8 -- 深入使用Spring -- 5...2 使用@Cacheable执行缓存
8.5.2 使用@Cacheable执行缓存
@Cacheable可用于修饰类或修饰方法,当使用@Cacheable修饰类时,用于告诉Spring在类级别上进行缓存 ------ 程序调用该类的实例的任何方法时都需要缓存,而且共享同一个缓存区;当使用@Cacheable修饰方法时,用于告诉Spring在方法级别上进行缓存 ------ 只有当程序调用该方法时才需要缓存。
1. 类级别的缓存
当使用@Cacheable修饰类时,就可控制Spring在类级别进行缓存,这样程序调用类的任意方法时,只要传入的参数相同,Spring就会使用缓存。
Component : UserServiceImpl
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.impl; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.UserService;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.bean.User; @Service(value="userService")
@Cacheable(value = "users")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Override
public User getUserByNameAndAge(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---");
return new User(name,age);
} @Override
public User getAnotherUser(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行findAnotherUser()查询方法---");
return new User(name,age);
} }
app_8_5_2_ehcache.xml:不成功,请使用SimpleCacheManager作为缓存管理器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- Spring 配置文件的根元素,使用Spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:P="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank">
</context:component-scan> <cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager" /> <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="name" value="default" />
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="name" value="users" />
</bean> </set>
</property>
</bean> <!--
<bean id="ehCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:app_8_5_2_ehcache.xml"/>
<property name="shared" value="false"/>
</bean>
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"/>
</bean> --> </beans>
Class : SpringTest
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.impl; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.UserService;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.bean.User; public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app_8_5_2_classrank.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
User userA = userService.getUserByNameAndAge("lime", 24);
User userB = userService.getAnotherUser("lime", 24);
System.out.println(userA == userB);
}
}
Console :
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
true
@Cacheable(value="users")指定UserServiceImple进行类级别的缓存,这样程序调用该类的任意方法时,只要传入的参数相同,Spring就会使用缓存,即时方法的返回值并不真正的同一个对象。
此处所指的缓存的意义是:当程序第一次调用该类的实例的某个方法时,Spring缓存机制会将该方法返回的数据放入指定缓存区 ------ 就是@Cacheable注解的value属性所指定的缓存区(此处指定将数据放入users缓存区,正是缓存管理器配置的users缓存区)。以后程序调用该类的实例的任何方法时,只要出入的参数相同,Spring将不会真正执行该方法,而是直接利用缓存区中的数据。
类级别的缓存默认以所有方法参数作为key来缓存方法返回的数据 ------ 同一类不管调用哪个方法,只要调用方法时传入的参数相同,Spring都会直接利用缓存区中的数据。
使用@Cacheable时可指定如下属性:
⊙ value : 必需属性。该属性可指定多个缓存区的名字,用于指定将方法返回值放入指定的缓存区内。
⊙ key : 通过SpEL表达式显式指定缓存的key。多个参数组合的key 用#name + #age + ...
⊙ condition : 该属性指定一个返回boolean值的SpEL表达式,只有当该表达式返回true时,Spring才会缓存方法返回值。
⊙ unless : 该属性指定一个返回boolean值的SpEL表达式,当该表达式返回true时,Spring就不缓存方法返回值。
提示:
与@Cacheable注解功能类似的还有一个@CachePut注解,@CachePut注解同样会让Spring将方法返回值放入缓存区。与@Cacheable不同的是,@CachePut修饰的方法不会读取缓存区中的数据 ------ 这意味着不管缓存区是否已有数据,@CachePut总会告诉Spring要重新执行这些方法,并再次将方法返回值放入缓存区。
修改UserServiceImpl : @Cacheable(value = “users” , key = “#name”) 显式指定以name参数作为缓存的key,这样只要调用的方法具有相同的name参数,Spring缓存机制就会生效。
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.service.cacheablekey.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.bean.User;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.service.cacheable.UserService; public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app_8_5_2_classrankkey.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
User userA = userService.getUserByNameAndAge("lime", 22);
User userB = userService.getAnotherUser("lime", 24);
System.out.println(userA == userB); }
}
Console :
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
true
使用@Cacheable注解显式指定key = “#name” ,这就意味着缓存使用name参数作为缓存的key。
condition属性与unless属性的功能基本相似,但规则恰好相反:当condition指定的条件为true时,Spring缓存机制才会执行缓存;当unless指定的条件为true时,Spring缓存机制就不执行缓存。
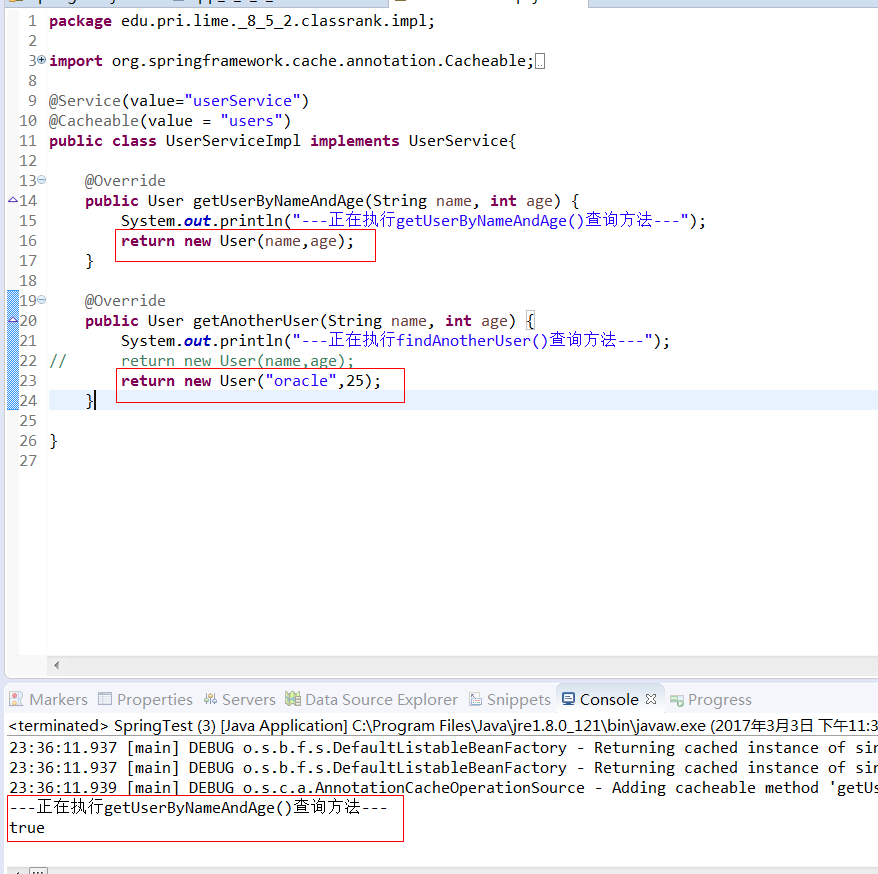
Class : UserServiceImpl
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.service.cacheablecondition.impl; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.bean.User;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.service.cacheablecondition.UserService; @Service("userService")
@Cacheable(value="users" ,condition="#age<100")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Override
public User getUserByNameAndAge(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---");
return new User(name,age);
} @Override
public User getAnotherUser(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行getAnotherUser()查询方法---");
return new User("oracle",25);
} }
XML :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- Spring 配置文件的根元素,使用Spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:P="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.classrank.service.cacheablecondition.impl">
</context:component-scan> <!-- 启用Spring缓存 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager" /> <!-- 使用simpleCacheManager缓存管理器 -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<!-- 配置缓存区 -->
<property name="caches">
<set>
<!-- 使用ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean工程Bean生产缓存区 -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<!-- 定义缓存区名称 -->
<property name="name" value="default" />
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<!-- 定义缓存区名称 -->
<property name="name" value="users" />
</bean> </set>
</property>
</bean> </beans>
Console :
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
---正在执行getAnotherUser()查询方法---
false
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
---正在执行getAnotherUser()查询方法---
false
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
---正在执行getAnotherUser()查询方法---
false
疑惑 : 跟想象中的不一样啊! 说好的condition表达式呢?
使用@Cacheable修饰方法时,可控制Spring在方法级别进行缓存,这样当程序调用该方法时,只要传入的参数相同,Spring就会使用缓存。
2.方法级别的缓存
Class : UserServiceImpl
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.service.impl; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.bean.User;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.service.UserService; @Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Override
@Cacheable(value="userA")
public User getUserByNameAndAge(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---");
return new User(name,age);
} @Override
@Cacheable(value="userB")
public User getAnotherUser(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("---正在执行findAnotherUser()查询方法---");
return new User("oracle",25);
} }
XML : app_8_5_2_functionrankvalue.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- Spring 配置文件的根元素,使用Spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:P="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 扫描Spring的组件 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.service.impl"/> <!-- 启用Spring缓存 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager" /> <!-- 使用simpleCacheManager缓存管理器 -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<!-- 配置缓存区 -->
<property name="caches">
<set>
<!-- 使用ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean工程Bean生产缓存区 -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<!-- 定义缓存区名称 -->
<property name="name" value="userA" />
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<!-- 定义缓存区名称 -->
<property name="name" value="userB" />
</bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Class : SpringTest
package edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.bean.User;
import edu.pri.lime._8_5_2.functionrank.service.UserService; public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app_8_5_2_functionrankvalue.xml");
UserService userService = ctx.getBean("userService",UserService.class);
User userA = userService.getUserByNameAndAge("lime", 24);
User userB = userService.getAnotherUser("lime", 24);
System.out.println(userA == userB);
User userC = userService.getUserByNameAndAge("lime", 24);
User userD = userService.getAnotherUser("lime", 24);
System.out.println(userA == userC); }
}
Console :
---正在执行getUserByNameAndAge()查询方法---
---正在执行findAnotherUser()查询方法---
false
true
方法级别的缓存中,方法之间使用不同的缓存区,因此它们不能共享缓存。
啦啦啦
啦啦啦
啦啦啦
啦啦啦
8 -- 深入使用Spring -- 5...2 使用@Cacheable执行缓存的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot中使用EhCache实现缓存支持
SpringBoot提供数据缓存功能的支持,提供了一系列的自动化配置,使我们可以非常方便的使用缓存.,相信非常多人已经用过cache了.因为数据库的IO瓶颈.一般情况下我们都会引入非常多的缓存策略, ...
- 【快学SpringBoot】Spring Cache+Redis实现高可用缓存解决方案
前言 之前已经写过一篇文章介绍SpringBoot整合Spring Cache,SpringBoot默认使用的是ConcurrentMapCacheManager,在实际项目中,我们需要一个高可用的. ...
- spring boot:使用spring cache+caffeine做进程内缓存(本地缓存)(spring boot 2.3.1)
一,为什么要使用caffeine做本地缓存? 1,spring boot默认集成的进程内缓存在1.x时代是guava cache 在2.x时代更新成了caffeine, 功能上差别不大,但后者在性能上 ...
- 当spring 容器初始化完成后执行某个方法
在做web项目开发中,尤其是企业级应用开发的时候,往往会在工程启动的时候做许多的前置检查. 比如检查是否使用了我们组禁止使用的Mysql的group_concat函数,如果使用了项目就不能启动,并指出 ...
- Spring Web MVC中的页面缓存支持 ——跟我学SpringMVC系列
Spring Web MVC中的页面缓存支持 ——跟我学SpringMVC系列
- 在Spring、Hibernate中使用Ehcache缓存(2)
这里将介绍在Hibernate中使用查询缓存.一级缓存.二级缓存,整合Spring在HibernateTemplate中使用查询缓存.,这里是hibernate3,使用hibernate4类似,不过不 ...
- spring boot整合reids 然后实现缓存分页(方法之一) 以及RedisTemplate存到reids 里面get 就消失的坑
业务需求 首页 实现缓存分页 spring boot 整合redis (我的是2.0.3版本的) 在pom 文件写上依赖包即可 <dependency><!--依赖包--> ...
- Spring + MySQL + Mybatis + Redis【二级缓存】执行流程分析
一级缓存基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该Session中的所有 Cache 就 ...
- (转)为Spring集成的Hibernate配置二级缓存
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52896195 前面我们已经集成了Spring4.2.5+Hibernate4.3.11+Str ...
随机推荐
- 应用栈解决迷宫问题的C语言实现
题目来自于严蔚敏<数据结构>,参考伪代码实现的程序: #include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> //记录通道块在迷宫矩阵当中的横 ...
- centos7安装单机rocketmq,图文教程
系统环境 1.操作系统:64位CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core) 2.jdk版本:1.8.0_121 3.IP地址:192.168.1.210 下载rocketm ...
- index-document-shard
1.index.shard.document理解: a.每个index包含有多个document,index采用数据路由将document存放在shard中, b.算法(数据路由): shard = ...
- Delphi中COM自动化对象中使用事件
unit SrvUnit2; interface uses ComObj, ActiveX, AxCtrls, Classes, SrvEvent_TLB, StdVcl, Srvunit1; typ ...
- 17、python对内存的使用
python对内存的使用 浅拷贝和深拷贝 所谓浅拷贝就是对引用的拷贝(只拷贝父对象) 所谓深拷贝就是对对象的资源的拷贝 解释一个例子: import copy a = [1,2,3,['a','b', ...
- 如何Python下载大文件?
我想用python脚本下载很多文件,但是经常就有那么几个出错,写了个error handling,跳了过去,但是把出错的链接保存了一下. 转过天来,研究了一下出的什么错. 一个报错如下: PS C:\ ...
- 使用lightProbe来模拟动态物体的照明shader
VertexLit path中读取lightProbe烘焙信息: Shader "VertexLitProbe" { Properties { _MainTex ("Ba ...
- RHEL磁盘修复
0. 1.基础工具:e2label /device/xxx [new label name] 显示/设定设备的label名称 2.e2fsck 修复工具,用-b 指定备用的superblock位置 ...
- 处理用千牛导出淘宝数据,供Logstash到Elasticsearch使用。(NodeJS)
var rf=require("fs"); // 加载编码转换模块 //npm install iconv-lite var iconv = require('iconv-lite ...
- android 对话框全屏
对话框风格 <style name="Lam.Dialog.FullScreen" parent="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Dialog&qu ...
