从flink-example分析flink组件(3)WordCount 流式实战及源码分析
前面介绍了批量处理的WorkCount是如何执行的
<从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析>
<从flink-example分析flink组件(2)WordCount batch实战及源码分析----flink如何在本地执行的?>
这篇从WordCount的流式处理开始
/**
* Implements the "WordCount" program that computes a simple word occurrence
* histogram over text files in a streaming fashion.
*
* <p>The input is a plain text file with lines separated by newline characters.
*
* <p>Usage: <code>WordCount --input <path> --output <path></code><br>
* If no parameters are provided, the program is run with default data from
* {@link WordCountData}.
*
* <p>This example shows how to:
* <ul>
* <li>write a simple Flink Streaming program,
* <li>use tuple data types,
* <li>write and use user-defined functions.
* </ul>
*/
public class WordCount { // *************************************************************************
// PROGRAM
// ************************************************************************* public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Checking input parameters
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args); // set up the execution environment
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); // make parameters available in the web interface
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params); // get input data
DataStream<String> text;
if (params.has("input")) {
// read the text file from given input path
text = env.readTextFile(params.get("input"));
} else {
System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set.");
System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input.");
// get default test text data
text = env.fromElements(WordCountData.WORDS);
} DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.keyBy(0).sum(1); //1 // emit result
if (params.has("output")) {
counts.writeAsText(params.get("output"));
} else {
System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path.");
counts.print();
} // execute program
env.execute("Streaming WordCount");//2
} // *************************************************************************
// USER FUNCTIONS
// ************************************************************************* /**
* Implements the string tokenizer that splits sentences into words as a
* user-defined FlatMapFunction. The function takes a line (String) and
* splits it into multiple pairs in the form of "(word,1)" ({@code Tuple2<String,
* Integer>}).
*/
public static final class Tokenizer implements FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> { @Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) {
// normalize and split the line
String[] tokens = value.toLowerCase().split("\\W+"); // emit the pairs
for (String token : tokens) {
if (token.length() > 0) {
out.collect(new Tuple2<>(token, 1));
}
}
}
} }
整个执行流程如下图所示:
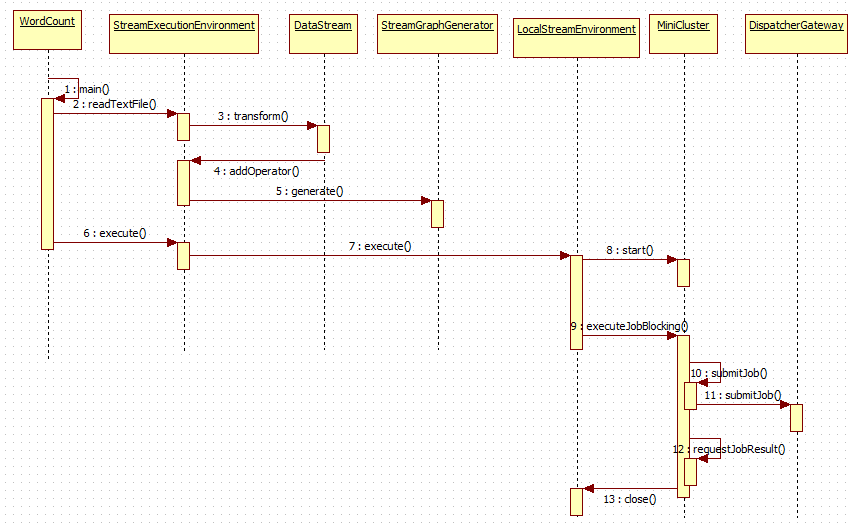
第1~4步:main方法读取文件,增加算子
private <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> createFileInput(FileInputFormat<OUT> inputFormat,
TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo,
String sourceName,
FileProcessingMode monitoringMode,
long interval) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputFormat, "Unspecified file input format.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(typeInfo, "Unspecified output type information.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(sourceName, "Unspecified name for the source.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(monitoringMode, "Unspecified monitoring mode."); Preconditions.checkArgument(monitoringMode.equals(FileProcessingMode.PROCESS_ONCE) ||
interval >= ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction.MIN_MONITORING_INTERVAL,
"The path monitoring interval cannot be less than " +
ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction.MIN_MONITORING_INTERVAL + " ms."); ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction<OUT> monitoringFunction =
new ContinuousFileMonitoringFunction<>(inputFormat, monitoringMode, getParallelism(), interval); ContinuousFileReaderOperator<OUT> reader =
new ContinuousFileReaderOperator<>(inputFormat); SingleOutputStreamOperator<OUT> source = addSource(monitoringFunction, sourceName)
.transform("Split Reader: " + sourceName, typeInfo, reader); //1 return new DataStreamSource<>(source);
}
增加算子的方法,当调用execute方法时,此时增加的算子会被执行。
/**
* Adds an operator to the list of operators that should be executed when calling
* {@link #execute}.
*
* <p>When calling {@link #execute()} only the operators that where previously added to the list
* are executed.
*
* <p>This is not meant to be used by users. The API methods that create operators must call
* this method.
*/
@Internal
public void addOperator(StreamTransformation<?> transformation) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(transformation, "transformation must not be null.");
this.transformations.add(transformation);
}
第5步:产生StreamGraph,从而可以得到JobGraph,即将Stream程序转换成JobGraph
// transform the streaming program into a JobGraph
StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph();
streamGraph.setJobName(jobName); JobGraph jobGraph = streamGraph.getJobGraph();
jobGraph.setAllowQueuedScheduling(true);
第6~8步启动MiniCluster,为执行job做准备
/**
* Starts the mini cluster, based on the configured properties.
*
* @throws Exception This method passes on any exception that occurs during the startup of
* the mini cluster.
*/
public void start() throws Exception {
synchronized (lock) {
checkState(!running, "MiniCluster is already running"); LOG.info("Starting Flink Mini Cluster");
LOG.debug("Using configuration {}", miniClusterConfiguration); final Configuration configuration = miniClusterConfiguration.getConfiguration();
final boolean useSingleRpcService = miniClusterConfiguration.getRpcServiceSharing() == RpcServiceSharing.SHARED; try {
initializeIOFormatClasses(configuration); LOG.info("Starting Metrics Registry");
metricRegistry = createMetricRegistry(configuration); // bring up all the RPC services
LOG.info("Starting RPC Service(s)"); AkkaRpcServiceConfiguration akkaRpcServiceConfig = AkkaRpcServiceConfiguration.fromConfiguration(configuration); final RpcServiceFactory dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory; if (useSingleRpcService) {
// we always need the 'commonRpcService' for auxiliary calls
commonRpcService = createRpcService(akkaRpcServiceConfig, false, null);
final CommonRpcServiceFactory commonRpcServiceFactory = new CommonRpcServiceFactory(commonRpcService);
taskManagerRpcServiceFactory = commonRpcServiceFactory;
dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory = commonRpcServiceFactory;
} else {
// we always need the 'commonRpcService' for auxiliary calls
commonRpcService = createRpcService(akkaRpcServiceConfig, true, null); // start a new service per component, possibly with custom bind addresses
final String jobManagerBindAddress = miniClusterConfiguration.getJobManagerBindAddress();
final String taskManagerBindAddress = miniClusterConfiguration.getTaskManagerBindAddress(); dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory = new DedicatedRpcServiceFactory(akkaRpcServiceConfig, jobManagerBindAddress);
taskManagerRpcServiceFactory = new DedicatedRpcServiceFactory(akkaRpcServiceConfig, taskManagerBindAddress);
} RpcService metricQueryServiceRpcService = MetricUtils.startMetricsRpcService(
configuration,
commonRpcService.getAddress());
metricRegistry.startQueryService(metricQueryServiceRpcService, null); ioExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Hardware.getNumberCPUCores(),
new ExecutorThreadFactory("mini-cluster-io"));
haServices = createHighAvailabilityServices(configuration, ioExecutor); blobServer = new BlobServer(configuration, haServices.createBlobStore());
blobServer.start(); heartbeatServices = HeartbeatServices.fromConfiguration(configuration); blobCacheService = new BlobCacheService(
configuration, haServices.createBlobStore(), new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), blobServer.getPort())
); startTaskManagers(); MetricQueryServiceRetriever metricQueryServiceRetriever = new RpcMetricQueryServiceRetriever(metricRegistry.getMetricQueryServiceRpcService()); dispatcherResourceManagerComponents.addAll(createDispatcherResourceManagerComponents(
configuration,
dispatcherResourceManagreComponentRpcServiceFactory,
haServices,
blobServer,
heartbeatServices,
metricRegistry,
metricQueryServiceRetriever,
new ShutDownFatalErrorHandler()
)); resourceManagerLeaderRetriever = haServices.getResourceManagerLeaderRetriever();
dispatcherLeaderRetriever = haServices.getDispatcherLeaderRetriever();
webMonitorLeaderRetrievalService = haServices.getWebMonitorLeaderRetriever(); dispatcherGatewayRetriever = new RpcGatewayRetriever<>(
commonRpcService,
DispatcherGateway.class,
DispatcherId::fromUuid,
20,
Time.milliseconds(20L));
resourceManagerGatewayRetriever = new RpcGatewayRetriever<>(
commonRpcService,
ResourceManagerGateway.class,
ResourceManagerId::fromUuid,
20,
Time.milliseconds(20L));
webMonitorLeaderRetriever = new LeaderRetriever(); resourceManagerLeaderRetriever.start(resourceManagerGatewayRetriever);
dispatcherLeaderRetriever.start(dispatcherGatewayRetriever);
webMonitorLeaderRetrievalService.start(webMonitorLeaderRetriever);
}
catch (Exception e) {
// cleanup everything
try {
close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
e.addSuppressed(ee);
}
throw e;
} // create a new termination future
terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>(); // now officially mark this as running
running = true; LOG.info("Flink Mini Cluster started successfully");
}
}
第9~12步 执行job
/**
* This method runs a job in blocking mode. The method returns only after the job
* completed successfully, or after it failed terminally.
*
* @param job The Flink job to execute
* @return The result of the job execution
*
* @throws JobExecutionException Thrown if anything went amiss during initial job launch,
* or if the job terminally failed.
*/
@Override
public JobExecutionResult executeJobBlocking(JobGraph job) throws JobExecutionException, InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(job, "job is null"); final CompletableFuture<JobSubmissionResult> submissionFuture = submitJob(job); final CompletableFuture<JobResult> jobResultFuture = submissionFuture.thenCompose(
(JobSubmissionResult ignored) -> requestJobResult(job.getJobID())); final JobResult jobResult; try {
jobResult = jobResultFuture.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), "Could not retrieve JobResult.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(e));
} try {
return jobResult.toJobExecutionResult(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(job.getJobID(), e);
}
}
先上传jar包文件,此时需要DispatcherGateway来执行上转任务,异步等待结果执行完毕
总结:
batch和stream的执行流程很相似,又有不同。
不同:Stream传递的是DataStream,Batch传递的是DataSet
相同:都转换成JobGraph执行
从flink-example分析flink组件(3)WordCount 流式实战及源码分析的更多相关文章
- SpringCloudGateway微服务网关实战与源码分析 - 中
实战 路由过滤器工厂 路由过滤器允许以某种方式修改传入的HTTP请求或传出的HTTP响应.路由过滤器的作用域是特定的路由.SpringCloud Gateway包括许多内置的GatewayFilter ...
- Vue3中的响应式对象Reactive源码分析
Vue3中的响应式对象Reactive源码分析 ReactiveEffect.js 中的 trackEffects函数 及 ReactiveEffect类 在Ref随笔中已经介绍,在本文中不做赘述 本 ...
- Flink sql 之AsyncIO与LookupJoin的几个疑问 (源码分析)
本文源码基于flink 1.14 被同事问到几个关于AsyncIO和lookUp维表的问题所以翻了下源码,从源码的角度解惑这几个问题 对于AsyncIO不了解的可以看看之前写的这篇 <Flin ...
- bootstrap_栅格系统_响应式工具_源码分析
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------margin 为负 使盒子重叠 等高 等高 ...
- Netty源码分析 (十二)----- 心跳服务之 IdleStateHandler 源码分析
什么是心跳机制? 心跳说的是在客户端和服务端在互相建立ESTABLISH状态的时候,如何通过发送一个最简单的包来保持连接的存活,还有监控另一边服务的可用性等. 心跳包的作用 保活Q:为什么说心跳机制能 ...
- 从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析
上一章<windows下flink示例程序的执行> 简单介绍了一下flink在windows下如何通过flink-webui运行已经打包完成的示例程序(jar),那么我们为什么要使用fli ...
- SpringCloudAlibaba注册中心与配置中心之利器Nacos实战与源码分析(上)
不断踩坑并解决问题是每个程序员进阶到资深的必要经历并以此获得满足感,而不断阅读开源项目源码和总结思想是每个架构师成长最佳途径.本篇拉开SpringCloud Alibaba最新版本实战和原理序幕,以工 ...
- SpringCloudAlibaba分布式流量控制组件Sentinel实战与源码分析(上)
概述 定义 Sentinel官网地址 https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/index.html 最新版本v1.8.4 Sentinel官网文档地址 https://senti ...
- SpringCloud Gateway微服务网关实战与源码分析-上
概述 定义 Spring Cloud Gateway 官网地址 https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-gateway/ 最新版本3.1.3 Spring Cl ...
随机推荐
- python实现常用查找算法
http://www.cnblogs.com/feixuelove1009/p/6148357.html
- Spring Boot:整合Spring Data JPA
综合概述 JPA是Java Persistence API的简称,是一套Sun官方提出的Java持久化规范.其设计目标主要是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合ORM技术,它为Java开发人员提供了一种 ...
- JIRA的安装部署问题
JIRA的安装部署问题: 因电脑上装了两人系统,导致我的JIRA服务不能和tomcat同时启动,让我弄了好久都不知道是啥原因,经过请教,总算得出原来是JIRA的Port和Tomcat的Port冲突.在 ...
- node.js的异步I/O、事件驱动、单线程
nodejs的特点总共有以下几点 异步I/O(非阻塞I/O) 事件驱动 单线程 擅长I/O密集型,不擅长CPU密集型 高并发 下面是一道很经典的面试题,描述了node的整体运行机制,相信很多人都碰到了 ...
- flume1.9 用户指南(中文版)
概述 Apache Flume是一个分布式,可靠且可用的系统,用于有效地从许多不同的source收集,聚合和移动大量日志数据到集中式数据存储. Apache Flume的使用不仅限于日志数据聚合.由于 ...
- HDU 1533:Going Home(KM算法求二分图最小权匹配)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 Going Home Problem Description On a grid map there ...
- [WPF自定义控件库]好用的VisualTreeExtensions
1. 前言 A long time ago in a galaxy far, far away....微软在Silverlight Toolkit里提供了一个好用的VisualTreeExtensio ...
- Docker笔记(二):Docker管理的对象
原文地址:http://blog.jboost.cn/2019/07/14/docker-2.html 在Docker笔记(一):什么是Docker中,我们提到了Docker管理的对象包含镜像.容器. ...
- java接口自动化(一) - 接口自动化测试整体认知 - 开山篇(超详解)
简介 了解什么是接口和为什么要做接口测试.并且知道接口自动化测试应该学习哪些技术以及接口自动化测试的落地过程.其实这些基本上在python接口自动化的文章中已经详细的介绍过了,不清楚的可以过去看看.了 ...
- Cookie起源与发展
上一篇我们在讲优酷弹幕爬虫的时候,引入了一个新的知识点:Cookie,由于篇幅有限当时只是简单的给大家介绍了一下它的作用,今天我们就来全面了解一下Cookie(小饼干)以及相关的知识! 相信很多同学肯 ...
