LeetCode链表专题
链表
套路总结
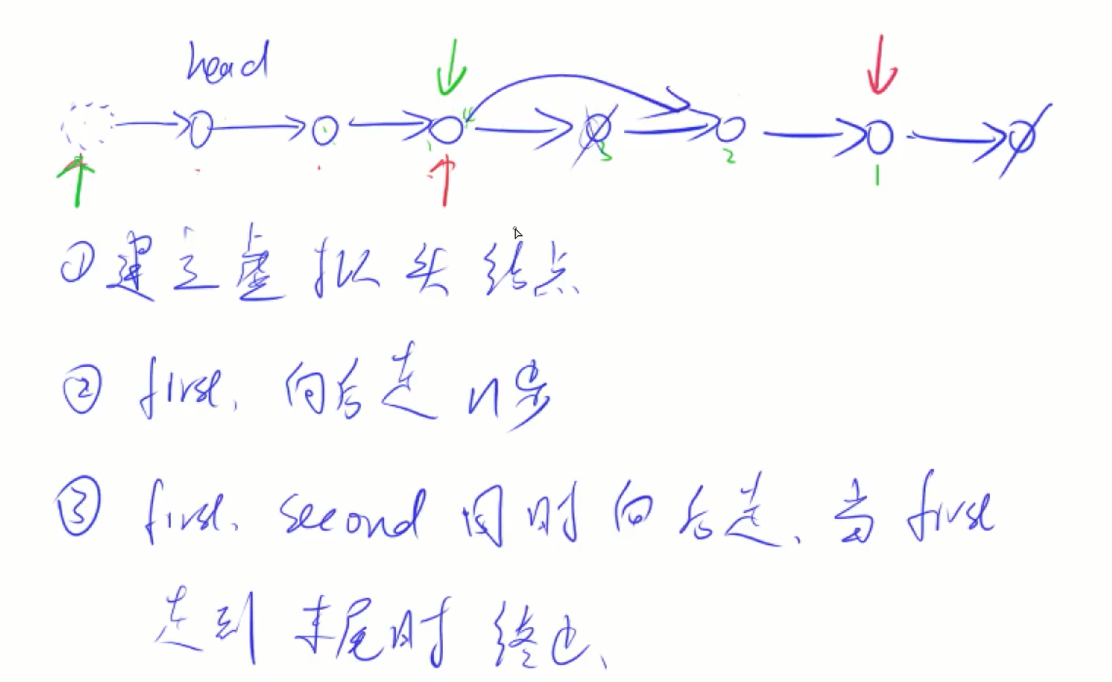
1.多个指针 移动
2.虚假链表头:凡是有可能删除头节点的都创建一个虚拟头节点,代码可以少一些判断(需要用到首部前一个元素的时候就加虚拟头指针)
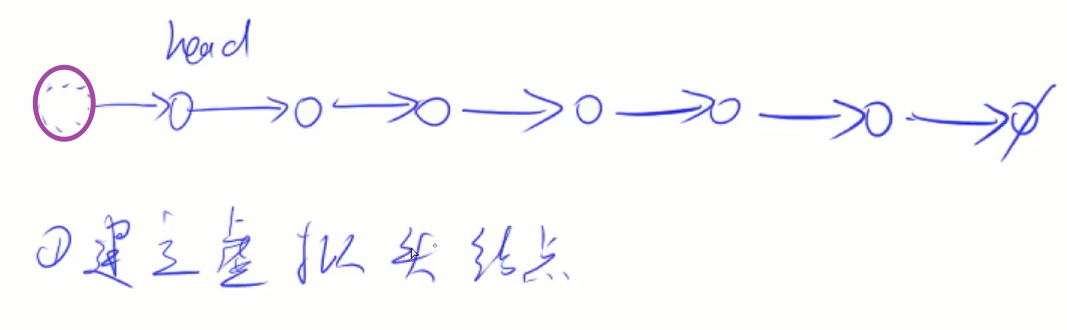
3.快慢指针
如leetcode142 快慢指针找链表环的起点
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目要求:只扫描一遍
删除链表,肯定要找到被删节点的前一个节点
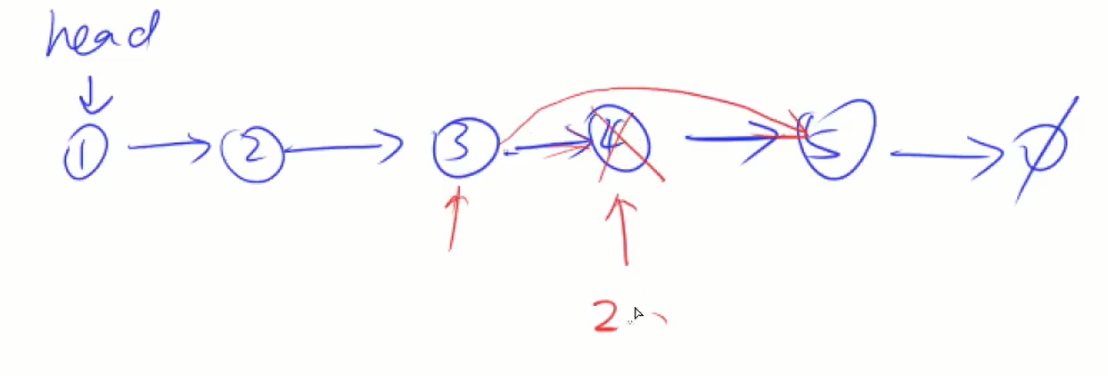
1.找到倒数第n个节点的前一个节点(倒数第n+1)
2.双指针
first指针指向第k个,second头指针指向虚假头节点,两个指针一起移动,当first指针指向最后一个节点的时候(first下一个节点为NULL),就说明second到达了倒数第k个节点
3.删除即可 second ->next = second->next->next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto first = dummy;
auto second = dummy;
while(n--) first = first->next;
while(first->next != NULL){
second = second->next;
first = first->next;
}
second->next = second->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
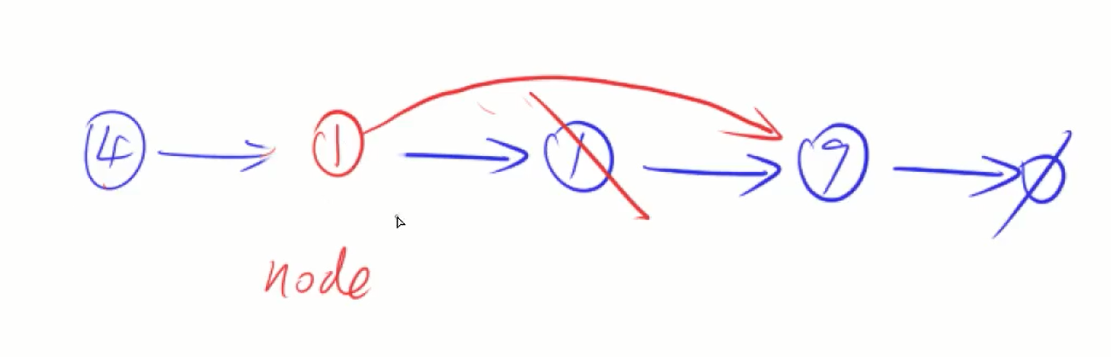
237. 删除链表中的节点
例如,给定node指向5这个点,删除5这个点
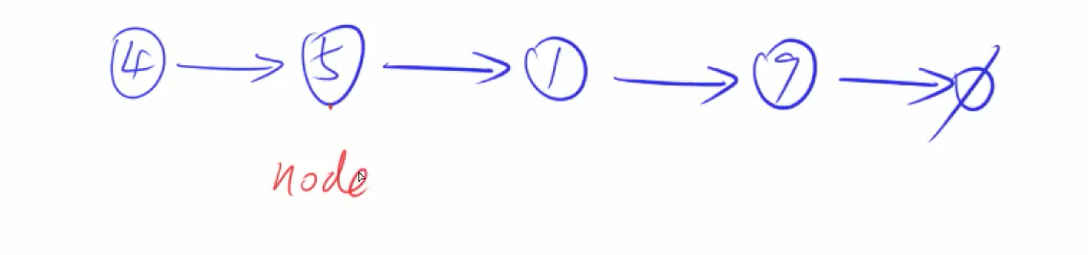
真正意义删除要知道被删除节点的上一个点
假装删除,把这个点的值伪装成下一个点的值,把下一个点删掉即可
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
if(node->next){
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
}
return;
}
};
C++语法把node两个属性的值都一起替换为下一个节点的属性

*(node) = *(node->next);
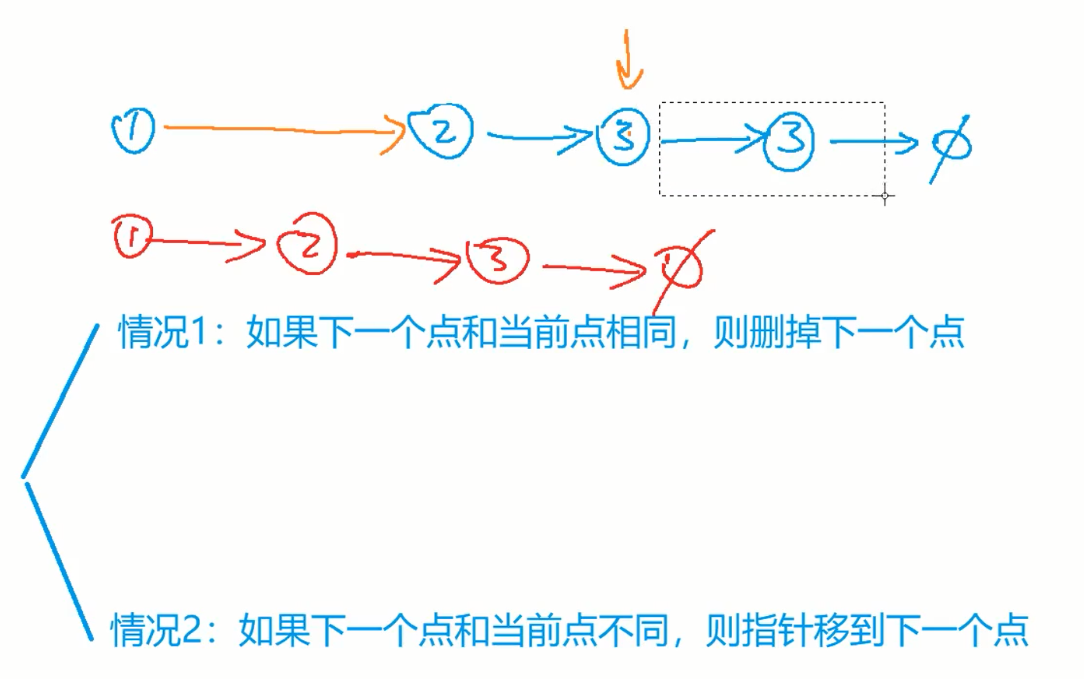
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
auto *first = head;
while(first && first->next){
if(first->val == first->next->val){
first->next = first->next->next;
}else{
first = first->next;
//这里first可能移动到了空 所以要判断first是否空
}
}
return head;
}
};
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto pre = dummy,cur = pre->next;
int cnt = 0;
while(pre && cur){
cnt = 0;
auto nxt = cur->next;
while(nxt && nxt->val == cur->val) {
cnt++;
nxt = nxt->next;
}
if(cnt >= 1){
pre->next = nxt;
cur = pre->next;
}else{
pre = pre->next;
cur = pre->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
61. 旋转链表
两个指针,距离为k
(不需要用到虚拟头节点,头节点会改变时用到)
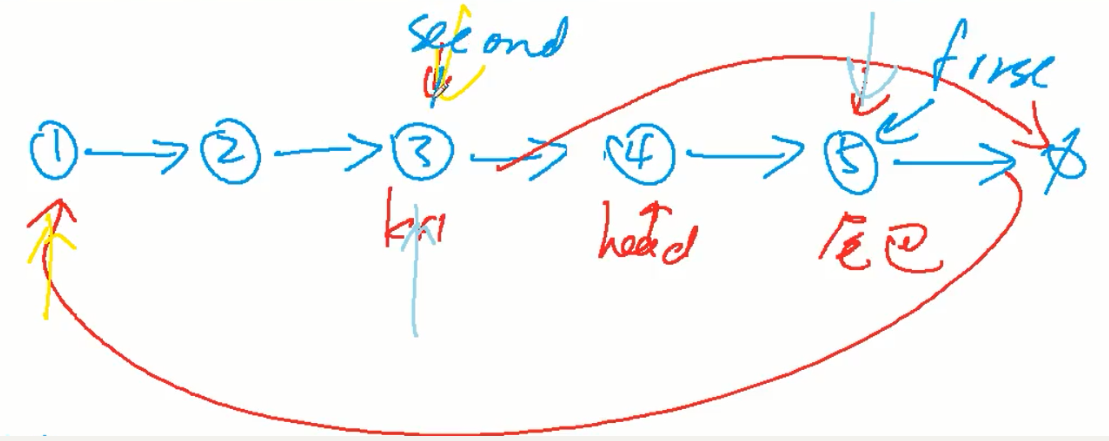

之后让first->next指向开头head,再让head指向现在的头(second->next)!
再让second->next指向空
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return NULL;
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head;p;p=p->next) n++;
k %= n;
auto first = head,second = head;
while(k--) first = first->next;
while(first->next){
first=first->next;
second=second->next;
}
first->next = head;
head = second->next;
second->next = NULL;
return head;
}
};
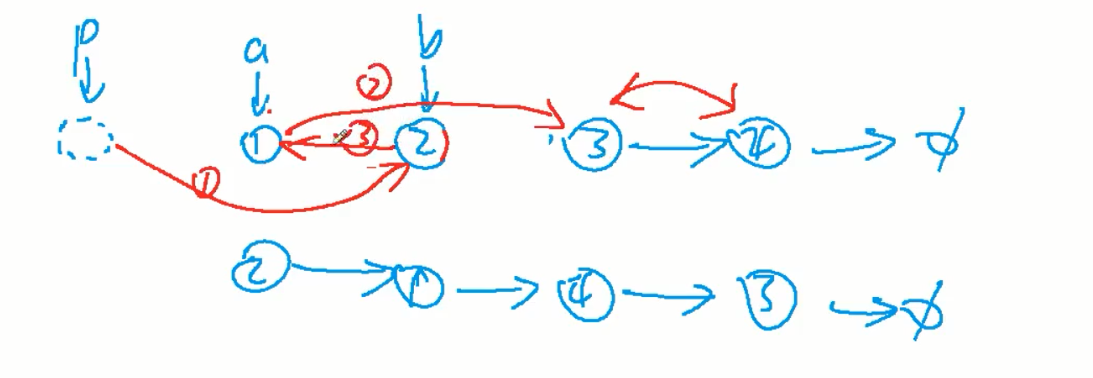
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
1.建立虚拟头节点,因为头节点可能会改变
2.三个指针

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
for(auto p = dummy;p->next && p->next->next;){
auto a = p->next,b = a->next;
p->next = b;
a->next = b->next;
b->next = a;
p = a; //指向下一个新的两对前的最后一个点
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
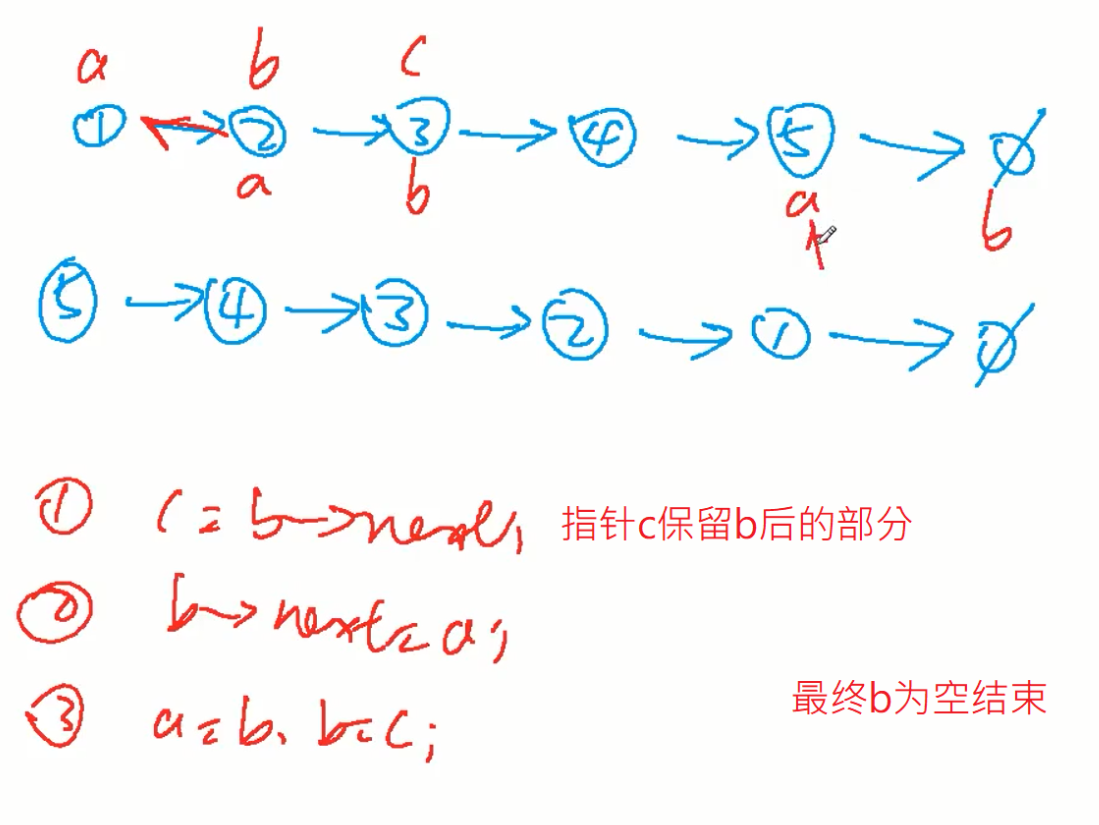
206. 反转链表
两个翻转指针a,b;一个保留指针c保留b后面的链防止被删除,不需要虚拟头节点因为不需要用到首部前一个
分三步
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return NULL;
auto a = head,b = head->next;
while(b){
auto c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
head->next = NULL;//原来头是原来的第一节点 现在的最后一个节点所以指向空
head = a;
return head;
}
};
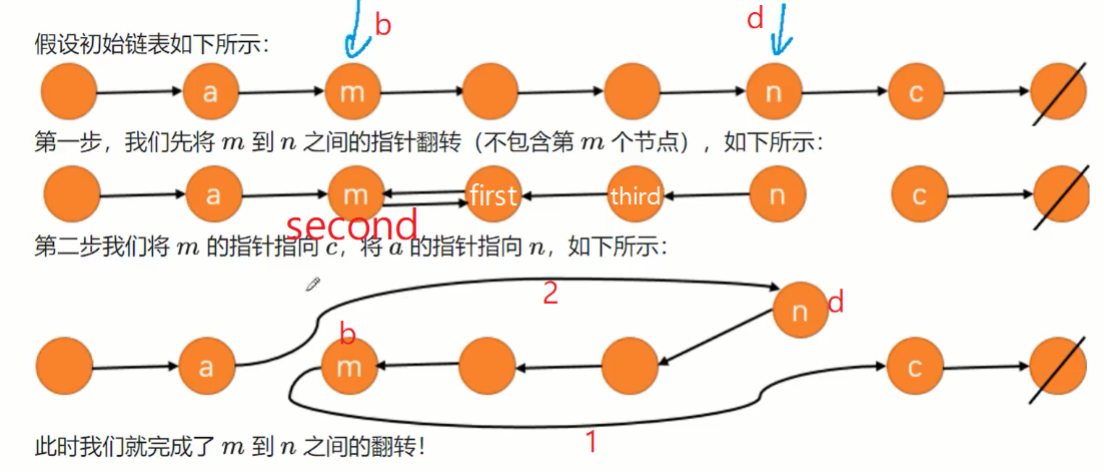
92. 反转链表 II
1.因为头节点会发生变化,设置虚拟头节点
2.a指针移动到翻转前一个点,b指针移动第一个翻转的点,d指针移动到最后一个翻转的点。c指针指向最后一个翻转的点的下一个点。然后翻转b~d之间的点和206题一样
3.连接a->d,b->c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(m == n) return head;
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1); //虚拟头节点
dummy->next = head;
//找到a和d
auto a = dummy,d = dummy;
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++) {
a = a->next;//不设置虚拟头节点的话,如果n=1就找不到了a
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) d = d->next;
//找到b和c
auto b = a->next, c = d->next;
//翻转b和d之间的数字
for(auto first = b->next,second = b; first != c;){
auto third = first->next;
first->next = second;
second = first,first = third;
}
//连接
b->next = c;
a->next = d;
return dummy->next;
}
};
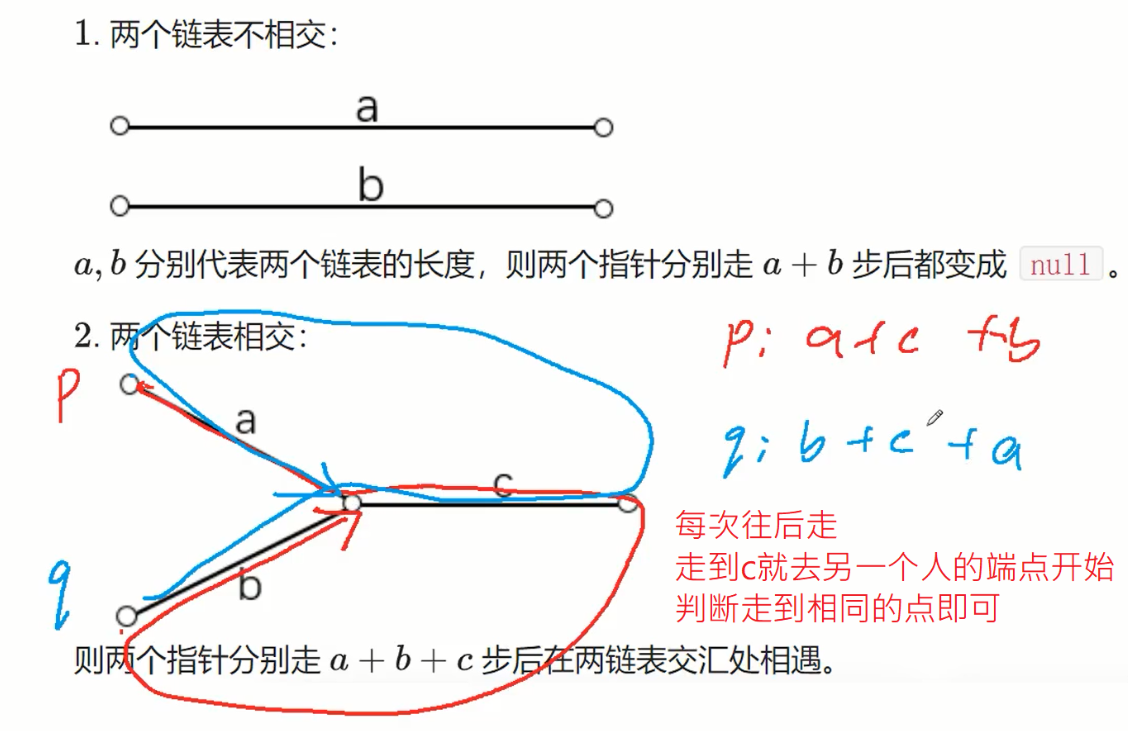
160. 相交链表
相遇:当指针p和指针q走的路程相等时相遇
考虑都走a+b+c的倍数,肯定会相遇
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto tempHeadA = headA;
auto tempHeadB = headB;
while(tempHeadA != tempHeadB){
if(tempHeadA) tempHeadA = tempHeadA->next;
else tempHeadA = headB;
if(tempHeadB) tempHeadB = tempHeadB->next;
else tempHeadB = headA;
}
return tempHeadB;
}
};
142. 环形链表 II
快慢指针
1.快指针慢指针从head头部出发,fast快指针每次走两步,slow慢指针每次走一步直到相遇。
2.把其中一个指针移动到head头部,快慢指针再每次走一步直到相遇,相遇点即为答案;
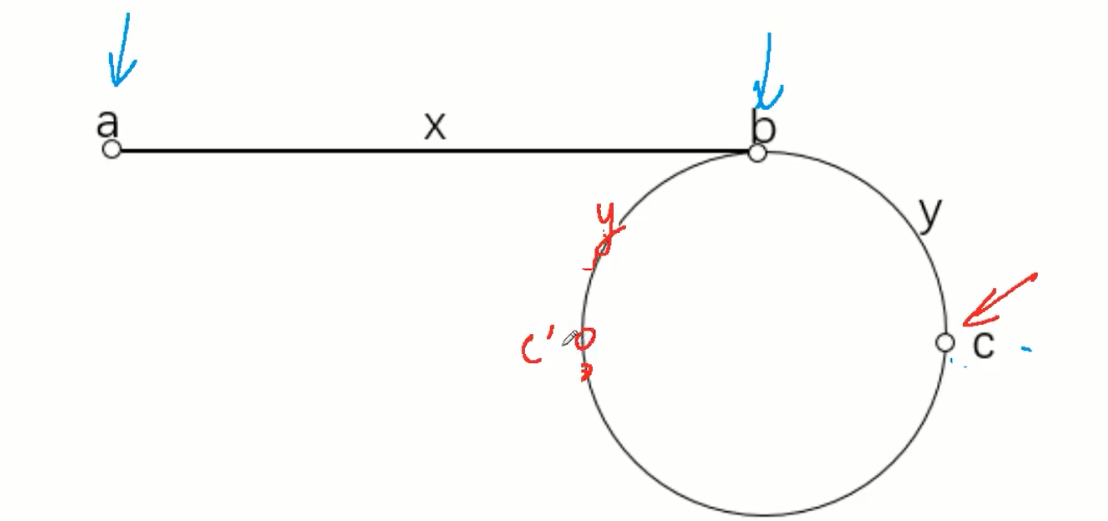
证明:利用快指针走动过的是慢指针的二倍,假设环起点坐标为x,第一次相遇点距离换起点距离为y。
可列公式2×(x+n1×c+y)=x+y+n2×c ,化简得x+y=(n2-n1)×c。
大白话说就是:非环部分的长度+环起点到相遇点之间的长度就是环的整数倍。
即x+y为环的整数倍
那么第一次相遇时我们现在距离环起点为y,所以只要再走x就到环起点了
再走x的话就让一个指针从head走,另一个从第一次相遇点走,每次都走1步
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
auto fast = head,slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next;
fast = fast->next; //快指针移动两次
slow = slow->next; //慢指针移动1次
if(fast == slow){ //当快慢指针相遇时退出
break;
}
}
if(fast==NULL || fast->next == NULL)
return NULL;
else{
slow = head; //让其中一个指针移动到头部
while(fast != slow){ //再走到相遇点即可
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
};
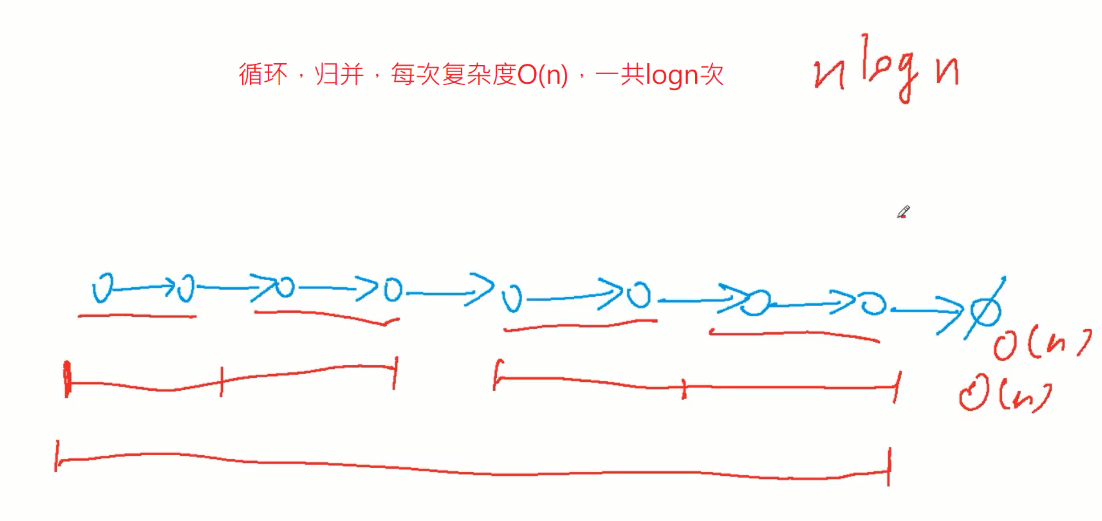
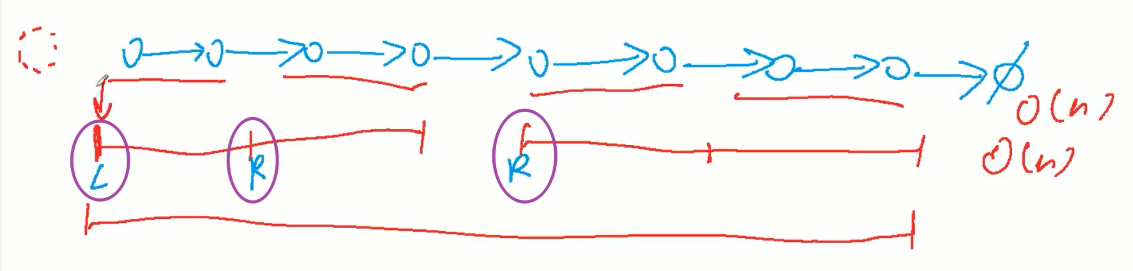
148. 排序链表
要求空间常数,时间O(nlogn)
因为快排用到递归(栈),空间为logn;递归版归并空间消耗大;所以用迭代版归并
自底向上代码写法:先枚举长度为2,分成一半,左右归并;再枚举长度为4...
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
int n = 0;
for(auto p = head; p ; p = p -> next) n++;
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
for(int i=1; i<n ; i*=2){ //枚举每一段的一半长
auto cur = dummy;
for(int j=0; j+i<n ; j+=i*2){
auto left = cur->next; //左半段边界指针
auto right = cur->next; //右半段边界指针
for(int k=0;k<i;k++) right = right->next;
int l = 0,r = 0;
while(l < i && r < i && right){ //归并比较左右哪个大
if(left->val <= right-> val){
cur->next = left;
cur = left;
left = left->next;
l++;
}else{
cur->next = right;
cur = right;
right = right->next;
r++;
}
}
//一个先到了末尾 所以要拼接另一端的剩余部分
while(l < i){
cur->next = left;
cur = left;
left = left->next;
l++;
}
while(r < i && right){
cur->next = right;
cur = right;
right = right->next;
r++;
}
cur->next = right; //拼接下一段 这里的right最终指向了下一段的left
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
21. 合并两个有序链表
(线性合并) O(n)O(n)
1.新建头部的保护结点 dummy,设置 cur 指针指向 dummy。
2.如果p的值比q小,就将cur->next = p,否则让cur -> next = q (选小的先连接)
循环以上步骤直到 l1l1 或 l2l2 为空。
3.将剩余的 p或 q连 接到 cur 指针后边。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
auto dummmy = new ListNode(-1);
auto cur = dummmy;
auto p = l1,q = l2;
//选小的优先
while(p && q){
if(p->val <= q->val){
cur->next = p;
cur = p;
p = p->next;
}else{
cur->next = q;
cur = q;
q = q->next;
}
}
//加入剩余
while(p){
cur->next = p;
p = p->next;
}
while(q){
cur->next = q;
q = q->next;
}
// cur->next = (p != NULL ? p : q);
return dummmy->next;
}
};
LeetCode链表专题的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 单链表专题 (一)
目录 LeetCode 单链表专题 <c++> \([2]\) Add Two Numbers \([92]\) Reverse Linked List II \([86]\) Parti ...
- LeetCode:链表专题
链表专题 参考了力扣加加对与链表专题的讲解,刷了些 leetcode 题,在此做一些记录,不然没几天就没印象了 出处:力扣加加-链表专题 总结 leetcode 中对于链表的定义 // 定义方式1: ...
- LeetCode刷题 链表专题
链表专题 链表题目的一般做法 单链表的结构类型 删除节点 方法一 方法二 增加节点 LeedCode实战 LC19.删除链表的倒数第N个结点 解法思路 LC24.两两交换链表中的节点 解法思路 LC6 ...
- LeetCode 字符串专题(一)
目录 LeetCode 字符串专题 <c++> \([5]\) Longest Palindromic Substring \([28]\) Implement strStr() [\(4 ...
- [LeetCode] [链表] 相关题目总结
刷完了LeetCode链表相关的经典题目,总结一下用到的技巧: 技巧 哑节点--哑节点可以将很多特殊case(比如:NULL或者单节点问题)转化为一般case进行统一处理,这样代码实现更加简洁,优雅 ...
- LeetCode树专题
LeetCode树专题 98. 验证二叉搜索树 二叉搜索树,每个结点的值都有一个范围 /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNod ...
- Leetcode链表
Leetcode链表 一.闲聊 边学边刷的--慢慢写慢慢更 二.题目 1.移除链表元素 题干: 思路: 删除链表节点,就多了一个判断等值. 由于是单向链表,所以要删除节点时要找到目标节点的上一个节点, ...
- [LeetCode 总结帖]: 链表专题
链表在笔试面试中都是出镜率极高的一种数据结构. 由于链表具有结构简单,代码量较少,变化多,可以较为全面的考察应聘者的逻辑思考能力以及应变能力的特点,而备受面试官青睐. 在本节中,我将Leetcode中 ...
- [LeetCode] 链表反转相关题目
暂时接触到LeetCode上与链表反转相关的题目一共有3道,在这篇博文里面总结一下.首先要讲一下我一开始思考的误区:链表的反转,不是改变节点的位置,而是改变每一个节点next指针的指向. 下面直接看看 ...
随机推荐
- GC日志分析详解
点击返回上层目录 原创声明:作者:Arnold.zhao 博客园地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zh94 GC日志分析详解 以ParallelGC为例,YoungGC日志解释如下 ...
- Android--sos闪光灯
Camera camera = null; Parameters parameters = null; Handler handler = new Handler() { @Override publ ...
- mac使用brew安装mysql5.7
安装mysql5.7 brew install mysql@5.7 设置环境变量(可能安装完自动生成过了,可以cat ~/.zshrc看一下,有了就不用添加了 ) echo 'export PATH= ...
- Openstack object list 一次最多有一万个 object
When you request a list of containers or objects, Object Storage returns a maximum of 10,000 names f ...
- Ubuntu 之 win10更新ubuntu启动项消失
问题描述: 昨晚windows更新,今天启动的时候发现启动项没有了,直接进入windows. 解决方案一: 首先进入BIOS看一看是否开启启动项选择,然后再把安全模式(secure boot)关闭(重 ...
- sed 和 awk
sed [选项] 动作 文件 -n #取消默认输出 ,有n必须要有p,有p加了n才不会有默认输出 -i #真正的替换,修改 -r #支持扩展正则 (* [A-z] '|') 内部命令: p #打印 - ...
- 【集群实战】NFS服务常见故障排查和解决方法
NFS,全名叫Network File System,中文叫网络文件系统,是Linux.UNIX系统的分布式文件系统的一个组成部分,可实现在不同网络上共享远程文件系统. NFS由Sun公司开发,目前已 ...
- time wait 整理
目录 状态转换图 1.谁会进入time wait状态: 主动发起断开连接的一方调用close()函数发送FIN并进入FIN WAIT 1状态,当收到对面反馈的ack之后会进入FIN WAIT2状态.之 ...
- 一句话教你分清楚UML组合聚合和联系!
组合:组合后的实体消失,则所有构成实体的部件都无意义,可以理解为不能独立存在 定义: 与聚合相比,组合描述的是这样的关联关系,部分离开整体后就没有实际意义了.所以我们说组合是一种很强的关联关系. 例子 ...
- 虚拟机上图片服务器搭建(FastDFS+nginx)
文件服务器 0.提前建好需要的文件夹(/home/fastdfs) /home/fastdfs/tracker /home/fastdfs/storage /home/fastdfs/storage/ ...
