行mahout:
mahout fpg -i output.dat -o patterns -k 10 -method mapreduce -regex '[\ ]' -s 10
指令的含义在mahout的网站上有详细说明,简要说下,-i表示输入,-o表示输出,-k 10表示找出和某个item相关的前十个频繁项,-method mapreduce表示使用mapreduce来运行这个作业,-regex '[\ ]'表示每个transaction里用空白来间隔item的,-s 10表示只统计最少出现10次的项。
成功运行后在patterns文件夹里会出现四个文件或者文件夹
- fList: 记录了每个item出现的次数的序列文件
- frequentpatterns: 记录了包含每个item的频繁项的序列文件
- fpGrowth
- parallelcounting
当然这些结果是在hdfs上面的,可以使用mahout命令查看下这些输出,在终端输入 mahout seqdumper -i patterns/frequentpatterns/part-r-00000
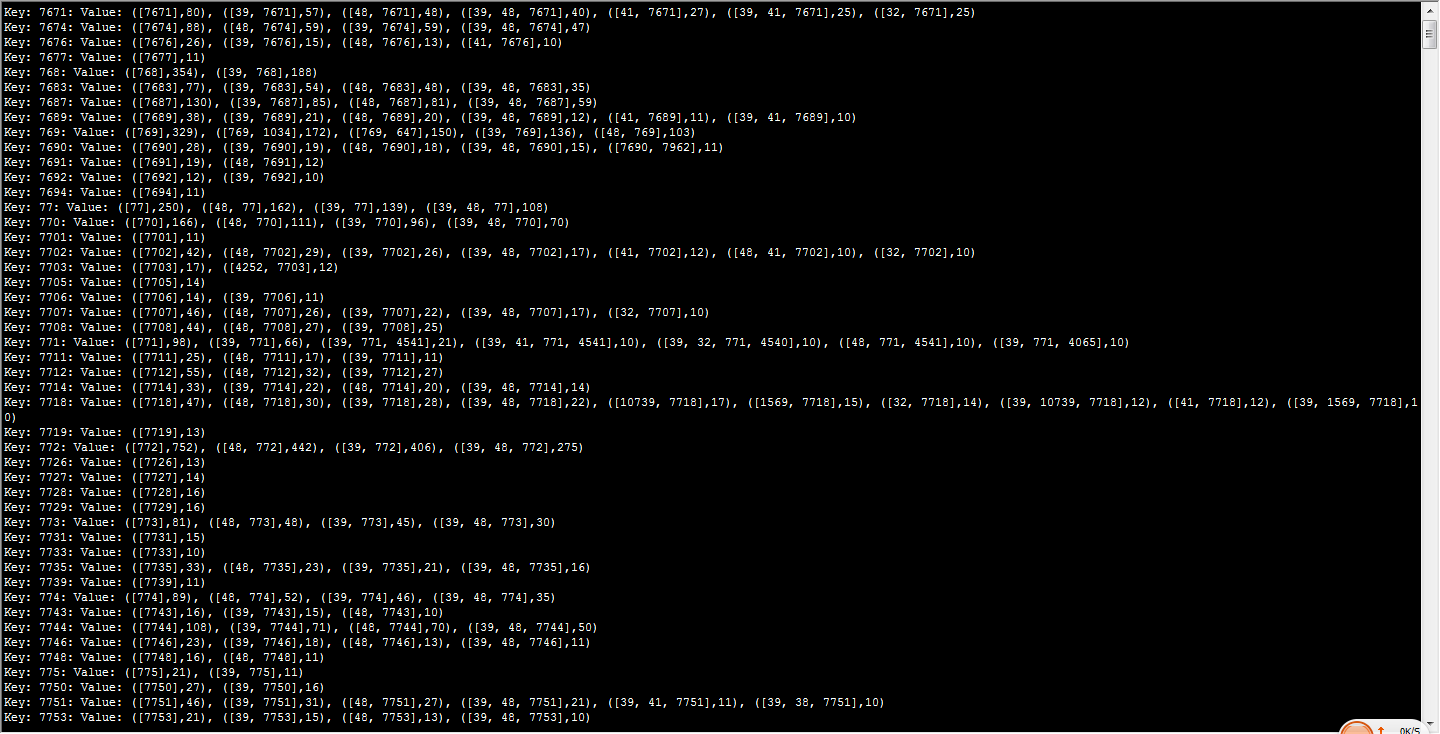
第一行显示了与item7671有关的前十个事务(按出现次数排序), ([7671],80) 表示item7671出现在80个事务中. ([39, 7671],57) 表示39和7671这两个item同时出现在57个事务里。关联规则可以由以下几个参数来推导:
- support
包含集合X的事务出现的频率:
- confidence
包含x的事务中含有同时包含Y的比例:
- lift 用来表示X和Y的相互独立程度:
- conviction 也是用来衡量X和Y的独立性的,这个值越大越好:
下面用程序来推导关联规则,先把hdfs上面的几个文件放到本地来,
hadoop fs -getmerge patterns/frequentpatterns frequentpatterns.seq
hadoop fs -get patterns/fList fList.seq
代码是java代码,怎么建工程都行,我是用的eclipse+maven,因为这样它可以自动帮我下载所需要的mahout的包,把两个序列文件拷到工程的根目录下,代码如下

package heyong; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.Reader;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.mahout.common.Pair;
import org.apache.mahout.fpm.pfpgrowth.convertors.string.TopKStringPatterns; public class ResultReaderS {
public static Map<Integer, Long> readFrequency(Configuration configuration, String fileName) throws Exception {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
Reader frequencyReader = new SequenceFile.Reader(fs,
new Path(fileName), configuration);
Map<Integer, Long> frequency = new HashMap<Integer, Long>();
Text key = new Text();
LongWritable value = new LongWritable();
while(frequencyReader.next(key, value)) {
frequency.put(Integer.parseInt(key.toString()), value.get());
}
return frequency;
} public static void readFrequentPatterns(
Configuration configuration,
String fileName,
int transactionCount,
Map<Integer, Long> frequency,
double minSupport, double minConfidence) throws Exception {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(configuration); Reader frequentPatternsReader = new SequenceFile.Reader(fs,
new Path(fileName), configuration);
Text key = new Text();
TopKStringPatterns value = new TopKStringPatterns(); while(frequentPatternsReader.next(key, value)) {
long firstFrequencyItem = -1;
String firstItemId = null;
List<Pair<List<String>, Long>> patterns = value.getPatterns();
int i = 0;
for(Pair<List<String>, Long> pair: patterns) {
List<String> itemList = pair.getFirst();
Long occurrence = pair.getSecond();
if (i == 0) {
firstFrequencyItem = occurrence;
firstItemId = itemList.get(0);
} else {
double support = (double)occurrence / transactionCount;
double confidence = (double)occurrence / firstFrequencyItem;
if ((support > minSupport
&& confidence > minConfidence)) {
List<String> listWithoutFirstItem = new ArrayList<String>();
for(String itemId: itemList) {
if (!itemId.equals(firstItemId)) { listWithoutFirstItem.add(itemId);
}
}
String firstItem = firstItemId;
listWithoutFirstItem.remove(firstItemId);
System.out.printf(
"%s => %s: supp=%.3f, conf=%.3f",
listWithoutFirstItem,
firstItem,
support,
confidence); if (itemList.size() == 2) {
// we can easily compute the lift and the conviction for set of
// size 2, so do it
int otherItemId = -1;
for(String itemId: itemList) {
if (!itemId.equals(firstItemId)) {
otherItemId = Integer.parseInt(itemId);
break;
}
}
long otherItemOccurrence = frequency.get(otherItemId);
double lift = (double)occurrence / (firstFrequencyItem * otherItemOccurrence);
double conviction = (1.0 - (double)otherItemOccurrence / transactionCount) / (1.0 - confidence);
System.out.printf(
", lift=%.3f, conviction=%.3f",
lift, conviction);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
i++;
}
}
frequentPatternsReader.close(); } public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception { int transactionCount = 88162;//事务总数
String frequencyFilename = "data/fList.seq";//
String frequentPatternsFilename = "data/frequentpatterns.seq";
double minSupport = 0.001;//支持度
double minConfidence = 0.3;//置信度 Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Map<Integer, Long> frequency = readFrequency(configuration, frequencyFilename);
readFrequentPatterns(configuration, frequentPatternsFilename,
transactionCount, frequency, minSupport, minConfidence); }
}

程序运行得到如下的结果
[39] => 3361: supp=0.003, conf=0.565, lift=0.000, conviction=0.977
[48] => 3361: supp=0.003, conf=0.560, lift=0.000, conviction=1.186
[39, 48] => 3361: supp=0.002, conf=0.396
[48] => 337: supp=0.001, conf=0.589, lift=0.000, conviction=1.271
[39] => 337: supp=0.001, conf=0.554, lift=0.000, conviction=0.952
[48] => 338: supp=0.009, conf=0.611, lift=0.000, conviction=1.344
[39] => 338: supp=0.008, conf=0.582, lift=0.000, conviction=1.018
[39, 48] => 338: supp=0.006, conf=0.405
[48] => 340: supp=0.005, conf=0.633, lift=0.000, conviction=1.422
………………
调整支持度和置信度的值,可以增强结果的满意度。至此,完成了使用mahout fpgrowth推导规则的一次入门实验室,灵活使用这个算法,还是可以在很多地方派上用场的。
我的实践:
数据:
I1 I2 I5
I2 I4
I2 I3
I1 I2 I4
I1 I3
I2 I3
I1 I3
I1 I2 I3 I5
I1 I2 I3
调用命令:
mahout fpg -i /user/hdfs/fp-growth/in/fpg.txt -o /user/hdfs/fp-growth/out -k 50 -method mapreduce -regex '[\ ]' -s 2
打印结果:
mahout seqdumper -i /user/hdfs/fp-growth/out/frequentpatterns/part-r-00000
Input Path: /user/hdfs/fp-growth/out/frequentpatterns/part-r-00000
Key: I1: Value: ([I1],6), ([I2, I1],4), ([I1, I3],4), ([I2, I1, I5],2), ([I2, I1, I3],2)
Key: I2: Value: ([I2],7), ([I2, I3],4), ([I2, I1],4), ([I2, I1, I5],2), ([I2, I1, I3],2), ([I2, I4],2)
Key: I3: Value: ([I3],6), ([I2, I3],4), ([I1, I3],4), ([I2, I1, I3],2)
Key: I4: Value: ([I2, I4],2)
Key: I5: Value: ([I2, I1, I5],2)
Count: 5
使用mahout fpgrowth算法求关联规则的更多相关文章
- Mahout源码分析:并行化FP-Growth算法
FP-Growth是一种常被用来进行关联分析,挖掘频繁项的算法.与Aprior算法相比,FP-Growth算法采用前缀树的形式来表征数据,减少了扫描事务数据库的次数,通过递归地生成条件FP-tree来 ...
- 数据挖掘算法之关联规则挖掘(二)FPGrowth算法
之前介绍的apriori算法中因为存在许多的缺陷,例如进行大量的全表扫描和计算量巨大的自然连接,所以现在几乎已经不再使用 在mahout的算法库中使用的是PFP算法,该算法是FPGrowth算法的分布 ...
- 数据挖掘系列(2)--关联规则FpGrowth算法
上一篇介绍了关联规则挖掘的一些基本概念和经典的Apriori算法,Aprori算法利用频繁集的两个特性,过滤了很多无关的集合,效率提高不少,但是我们发现Apriori算法是一个候选消除算法,每一次消除 ...
- 数据挖掘进阶之关联规则挖掘FP-Growth算法
数据挖掘进阶之关联规则挖掘FP-Growth算法 绪 近期在写论文方面涉及到了数据挖掘,需要通过数据挖掘方法实现软件与用户间交互模式的获取.分析与分类研究.主要涉及到关联规则与序列模式挖掘两块.关联规 ...
- 关联规则之FpGrowth算法
Aprori算法利用频繁集的两个特性,过滤了很多无关的集合,效率提高不少,但是我们发现Apriori算法是一个候选消除算法,每一次消除都需要扫描一次所有数据记录,造成整个算法在面临大数据集时显得无能为 ...
- 使用 FP-growth 算法高效挖掘海量数据中的频繁项集
前言 对于如何发现一个数据集中的频繁项集,前文讲解的经典 Apriori 算法能够做到. 然而,对于每个潜在的频繁项,它都要检索一遍数据集,这是比较低效的.在实际的大数据应用中,这么做就更不好了. 本 ...
- 使用Apriori算法和FP-growth算法进行关联分析
系列文章:<机器学习实战>学习笔记 最近看了<机器学习实战>中的第11章(使用Apriori算法进行关联分析)和第12章(使用FP-growth算法来高效发现频繁项集).正如章 ...
- 关联分析Apriori算法和FP-growth算法初探
1. 关联分析是什么? Apriori和FP-growth算法是一种关联算法,属于无监督算法的一种,它们可以自动从数据中挖掘出潜在的关联关系.例如经典的啤酒与尿布的故事.下面我们用一个例子来切入本文对 ...
- 机器学习之Apriori算法和FP-growth算法
1 关联分析 无监督机器学习方法中的关联分析问题.关联分析可以用于回答"哪些商品经常被同时购买?"之类的问题. 2 Apriori算法 频繁项集即出现次数多的数据集 支持度 ...
随机推荐
- [原创]关于tomcat启动时时候端口被占用,8080,8005,8009
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- CustomizaitonSpec Clone_VM
克隆虚拟机可以加上CustomizationSpec来自动配置好:IP地址.DNS.Domain等信息 1.可以利用PyVmimo中的vim模块在python中完全自定义CustomizationSp ...
- Delphi 的进制转换
1.10进制转16进制 intTohex(10,4); //第一个参数为要转换的数据,第二个参数为要转换后的16进制位数:得到:000A; 2. 16进制转10进制 strToInt('$'+'64 ...
- Qt中 QTableWidget用法总结
转自--> http://edsionte.com/techblog/archives/3014 http://hi.baidu.com/fightiger/item/693aaa0f0f87d ...
- 大话设计模式--工厂模式 factory -- C++实现实例
实现<大话设计模式>的C++版本... 1. 工厂模式 使用的范围是 同一个基类,下面很多子类. (1)这里很容易出现的一个问题n多的子类继承自抽象基类,我们不得不在每次要用到子类的地方就 ...
- maven 3.2.5 的安装及简单示例
http://www.mvnrepository.com 一直没有使用maven,它的作用就不说了,这二天需要用到,发现网上都是以前的版本,所以,我一边配置,一边记录. 一 下载maven 现在很多I ...
- 分享知识-快乐自己:解决 Maven 无法下载 fastdfs-client-java 依赖。
因为fastdfs-client-java-1.27-SNAPSHOT.jar这个依赖包在maven中央仓库是没有的. 需要自己编译源码成jar本地安装到maven 的本地仓库,安装完以后就能正常引用 ...
- Linux tar.gz 、zip、rar 解压 压缩命令
tar -c: 建立压缩档案 -x:解压 -t:查看内容 -r:向压缩归档文件末尾追加文件 -u:更新原压缩包中的文件 这五个是独立的命令,压缩解压都要用到其中一个,可以和别的命令连用但只能用其中一个 ...
- Arc065_E Manhattan Compass
平面上有$N$个点$(X_i\space, Y_i)$,定义$D(a,b)=|X_a-X_b|+|Y_a-Y_b|$. 如果你当前在$(p,q)$,这个无序二元组(即$(p,q)$和$(q,p)$被认 ...
- 点分治Day1
树套树Day2暂且搁置...因为Day1的题我各种不会做... 唯一过了一道还是整体二分过的... 我们来一点愉快的算法,先不考虑数据结构这种骚东西了 毕竟还在发烧,就先码码这几天在搞的点分治吧 hx ...
