Android示例程序剖析之记事本(一)
Android SDK提供了很多示例程序,从这些示例代码的阅读和试验中能够学习到很多知识。本系列就是要剖析Android记事本示例程序,用意就是一步步跟着实例进行动手操作,在实践中体会和学习Android开发。该系列共有四篇文章,本文是第一篇。
前期准备
搭建开发环境,尝试编写"Hello World”,了解Android的基本概念,熟悉Android的API(官方文档中都有,不赘述)。
记事本程序运行界面
先来简单了解下程序运行的效果:
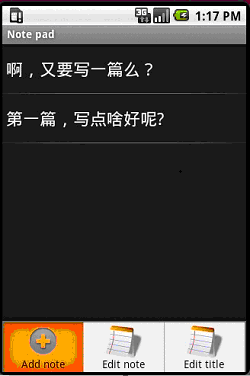

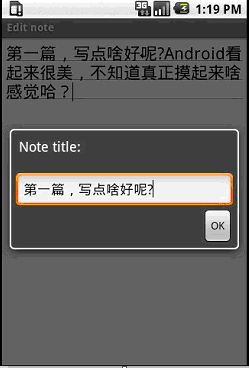
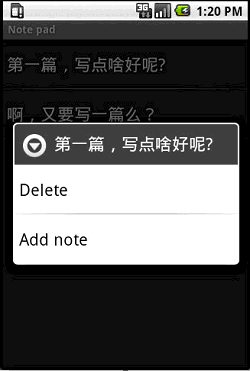
程序入口点
类似于win32程序里的WinMain函数,Android自然也有它的程序入口点。它通过在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置来指明,可以看到名为NotesList的activity节点下有这样一个intent-filter,其action为android.intent.action.MAIN, Category指定为 android.intent.category.LAUNCHER,这就指明了这个activity是作为入口activity,系统查找到它后,就会创建这个activity实例来运行,若未发现就不启动(你可以把MAIN改名字试试)。
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
- </intent-filter>
NotesList详解
就从入口点所在的activity(见图1)开始,可以看到这个activity最重要的功能就是显示日志列表。这个程序的日志都存放在Sqlite数据库中,因此需要读取出所有的日志记录并显示。先来看两个重要的私有数据,第一个PROJECTION字段指明了“日志列表“所关注的数据库中的字段(即只需要ID和Title就可以了)。
- private static final String[] PROJECTION = new String[] {
- Notes._ID, // 0
- Notes.TITLE, // 1
- };
第二个字段COLUMN_INDEX_TITLE指明title字段在数据表中的索引。
private static final int COLUMN_INDEX_TITLE = 1;
然后就进入第一个调用的函数onCreate。
- Intent intent = getIntent();
- if (intent.getData() == null)
- {
- intent.setData(Notes.CONTENT_URI);
- }
因为NotesList这个activity是系统调用的,此时的intent是不带数据和操作类型的,系统只是在其中指明了目标组件是Notelist,所以这里把“content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”保存到intent里面,这个URI地址指明了数据库中的数据表名(参见以后的NotePadProvider类),也就是保存日志的数据表notes。
Cursor cursor = managedQuery(getIntent().getData(), PROJECTION, null, null, Notes.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER);
然后调用managedQuery函数查询出所有的日志信息,这里第一个参数就是上面设置的” content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”这个URI,即notes数据表。PROJECTION 字段指明了结果中所需要的字段,Notes.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER 指明了结果的排序规则。实际上managedQuery并没有直接去查询数据库,而是通过Content Provider来完成实际的数据库操作,这样就实现了逻辑层和数据库层的分离。
- SimpleCursorAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this, R.layout.noteslist_item, cursor,
- new String[] { Notes.TITLE }, new int[] { android.R.id.text1 });
- setListAdapter(adapter);
查询出日志列表后,构造一个CursorAdapter,并将其作为List View的数据源,从而在界面上显示出日志列表。可以看到,第二个参数是R.layout.noteslist_item,打开对应的noteslist_item.xml文件:
- <TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:id="@android:id/text1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeight"
- android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
- android:gravity="center_vertical"
- android:paddingLeft="5dip"
- android:singleLine="true"
- />
就是用来显示一条日志记录的TextView,最后两个字段指明了实际的字段映射关系,通过这个TextView来显示一条日志记录的title字段。
处理“选择日志”事件
既然有了“日志列表”,就自然要考虑如何处理某一条日志的单击事件,这通过重载onListItemClick方法来完成:
- @Override
- protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
- Uri uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(getIntent().getData(), id);
- String action = getIntent().getAction();
- if (Intent.ACTION_PICK.equals(action) || Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT.equals(action)) {
- // The caller is waiting for us to return a note selected by
- // the user. The have clicked on one, so return it now.
- setResult(RESULT_OK, new Intent().setData(uri));
- } else {
- // Launch activity to view/edit the currently selected item
- startActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT, uri));
- }
- }
首先通过”content:// com.google.provider.NotePad/notes”和日志的id 号拼接得到选中日志的真正URI,然后创建一个新的Intent,其操作类型为Intent.ACTION_EDIT,数据域指出待编辑的日志URI(这里只分析else块)。
Intent深度剖析
那么,上面这句startActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT, uri))执行后会发生什么事情呢?这时候Android系统就跳出来接管了,它会根据intent中的信息找到对应的activity,在这里找到的是NoteEditor这个activity,然后创建这个activity的实例并运行。
那么,Android又是如何找到NoteEditor这个对应的activity的呢?这就是intent发挥作用的时刻了。
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_EDIT, uri)
这里的Intent.ACTION_EDIT=” android.intent.action.EDIT”,另外通过设置断点,我们看下这里的uri值:
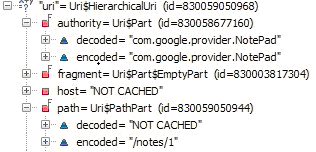
可以看到选中的日志条目的URI是:content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1。然后我们再来看下Androidmanfest.xml,其中有这个provider:
- <provider android:name="NotePadProvider"
- android:authorities="com.google.provider.NotePad"/>
发现没有?它也有com.google.provider.NotePad,这个是content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1的一部分,同时:
- <activity android:name="NoteEditor"
- android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Light"
- android:label="@string/title_note"
- android:screenOrientation="sensor"
- android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation"
- >
- <!-- This filter says that we can view or edit the data of
- a single note -->
- <intent-filter android:label="@string/resolve_edit">
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />
- <action android:name="com.android.notepad.action.EDIT_NOTE" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- <data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note" />
- </intent-filter>
- <!-- This filter says that we can create a new note inside
- of a directory of notes. -->
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.INSERT" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- <data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.google.note" />
- </intent-filter>
- </activity>
上面第一个intent-filter中有一个action 名为android.intent.action.EDIT,而前面我们创建的Intent也正好是Intent.ACTION_EDIT=” android.intent.action.EDIT”,想必大家已经明白是怎么回事了吧。
下面就进入activity选择机制了:
系统从intent中获取道uri,得到了content://com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1,去掉开始的content:标识,得到com.google.provider.NotePad/notes/1,然后获取前面的com.google.provider.NotePad,然后就到Androidmanfest.xml中找到authorities为com.google.provider.NotePad的provider,这个就是后面要讲的contentprovider,然后就加载这个content provider。
- <provider android:name="NotePadProvider"
- android:authorities="com.google.provider.NotePad"/>
在这里是NotePadProvider,然后调用NotePadProvider的gettype函数,并把上述URI传给这个函数,函数返回URI所对应的类型(这里返回Notes.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE,代表一条日志记录,而CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE = " vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note ")。
- @Override
- public String getType(Uri uri) {
- switch (sUriMatcher.match(uri)) {
- case NOTES:
- return Notes.CONTENT_TYPE;
- case NOTE_ID:
- return Notes.CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE;
- default:
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri);
- }
- }
上面的sUriMatcher.match是用来检测uri是否能够被处理,而sUriMatcher.match(uri)返回值其实是由决定的。
sUriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
sUriMatcher.addURI(NotePad.AUTHORITY, "notes", NOTES);
sUriMatcher.addURI(NotePad.AUTHORITY, "notes/#", NOTE_ID);
然后系统使用获得的" vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note "和”android.intent.action.EDIT”到androidmanfest.xml中去找匹配的activity。
- <intent-filter android:label="@string/resolve_edit">
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />
- <action android:name="com.android.notepad.action.EDIT_NOTE" />
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- <data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note" />
- </intent-filter>
正好NoteEditor这个activity的intent-filter满足上述条件,这样就找到了NoteEditor。于是系统加载这个类并实例化,运行,然后就到了NoteEditor的OnCreate函数中(见后续文章)。
小技巧
1. 在命令行中使用”adb shell”命令进入系统中,然后”cd app”进入应用程序所在目录,”rm XXX”就可以删除你指定的apk,从而去掉其在系统顶层界面占据的图标,若两次”cd data”则可以进入应用程序使用的数据目录,你的数据可以保存在这里,例如Notepad就是把其数据库放在它的databases目录下,名为note_pad.db.
2. 第一次启动模拟器会比较慢,但以后就别关闭模拟器了,修改代码,调试都不需要再次启动的,直接修改后run或debug就是。
Android示例程序剖析之记事本(一)的更多相关文章
- MindSpore部署图像分割示例程序
MindSpore部署图像分割示例程序 本端侧图像分割Android示例程序使用Java实现,Java层主要通过Android Camera 2 API实现摄像头获取图像帧,进行相应的图像处理,之后调 ...
- android的程序运行数据存放在哪里?
Android应用开发中,给我们提供了5种数据的存储方式1 使用SharedPreferences存储数据2 文件存储数据3 SQLite数据库存储数据4 使用ContentProvider存储数据5 ...
- 使用 Eclipse PhoneGap 构建 Android 应用程序入门
Eclipse 是一种支持多种技术的开源集成开发环境 (IDE),但本文重点介绍 Java 支持,这也是 Android 应用程序的“母语”.Android 是 Google 发布的开源移动操作系统. ...
- IONIC 开发的Android应用程序签名(或重新签名)详解
完全通过DOS命令来完成apk签名 给apk签名一共要用到3个工具,或者说3个命令,分别是:keytool.jarsigner和zipalign,下面是对这3个工具的简单介绍: ...
- 如何编译ReactNative示例程序Examples
通过示例程序可以看到一些基本组件的使用,对于学习ReactNative是很有帮助的. 编译示例程序需要将整个项目导入到androidStudio中,androidStudio导入项目时选择react- ...
- OSG中的示例程序简介
OSG中的示例程序简介 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/indif/archive/2011/05/13/2045136.html 1.example_osganimate一)演示 ...
- Android应用程序签名详解 简介
转自: http://blog.csdn.net/lyq8479/article/details/6401093 本文主要讲解Android应用程序签名相关的理论知识,包括:什么是签名.为什么要给应用 ...
- Android源码剖析之Framework层升级版(窗口、系统启动)
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/liuxian13183/ ,引用必须注明出处! 看本篇文章之前,建议先查看: Android源码剖析之Framework层基础版 前面讲了frame ...
- 如何在Android应用程序中使用传感器模拟器SensorSimulator
原文地址; 如何在Android应用程序中使用传感器模拟器 - 移动平台应用软件开发技术 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET http://blog.csdn.net/pku_android/arti ...
随机推荐
- DVWA实验之Brute Force(暴力破解)- Medium
DVWA实验之Brute Force(暴力破解)- Medium 有关DVWA环境搭建的教程请参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/0yst3r-2046/p/10928380. ...
- win10使用L2TP连接失败,报远程服务器未响应错误解决办法,亲测可用!
报错如下: 原因是L2TP连接需要IPSec加密,远程服务器未响应说明IPSec加密被禁用了,需要在注册表启用它,具体步骤如下: 1.以管理员账号身份打开CMD,win10 是 win+x键 2.找到 ...
- 【原】简单shell练习(五)
1.查询一个文件中某个单词出现的次数 # grep -o 'ts' ./test/txt |wc -l 2.统计当前文件夹下文件的个数 ls -l |grep "^-"|wc -l ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(三)——Springboot配置文件
SpringBoot不像之前用spring+springMVC做项目的时候,他不需要配置大量的看上去很乱很复杂的xml配置文件.在SpringBoot中你可以通过java代码和注解配置项目,也可以通过 ...
- C++11常用特性介绍——for循环新用法
一.for循环新用法——基于范围的for循环 for(元素类型 元素对象 : 容器对象) { //遍历 } 1)遍历字符串 std::string str = "hello world&qu ...
- TCP通讯代码
服务端代码: import socket server_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) # 使用固定端口 server_ ...
- centos7的网络管理(参考使用)
How to Setup network on centos 7 Posted krizna Centos, Centos 7 After installing Centos 7, You may ...
- Caffe2 手册(Intro Tutorial)[2]
Caffe2的相关概念 接下来你可以学到更多Caffe2中主要的概念,这些概念对理解和开发Caffe2相当重要. Blobs and Workspace,Tensors Caffe2中,数据是 ...
- WPS 2019文档编辑 技巧
wps2019文档怎么设置粘贴时自动匹配当前的格式: 菜单栏 文件 -- 选项 -- 编辑 -- 默认粘贴方式 设置为 匹配当前格式. 在编辑文档左侧或右侧显示/隐藏 目录/书签: 视图 -- 导航窗 ...
- c++继承:公有、私有、保护(对应p12访问限制)
公有继承(public).私有继承(private).保护继承(protected)是常用的三种继承方式. 1. 公有继承(public) 公有继承的特点是基类的公有成员和保护成员作为派生类的成员时, ...
