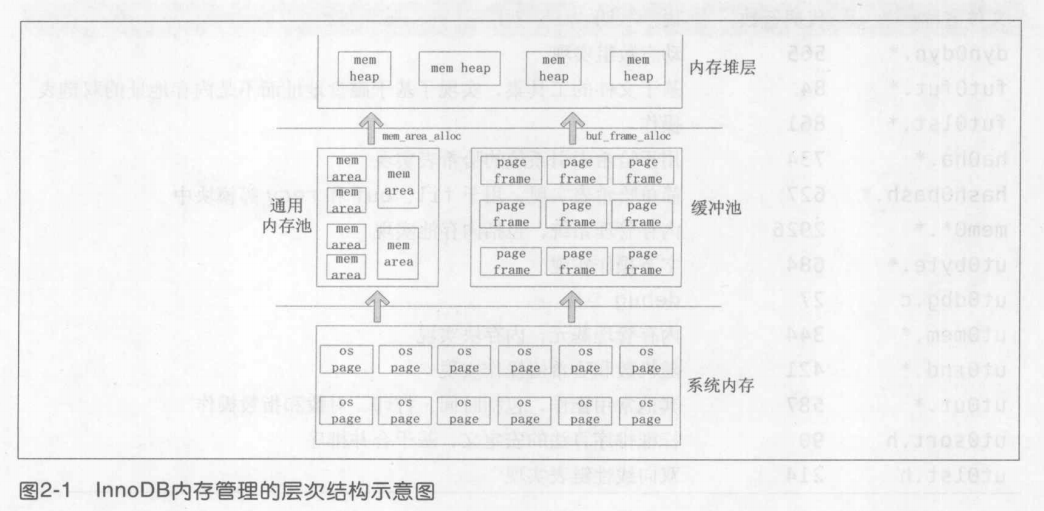
innodb源码解析 - mem0_.c - 基本内存管理
The basic element of the memory management is called a memory
heap. A memory heap is conceptually a
stack from which memory can be allocated. The stack may grow infinitely.
The top element of the stack may be freed, or
the whole stack can be freed at one time. The advantage of the
memory heap concept is that we can avoid using the malloc and free
functions of C which are quite expensive, for example, on the Solaris + GCC
system (50 MHz Sparc, 1993) the pair takes 3 microseconds,
on Win NT + 100MHz Pentium, 2.5 microseconds.
When we use a memory heap,
we can allocate larger blocks of memory at a time and thus
reduce overhead. Slightly more efficient the method is when we
allocate the memory from the index page buffer pool, as we can
claim a new page fast. This is called buffer allocation.
When we allocate the memory from the dynamic memory of the
C environment, that is called dynamic allocation.
Innodb内存管理的基本概念是一个内存堆,内存堆在概念上是一个stack,这个stack可能无限增长。这样的分配方式可以将多次的内存分配合并为单次进行,之后的内存请求就可以在Innodb内部进行,避免了多次频繁调用malloc和free的性能开销。此外,Innodb存储引擎还允许从缓冲池中分配内存建立内存堆,这样可以更快速的请求内存页。这种分配方式为缓冲区分配。将使用malloc分配内存的方法称为动态分配。
The default way of operation of the memory heap is the following.
First, when the heap is created, an initial block of memory is
allocated. In dynamic allocation this may be about 50 bytes.
If more space is needed, additional blocks are allocated
and they are put into a linked list.
After the initial block, each allocated block is twice the size of the previous, until a threshold is attained, after which the sizes of the blocks stay the same. An exception is, of course, the case where the caller requests a memory buffer whose size is bigger than the threshold. In that case a block big enough must be allocated.
The heap is physically arranged so that if the current block
becomes full, a new block is allocated and always inserted in the chain of blocks as the last block.
内存堆的分配方式如下:
首先,创建内存堆时,会使用动态分配创建一个大约的50bytes(64B)的初始的内存块。如果需要额外的空间,则分配更多的内存块,大小为前一个内存块的2倍,直到达到最阈值,之后的内存块大小保持不变,与之前的内存块组成一个 linked list。
当调用方请求的内存缓冲区大小超出阈值,则直接分配一个足够大小的内存块。
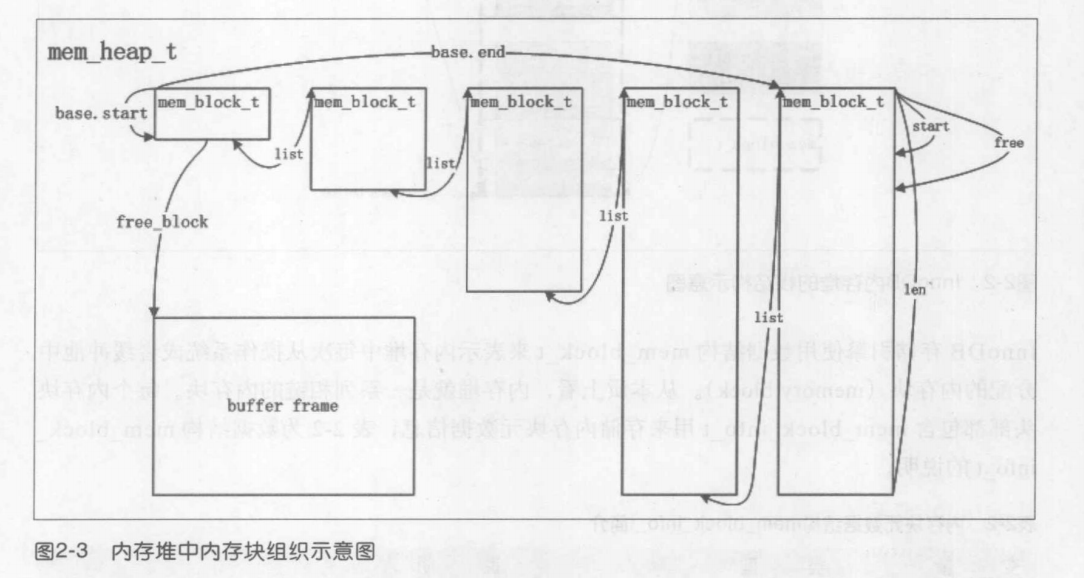
Innodb存储引擎使用 mem_block_t 来表示从内存或者缓冲池中分配的内存块,每个内存块头部都有一个mem_block_info_t 来保存内存堆的元数据信息。
struct mem_block_info_struct {
ulint magic_n;/* magic number for debugging */
//内存堆创建的文件名
char file_name[8];/* file name where the mem heap was created */
//内存堆创建的文件行号
ulint line; /* line number where the mem heap was created */
//用于链接内存堆中内存块的链表基节点,仅在内存堆的第一个内存块中定义
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(mem_block_t) base; /* In the first block in the
the list this is the base node of the list of blocks;
in subsequent blocks this is undefined */
//用于链接内存堆中各内存块的链表节点
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_block_t) list; /* This contains pointers to next
and prev in the list. The first block allocated
to the heap is also the first block in this list,
though it also contains the base node of the list. */
//内存块的大小
ulint len; /* physical length of this block in bytes */
//内存块的类型,分为以下三类:MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC MEM_HEAP_BUF MEM_HEAR_BTR_SEARCH
ulint type; /* type of heap: MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC, or
MEM_HEAP_BUF possibly ORed to MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH */
//如果为true,表示该内存块用于快速创建内存堆:内存将被创建者释放,而不是 mem_heap_free
ibool init_block; /* TRUE if this is the first block used in fast
creation of a heap: the memory will be freed
by the creator, not by mem_heap_free */
//内存块的空闲位置相对与起始位置的偏移量
ulint free; /* offset in bytes of the first free position for
user data in the block */
// 内存块创建时的free字段偏移位置
ulint start; /* the value of the struct field 'free' at the
creation of the block */
// 在 MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH 类型的堆中用来包含一个可作为堆空闲块的缓冲页框。该字段仅在堆需要更多空间时使用
byte* free_block;
/* if the MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH bit is set in type,
and this is the heap root, this can contain an
allocated buffer frame, which can be appended as a
free block to the heap, if we need more space;
otherwise, this is NULL */
#ifdef MEM_PERIODIC_CHECK
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_block_t) mem_block_list;
/* List of all mem blocks allocated; protected
by the mem_comm_pool mutex */
#endif
};
Innodb存储引擎定义了三种内存堆类型:
MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC:堆的内存调用通用内存池接口申请,使用malloc分配
MEM_HEAP_BUF:堆的内存从缓冲池中申请
MEM_HEAR_BTR_SEARCH:MEM_HEAP_BUF的子类型,仅在自适应hash索引中使用。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The main components of the memory consumption are:
1. buffer pool,
2. parsed and optimized SQL statements,
3. data dictionary cache,
4. log buffer,
5. locks for each transaction,
6. hash table for the adaptive index,
7. state and buffers for each SQL query currently being executed,
8. session for each user, and
9. stack for each OS thread.
Items 1-3 are managed by an LRU algorithm. Items 5 and 6 can potentially
consume very much memory. Items 7 and 8 should consume quite little memory,
and the OS should take care of item 9, which too should consume little memory.
MySQL内存管理的主要组成部分是:
1. 缓冲池
2. 分析优化过的SQL语句
3. 数据字典缓存
4. 日志缓冲区(redo)
5. 事务的锁
6. 自适应hash索引的hash表
7. 正在执行的SQL语句的查询的状态和缓冲区
8. 用户session
9. os 线程堆栈
其中,1~3通过LRU算法进行管理,5~6可能占用大量的内存,7~8占用少量的内存。操作系统处理9,也会占用少量的内存。
以上9大块通过4个部分进行管理:
1. buffer pool
2. redo log buffer
3. common buffer (2,3,5,6,7,8)
4. 8(用户session)
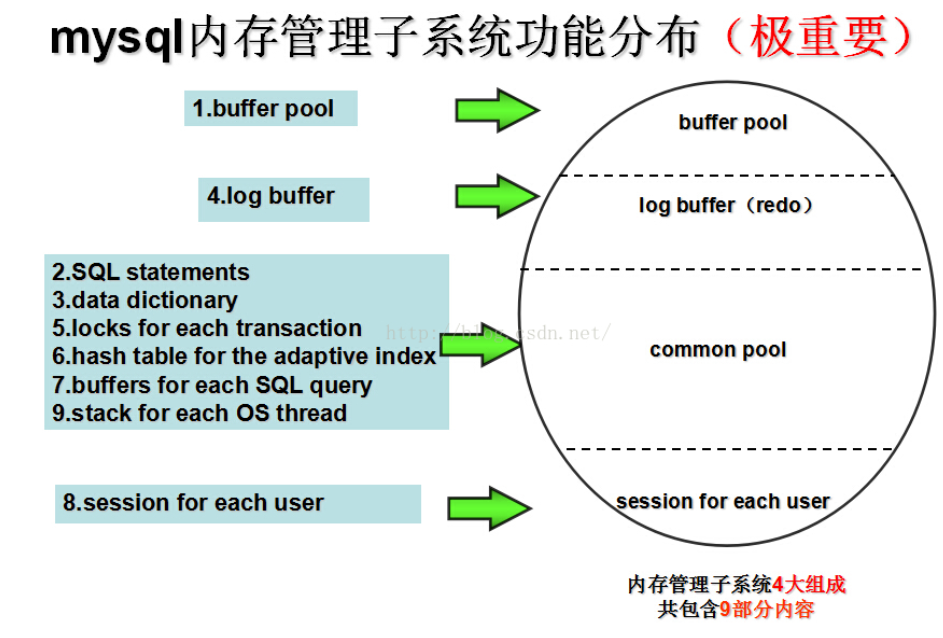
对于 5(事务的锁)和6(自适应hash索引),可能占用大量的内存,因此,最多可以占用通用缓冲池的大小,而后,将从buffer pool中获取内存。
在 Innodb存储引擎启动时,会有一个mem_comm_pool对象,代表着通用内存池,数据结构通过 mem_pool_struct来定义。
/* Data structure for a memory pool. The space is allocated using the buddy
algorithm, where free list i contains areas of size 2 to power i. */
struct mem_pool_struct{
// 内存池从操作系统中分配到的内存指针
byte* buf; /* memory pool */
// 内存池大小
ulint size; /* memory common pool size */
// 内存池中已经分配的内存大小
ulint reserved; /* amount of currently allocated
memory */
// mutex锁
mutex_t mutex; /* mutex protecting this struct */
// 可用内存区域列表, 用于内存池中内存单元的管理;内存池中所有内存区指针都包含在 free_list[64]数组中。[伙伴系统]
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(mem_area_t)
free_list[64]; /* lists of free memory areas: an
area is put to the list whose number
is the 2-logarithm of the area size */
}; struct mem_area_struct{
// 内存区的大小和是否空闲
ulint size_and_free; /* memory area size is obtained by
anding with ~MEM_AREA_FREE; area in
a free list if ANDing with
MEM_AREA_FREE results in nonzero */
// 用于将该内存区连接到 free_list[64]链表中
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_area_t)
free_list; /* free list node */
};
伙伴系统: 从内存池的管理角度分析,如果频繁的请求和释放不同大小的内存,会导致在内存池中存在大量的碎片化的小内存区。引发的问题是,即使内存池中有足够多的空闲内存可用,但是却无法分配一个大块的连续内存。Innodb内存池使用伙伴系统来解决问题:
1. 通用内存池通过 free_list 和 mem_area_struct组成伙伴系统,把内存池中内存分组为64个内存区链表,每个区链表分别包含 2^0,2^1,2^2 ... 2^64大小的内存区。
2. 对于通用内存池,如果申请一块64B的内存,则现在free_list[6] 链表中检查是否有一个空闲块。如果没有这样的块, 则在free_list[7]中寻找,如果存在,则内存池把free_list[7] 中的第一个128B内存块分为两等份,一半用于满足请求,一半插入到free_list[6]链表中。如果free_list[7]中也没有,就继续往上找。
3. 假设内存池大小为1M,初始化后为完整的内存。这时申请128KB大小的内存,内存池中没有128KB大小的内存,则往上找256KB大小,一直找到1024KB内存区。所以,此次分配会导致内存池将1M内存块分裂为 512KB,256KB和2个128KB内存区。
4. 当一个请求释放64KB内存,如果内存池中相邻一个空闲的64KB内存区,则合并为128KB的内存区。
innodb源码解析 - mem0_.c - 基本内存管理的更多相关文章
- LevelDB(v1.3) 源码阅读之 Arena(内存管理器)
LevelDB(v1.3) 源码阅读系列使用 LevelDB v1.3 版本的代码,可以通过如下方式下载并切换到 v1.3 版本的代码: $ git clone https://github.com/ ...
- Spark源码分析之九:内存管理模型
Spark是现在很流行的一个基于内存的分布式计算框架,既然是基于内存,那么自然而然的,内存的管理就是Spark存储管理的重中之重了.那么,Spark究竟采用什么样的内存管理模型呢?本文就为大家揭开Sp ...
- LevelDB源码分析之:arena内存管理
一.原理 arena是LevelDB内部实现的内存池. 我们知道,对于一个高性能的服务器端程序来说,内存的使用非常重要.C++提供了new/delete来管理内存的申请和释放,但是对于小对象来说,直接 ...
- 【Linux内存源码分析】vmalloc不连续内存管理(转)
https://www.jeanleo.com/2018/09/09/%E3%80%90linux%E5%86%85%E5%AD%98%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E ...
- Flink 源码解析 —— 深度解析 Flink 是如何管理好内存的?
前言 如今,许多用于分析大型数据集的开源系统都是用 Java 或者是基于 JVM 的编程语言实现的.最着名的例子是 Apache Hadoop,还有较新的框架,如 Apache Spark.Apach ...
- jQuery2.x源码解析(缓存篇)
jQuery2.x源码解析(构建篇) jQuery2.x源码解析(设计篇) jQuery2.x源码解析(回调篇) jQuery2.x源码解析(缓存篇) 缓存是jQuery中的又一核心设计,jQuery ...
- Spring IoC源码解析——Bean的创建和初始化
Spring介绍 Spring(http://spring.io/)是一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,同时也是轻量级的IoC和AOP的容器框架,主要是针对JavaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器 ...
- Python2 基本数据结构源码解析
Python2 基本数据结构源码解析 Contents 0x00. Preface 0x01. PyObject 0x01. PyIntObject 0x02. PyFloatObject 0x04. ...
- 源码解析-Volley(转自codeKK)
Volley 源码解析 本文为 Android 开源项目源码解析 中 Volley 部分项目地址:Volley,分析的版本:35ce778,Demo 地址:Volley Demo分析者:grumoon ...
随机推荐
- Parrot Linux安装教程
镜像下载.域名解析.时间同步请点击 阿里云开源镜像站 一.Parrot Linux介绍 Parrot 是一个由开发人员和安全专家组成的全球社区,他们共同构建一个共享的工具框架,使他们的工作更轻松.标准 ...
- oracle中regexp_like/instr/substr/replace介绍和例子
ORACLE中的支持正则表达式的函数主要有下面四个: 1,REGEXP_LIKE :与LIKE的功能相似 2,REGEXP_INSTR :与INSTR的功能相似 3,REGEXP_SUBSTR :与S ...
- 线程池提交任务时submit()和execute()的区别
因为之前一直是用的execute方法,最近有个情况需要用到submit方法,所以研究了下. 他们的区别: 1.execut()可以添加一个Runable任务,submit()不仅可以添加Runable ...
- C#: .net序列化及反序列化 [XmlElement(“节点名称”)] [XmlAttribute(“节点属性”)] (下篇)
介绍 XML 序列化 .NET Framework 开发员指南 序列化是将对象转换为容易传输的格式的过程.例如,可以序列化一个对象,然后使用 HTTP 通过 Internet 在客户端和服务器之间 ...
- strcpy、strncpy 和安全的strncpy_s
strcpy和strncpy摘于linux 内核源码的/lib/string.c char *self_strcpy(char *dest, const char *src) { char *tmp ...
- SP接口的全双工首发接口整合
unsigned char bits = 8; unsigned int speed = 50000; unsigned short delay; static void spi_transfer_d ...
- 什么是Java序列化,如何实现Java序列化?或者请解释Serializable接口的作用?
象序列化的目标是将对象保存到磁盘中,或允许在网络中直接传输对象,对象序列化机制允许把内存中的Java对象转换成平台无关的二进制流,从而允许把这种二进制流持久保存在磁盘上,通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另 ...
- 如何在 Spring Boot 中禁用 Actuator 端点安全性?
默认情况下,所有敏感的 HTTP 端点都是安全的,只有具有 ACTUATOR 角色的用户才能访问它们.安全性是使用标准的 HttpServletRequest.isUserInRole 方法实施的. ...
- springboot服务引入外部jar包在windows运行正常,在linux环境上无法加载到引入jar包的类
一.问题描述 最近开发了一个springboot程序,需要依赖第三方jar包,这个jar包无法直接通过pom远程仓库下载,需要从自己本地引入,于是配置pom文件如下:将本地jar包引入工程,syste ...
- 学习Redis(三)
一.安装部署 1.常规安装 1.安装 # wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.0.7.tar.gz # tar xf redis-3.0.7. ...
