ELK搭建-windows
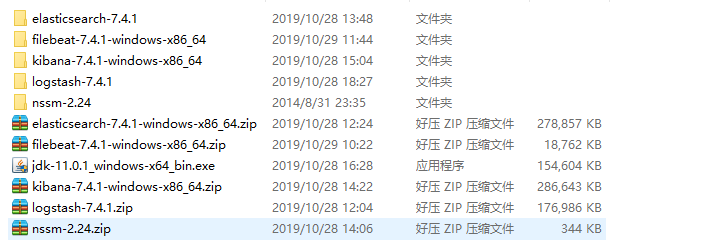
一、E

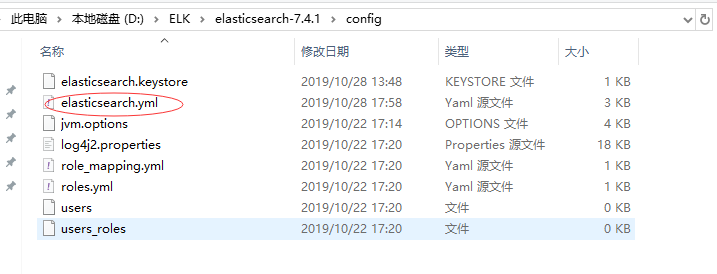
二、L

启动

三、K

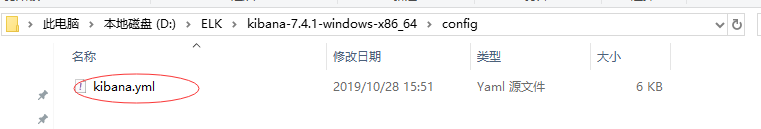
四、filebeat

五、配置文件使用
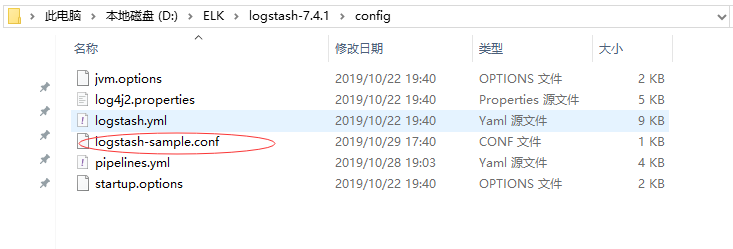
1、logstash-sample.conf
# Sample Logstash configuration for creating a simple
# Beats -> Logstash -> Elasticsearch pipeline. input {
redis {
batch_count => 1
type => "redis-input"
data_type => "list"
key => "logstash_test_list"
host => "127.0.0.1"
port => 6379
password => "Aroot1234@A"
db => 0
threads => 5
codec => "json" } beats{
host => "127.0.0.1"
port => 5044
}
}
filter { }
output {
if [fields][document_type]=="api" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["127.0.0.1:9200"]
index => "apinadiyi-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
# template_name => "apinadiyi"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
} if [type]=="redis-input" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["127.0.0.1:9200"]
index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
# document_type => "logs" # 7之后不支持了
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
} }
2、filebeat.yml
###################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### # This file is an example configuration file highlighting only the most common
# options. The filebeat.reference.yml file from the same directory contains all the
# supported options with more comments. You can use it as a reference.
#
# You can find the full configuration reference here:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html # For more available modules and options, please see the filebeat.reference.yml sample
# configuration file. #=========================== Filebeat inputs ============================= filebeat.inputs: # Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so
# you can use different inputs for various configurations.
# Below are the input specific configurations. - type: log # Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
#- /var/log/*.log
#- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*
- C:\PythonLog\*.log
#定义写入 ES 时的 _type 值 fields:
document_type: "api"
# logsource: 192.168.2.116
# logtype: nginx
# logdj: baseapi # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#exclude_lines: ['^DBG'] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#include_lines: ['^ERR', '^WARN'] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that
# are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped.
#exclude_files: ['.gz$'] # Optional additional fields. These fields can be freely picked
# to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering
#fields:
# level: debug
# review: 1 ### Multiline options # Multiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common
# for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [
#multiline.pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false.
#multiline.negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern
# that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate.
# Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash
#multiline.match: after #============================= Filebeat modules =============================== filebeat.config.modules:
# Glob pattern for configuration loading
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml # Set to true to enable config reloading
reload.enabled: true # Period on which files under path should be checked for changes
#reload.period: 10s #==================== Elasticsearch template setting ========================== setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
#index.codec: best_compression
#_source.enabled: false #================================ General ===================================== # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group
# all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface.
#name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each
# transaction published.
#tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Optional fields that you can specify to add additional information to the
# output.
#fields:
# env: staging #============================== Dashboards =====================================
# These settings control loading the sample dashboards to the Kibana index. Loading
# the dashboards is disabled by default and can be enabled either by setting the
# options here or by using the `setup` command.
#setup.dashboards.enabled: false # The URL from where to download the dashboards archive. By default this URL
# has a value which is computed based on the Beat name and version. For released
# versions, this URL points to the dashboard archive on the artifacts.elastic.co
# website.
#setup.dashboards.url: #============================== Kibana ===================================== # Starting with Beats version 6.0.0, the dashboards are loaded via the Kibana API.
# This requires a Kibana endpoint configuration.
setup.kibana: # Kibana Host
# Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 5601)
# In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:5601/path
# IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:5601
#host: "localhost:5601" # Kibana Space ID
# ID of the Kibana Space into which the dashboards should be loaded. By default,
# the Default Space will be used.
#space.id: #============================= Elastic Cloud ================================== # These settings simplify using Filebeat with the Elastic Cloud (https://cloud.elastic.co/). # The cloud.id setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.hosts` and
# `setup.kibana.host` options.
# You can find the `cloud.id` in the Elastic Cloud web UI.
#cloud.id: # The cloud.auth setting overwrites the `output.elasticsearch.username` and
# `output.elasticsearch.password` settings. The format is `<user>:<pass>`.
#cloud.auth: #================================ Outputs ===================================== # Configure what output to use when sending the data collected by the beat. #-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
#hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials.
#protocol: "https"
#username: "elastic"
#password: "changeme" #----------------------------- Logstash output --------------------------------
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["127.0.0.1:5044"] # Optional SSL. By default is off.
# List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications
#ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for SSL client authentication
#ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key
#ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" #================================ Processors ===================================== # Configure processors to enhance or manipulate events generated by the beat. processors:
- add_host_metadata: ~
- add_cloud_metadata: ~ #================================ Logging ===================================== # Sets log level. The default log level is info.
# Available log levels are: error, warning, info, debug
#logging.level: debug # At debug level, you can selectively enable logging only for some components.
# To enable all selectors use ["*"]. Examples of other selectors are "beat",
# "publish", "service".
#logging.selectors: ["*"] #============================== X-Pack Monitoring ===============================
# filebeat can export internal metrics to a central Elasticsearch monitoring
# cluster. This requires xpack monitoring to be enabled in Elasticsearch. The
# reporting is disabled by default. # Set to true to enable the monitoring reporter.
#monitoring.enabled: false # Sets the UUID of the Elasticsearch cluster under which monitoring data for this
# Filebeat instance will appear in the Stack Monitoring UI. If output.elasticsearch
# is enabled, the UUID is derived from the Elasticsearch cluster referenced by output.elasticsearch.
#monitoring.cluster_uuid: # Uncomment to send the metrics to Elasticsearch. Most settings from the
# Elasticsearch output are accepted here as well.
# Note that the settings should point to your Elasticsearch *monitoring* cluster.
# Any setting that is not set is automatically inherited from the Elasticsearch
# output configuration, so if you have the Elasticsearch output configured such
# that it is pointing to your Elasticsearch monitoring cluster, you can simply
# uncomment the following line.
#monitoring.elasticsearch: #================================= Migration ================================== # This allows to enable 6.7 migration aliases
#migration.6_to_7.enabled: true
六、别人配置文件参考
1、filebeat.yml
###################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### # This file is an example configuration file highlighting only the most common
# options. The filebeat.full.yml file from the same directory contains all the
# supported options with more comments. You can use it as a reference.
#
# You can find the full configuration reference here:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html #=========================== Filebeat prospectors ============================= filebeat.prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Most options can be set at the prospector level, so
# you can use different prospectors for various configurations.
# Below are the prospector specific configurations. - input_type: log # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
- /usr/local/nginx/logs/api/api.filebeat_*.log
- /usr/local/nginx/logs/api/msg/api.message_*.log
#定义写入 ES 时的 _type 值
document_type: "api"
fields:
logsource: 192.168.2.116
logtype: nginx
logdj: baseapi #排除更改时间超过定义的文件,时间字符串可以用2h表示2小时,5m表示5分钟,默认0
ignore_older: 0
#prospector扫描新文件的时间间隔,默认10秒
scan_frequency: 5s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file, 16K
#harvester_buffer_size: 16384 #单文件最大收集的字节数,单文件超过此字节数后的字节将被丢弃,默认10MB,需要增大,保持与日志输出配置的单文件最大值一致即可
# Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have
# All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. 10485760
# This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large.
max_bytes: 1048576000 # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are
# matching any regular expression from the list.
#include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that
# are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped.
#exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked
# to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering
#fields:
# level: debug
# review: 1 ### Multiline options # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common
# for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [
#multiline.pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false.
#multiline.negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern
# that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate.
# Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash
#multiline.match: after #========================= Filebeat global options ============================ # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded
#filebeat.spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!)
#filebeat.publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is
# Flush even though spool_size is not reached.
#filebeat.idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. If a relative path is used, it is considered relative to the
# data path.
#filebeat.registry_file: ${path.data}/registry #
# These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only
# the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored.
# The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in.
#filebeat.config_dir: # How long filebeat waits on shutdown for the publisher to finish.
# Default is 0, not waiting.
#filebeat.shutdown_timeout: 0 #================================ General ===================================== # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group
# all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface.
#name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each
# transaction published.
#tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Optional fields that you can specify to add additional information to the
# output.
#fields:
# env: staging #处理管道中单个事件内的队列大小,默认1000
# Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline
queue_size: 2000 # The internal queue size for bulk events in the processing pipeline.
# Do not modify this value.
#bulk_queue_size: 0 #================================ Outputs ===================================== # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat.
# Multiple outputs may be used. #-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
#hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials.
#protocol: "https"
#username: "elastic"
#password: "changeme" #----------------------------- Logstash output --------------------------------
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["192.168.6.204:4501"] # Optional SSL. By default is off.
# List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications
#ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for SSL client authentication
#ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key
#ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" #================================ Logging ===================================== # Sets log level. The default log level is info.
# Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug
#logging.level: debug # At debug level, you can selectively enable logging only for some components.
# To enable all selectors use ["*"]. Examples of other selectors are "beat",
# "publish", "service".
#logging.selectors: ["*"]
2、nginx_log.conf
input {
file {
path => "/opt/logstash-6.7.0/data/*.test.json"
type => "test"
start_position => "beginning"
sincedb_path => "/opt/logstash-6.7.0/data/test-sincedb"
}
}
input {
beats {
port => 4501
ssl => false
}
}
filter {
if [fields][logtype] in ["test", "nginx"] or [type]=="test" {
grok {
#设置自定义正则路径
patterns_dir => ["/opt/logstash-6.7.0/config/patterns/nginx"]
match => {
"message" => "%{NGINXACCESS}"
}
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp" , "dd/MMM/YYYY:HH:mm:ss Z" ]
target => "@timestamp"
locale => "cn"
}
useragent{
source => "agent"
prefix => "agent_"
remove_field => "agent"
}
#定义客户端的IP是哪个字段(上面定义的数据格式)
if [clientip] {
geoip {
source => "clientip" # 取自nginx中的客户端ip
}
}
if ![request_time] {
mutate {
add_field => {
"request_time" => "0.0"
}
}
}
if ![upstream_response_time] {
mutate {
add_field => {
"upstream_response_time" => "0.0"
}
}
}
#需要进行转换的字段,这里是将访问的时间转成int,再传给Elasticsearch
mutate {
convert => ["bytes", "integer"]
convert => ["[geoip][coordinates]", "float" ]
convert => ["request_time", "float"]
convert => ["upstream_response_time", "float"]
}
}
# 对模板点击参数进行分解
# /Mould/GetLmsgBoard/?t=1554737610678&id=1&m_no=F2018_11_21_00100
# func=Mould
# module=GetLmsgBoard
# para=?t=...
if [type]=="api" {
mutate{
add_field => {
"tempmessage" => "%{[request]}"
}
}
mutate{
split => ["tempmessage","/"]
add_field => {
"module" => "%{[tempmessage][1]}"
}
add_field => {
"func" => "%{[tempmessage][2]}"
}
add_field => {
"para" => "%{[tempmessage][3]}"
}
}
if [func] == "GetLmsgBoard" {
kv {
source => "para"
include_keys => ["id","m_no"]
prefix => "msg_"
field_split => "&? "
add_field => {
"type" => "api"
}
}
mutate{
convert => [ "meg_id", "integer"]
replace => { "type" => "message"}
}
}
mutate{
remove_field => "tempmessage"
remove_field => "para"
}
}
#####################################################################
# Baidu
#####################################################################
if [type]=="baidu" {
date {
match => ["datetime", "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss Z"]
target => "@timestamp"
locale => "cn"
timezone => "Asia/Shanghai"
}
#定义客户端的IP是哪个字段(上面定义的数据格式)
geoip {
source => "ip"
}
mutate {
convert => { "datetime" => "string" }
}
}
#####################################################################
# ERP User
#####################################################################
if [type]=="erpuser" {
date {
match => ["time", "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss Z"]
target => "@timestamp"
locale => "cn"
timezone => "Asia/Shanghai"
}
#定义客户端的IP是哪个字段(上面定义的数据格式)
geoip {
source => "ip"
}
mutate {
convert => { "time" => "string" }
}
}
}
output {
if [type]=="fanyi" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-fanyi-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="api" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "apinadiyi-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
template_name => "apinadiyi"
}
}
if [type]=="message" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "message-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
template_name => "message"
}
}
if [type]=="beimu" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-beimu-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="syd" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-syd-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="nadiyi" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-nadiyi-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="jiajiao" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-jiajiao-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="tingclass" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-tingclass-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "nginx"
}
}
if [type]=="baidu" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "baidu-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
template_name => "baidu"
}
#stdout {
# codec => rubydebug
#}
}
if [type]=="erpuser" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "erpuser-new-%{+YYYY.MM}"
template_name => "erpuser"
}
}
if [type] == "test" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.6.204:9200"]
index => "nginx-access-test-%{+YYYY.MM}"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
}
3、nginx_template.json
PUT _template/nginx
{
"order" : 0,
"version" : 190407,
"index_patterns" : [
"nginx-*"
],
"settings" : {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"index" : {
"refresh_interval" : "30s"
}
},
"mappings" : {
"doc" : {
"dynamic_templates" : [
{
"message_field" : {
"path_match" : "message",
"mapping" : {
"index": "false",
"norms" : false,
"type" : "text"
},
"match_mapping_type" : "string"
}
},
{
"string_fields" : {
"mapping" : {
"index": "true",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart",
"norms" : false,
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"ignore_above" : 512,
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
},
"match_mapping_type" : "string",
"match" : "*"
}
}
],
"properties" : {
"@timestamp" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"geoip" : {
"dynamic" : true,
"properties" : {
"ip" : {
"type" : "ip"
},
"latitude" : {
"type" : "half_float"
},
"location" : {
"type" : "geo_point"
},
"longitude" : {
"type" : "half_float"
}
}
},
"@version" : {
"type" : "keyword"
}
}
}
},
"aliases" : {
"nginx_this_week":{}
}
}
4、nginx
URIPATH1 (?:/[\\A-Za-z0-9$.+!*'(){},~:;=@#% \[\]_<>^\-&?]*)+
URI1 %{URIPROTO}://(?:%{USER}(?::[^@]*)?@)?(?:%{URIHOST})?(?:%{URIPATH1 })?
NGINXACCESS %{IPORHOST:clientip} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\] %{NUMBER:response} (?:%{WORD:catch}|-) %{WORD:verb} %{URIPATH1:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion} (?:%{NUMBER:bytes}|-) (?:%{NUMBER:request_time}|-) (?:%{NUMBER:upstream_response_time}|-) (?:%{URI1:referrer}|-) (?:%{QS:agent}|-) (?:(%{IPORHOST:upsteam_server}:%{POSINT:up_port})|-) (?:%{NUMBER:up_request}|-)
ELK搭建-windows的更多相关文章
- 2018年ElasticSearch6.2.2教程ELK搭建日志采集分析系统(教程详情)
章节一 2018年 ELK课程计划和效果演示1.课程安排和效果演示 简介:课程介绍和主要知识点说明,ES搜索接口演示,部署的ELK项目演示 es: localhost:9200 k ...
- 【Lua学习笔记之:Lua环境搭建 Windows 不用 visual studio】
Lua 环境搭建 Windows 不用 visual studio 系统环境:Win7 64bit 联系方式:yexiaopeng1992@126.com 前言: 最近需要学习Unity3d游戏中的热 ...
- 转:WIN7上搭建Windows Phone 8 开发环境——VMware Workstation下Win8 “无法安装Hyper-V, 某个虚拟机监控程序正在运行”问题解决的办法
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shaddock2013/p/3155024.html 最近在试着在Windows 7上搭建Windows Phone 8的开发调试环境,使用的是V ...
- WIN7上搭建Windows Phone 8 开发环境——VMware Workstation下Win8 “无法安装Hyper-V, 某个虚拟机监控程序正在运行”问题解决的办法
最近在试着在Windows 7上搭建Windows Phone 8的开发调试环境,使用的是VMware Workstation + Win8 Pro的虚拟环境, 在漫长的WPexpress_full下 ...
- OpenGL环境搭建Windows+Mac+Linux
OpenGL环境搭建Windows+Mac+Linux Mac平台下 下载列表:GLFWcmake 下载的GLFW解压缩 然后安装cmake, 安装好cmake之后打开 1.browse source ...
- Python环境搭建(windows)
Python环境搭建(windows) Python简介 Python(英国发音:/ˈpaɪθən/ 美国发音:/ˈpaɪθɑːn/),是一种面向对象.直译式计算机编程语言,具有近二十年的发展历史,成 ...
- 图文详解如何搭建Windows的Android C++开发环境
原地址:http://www.apkbus.com/android-18595-1-1.html //================================================= ...
- 搭建Windows SVN服务器及TortoiseSVN使用帮助和下载
搭建Windows SVN服务器: 用的SVN服务器通常为外部,例如Google Code的服务器,不过,做为一个程序开发人员,就算自己一个人写程序,也应该有一个SVN版本控制系统,以便对开发代码进行 ...
- (1)cocos2d-x-2.2.4搭建windows开发环境
Cocos2d-x-2.2.4搭建windows环境 软件需求 Windows系统(windows7或之后的系统): cocos2d-x-2.2.4压缩包. python安装包(推荐使用2.7.3版本 ...
随机推荐
- WinDBg定位asp.net mvc项目异常崩溃源码位置
项目介绍:asp.net mvc + angular +iis(windows)+windows server 系统莫名崩溃 最近有个系统默认奇妙崩溃50x,服务整体变成无响应,当运维告知我只有重启应 ...
- php中var关键字用法
见很多朋友说在php中定义变量用不用var都没关系,其实不然. 看看例子,如果我这样使用var: 1 var $a=123; 2 echo $a; 3 //那么程序会提示语法错误,要去掉var这个变量 ...
- 修正js跳转
var urls = new Array();urls["pc"] = "./hp"; //pcurls["sj"] = "./h ...
- 关于Eclipse Debug断点调试出现 Search not found 页面的解决办法
1. 在代码中鼠标右键 Debug AS ---> Debug Configurations... ----> 找到Source选项 ---> 点击add ---> 选择 j ...
- Spring Security 上
Spring Security 上 Security-dome 1.创建项目 创建一个Spring Boot项目,不用加入什么依赖 2.导入依赖 <dependencies> <!- ...
- [转]自建CDN防御DDoS
自建CDN防御DDoS(1):知己知彼,建设持久防线 前言 本议题是我们在OWASP杭州区2013年岁末年初安全沙龙中进行分享的内容,在此我们对这个议题的整体内容进行了重新归纳梳理,形成了文字版. 在 ...
- Python编写基于socket的非阻塞多人聊天室程序(单线程&多线程)
前置知识:socket非阻塞函数(socket.setblocking(False)),简单多线程编程 代码示例: 1. 单线程非阻塞版本: 服务端: #!/usr/bin/env python # ...
- Python多线程_thread和Threading
目录 多线程 _thread模块 使用 _thread模块创建线程 threading 使用 threading模块创建线程 线程同步 在讲多线程之前,我们先看一个单线程的例子: import _th ...
- Python脚本扫描给定网段的MAC地址表(scapy或 python-nmap)
目录 用scapy模块写 用 python-nmap 模块写 python3.7 windows环境 以下两个都可以扫描指定主机或者指定网段的 IP 对应的 MAC 地址,然后保存到 csv 文件中 ...
- 详解 WebRTC 传输安全机制:一文读懂 DTLS 协议
作者|进学 审校|泰一 DTLS (Datagram Transport Layer Security) 基于 UDP 场景下数据包可能丢失或重新排序的现实情况下,为 UDP 定制和改进的 TLS 协 ...
