【转换模型+扫描线】【UVA1398】Meteor
The famous Korean internet company nhn has provided an internet-based photo service which allows The famous Korean internet company users to directly take a photo of an astronomical phenomenon in
space by controlling a high-performance telescope owned by nhn. A few days later, a meteoric shower, known as the biggest one in this century, is expected. nhn has announced a photo competition which awards the user who takes a photo containing as many meteors
as possible by using the photo service. For this competition, nhn provides the information on the trajectories of the meteors at their web page in advance. The best way to win is to compute the moment (the time) at which the telescope can catch the maximum
number of meteors.
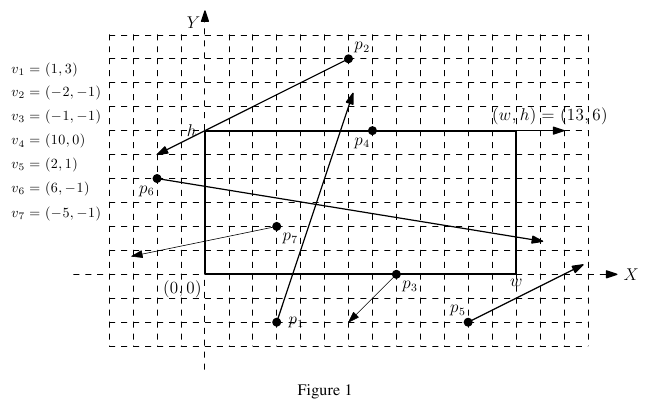
You have n meteors, each moving in uniform linear motion; the meteor mi moves along the trajectory pi + t×vi over
time t , wheret is a non-negative real value, pi is the starting point of mi and vi is
the velocity of mi . The point pi = (xi, yi) is represented by X -coordinate xi and Y -coordinate yi in
the (X, Y) -plane, and the velocity vi = (ai, bi) is a non-zero vector with two components ai and bi in
the (X, Y) -plane. For example, if pi = (1, 3) and vi = (-2, 5) , then the meteor mi will
be at the position (0, 5.5) at time t = 0.5 because pi + t×vi = (1, 3) + 0.5×(-2, 5) = (0, 5.5) . The telescope has a rectangular frame with the lower-left
corner (0, 0) and the upper-right corner (w, h) . Refer to Figure 1. A meteor is said to be in the telescope frame if the meteor is in the interior of the frame (not on the boundary of the frame). For exam! ple,
in Figure 1, p2,p3, p4 , and p5 cannot be taken by the telescope at any time because they do not pass the interior of the frame
at all. You need to compute a time at which the number of meteors in the frame of the telescope is maximized, and then output the maximum number of meteors.
Input
Your program is to read the input from standard input. The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases T is given in the first line
of the input. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers w and h (1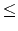 w, h
w, h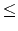 100,
100,
000) , the width and height of the telescope frame, which are separated by single space. The second line contains an integer n , the number of input points (meteors), 1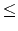 n
n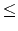 100,
100,
000 . Each of the next n lines contain four integers xi, yi, ai , and bi ; (xi, yi) is
the starting point pi and (ai, bi) is the nonzero velocity vector vi of the i -th
meteor; xi and yi are integer values between -200,000 and 200,000, and ai and bi are
integer values between -10 and 10. Note that at least one of ai and bi is not zero. These four values are separated by single spaces. We assume that all starting points pi are
distinct.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. Print the maximum number of meteors which can be in the telescope frame at some moment.
2
4 2
2
-1 1 1 -1
5 2 -1 -1
13 6
7
3 -2 1 3
6 9 -2 -1
8 0 -1 -1
7 6 10 0
11 -2 2 1
-2 4 6 -1
3 2 -5 -1
1
2
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#define oo 2000000;
#define maxn 100001
using namespace std;
struct point
{
double x;
int flag;
};
point P[maxn*10]; int tot=0;
int w,h,n;
int x,y,a,b;
int getQuJian()
{
double t1,t2;
double t3,t4;
if(a!=0)
t1=((double)(-x)/a),t2=(double)(w-x)/a;
else
{
if (0<x&&x<w) { t1=0,t2=oo;}
else
{
t1=0;t2=0;
}
} if(b!=0)
t3=((double)(-y)/b),t4=(double)(h-y)/b;
else
{
if(0<y&&y<h){t3=0,t4=oo;}
else t3=0,t4=0;
}
if(a<0) swap(t1,t2);
if(b<0) swap(t3,t4);
if(t1>t2) return 0;
if(t3>t4) return 0;
if(t1<=t3)
{
if(t3<=t2)
{
if(t2<=t4)
{
if(t2!=t3)
{
if(t3<0&&t2>0) t3=0;
P[++tot].x=t3;P[tot].flag=0;
P[++tot].x=t2;P[tot].flag=1;
}
}
else
{
if(t3!=t4)
{
if(t3<0&&t4>0) t3=0;
P[++tot].x=t3;P[tot].flag=0;
P[++tot].x=t4;P[tot].flag=1;
}
}
}
else;
}
else
{
if(t1<=t4)
{
if(t4<=t2)
{
if(t1!=t4)
{
if(t1<0&&t4>0) t1=0;
P[++tot].x=t1;P[tot].flag=0;
P[++tot].x=t4;P[tot].flag=1;
}
}
else
{
if(t1!=t2)
{
if(t1<0&&t2>0) t1=0;
P[++tot].x=t1;P[tot].flag=0;
P[++tot].x=t2;P[tot].flag=1;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int cmp(const void *i,const void *j)
{
point *ii=(point *)i,*jj=(point *)j;
if(ii->x!=jj->x)
if(ii->x>jj->x) return 1;
else return -1;
else return jj->flag-ii->flag;
}
int main()
{
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
int T,ans,now;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
tot=0,ans=0,now=0;
cin>>w>>h;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>x>>y>>a>>b;
getQuJian();
}
qsort(P+1,tot,sizeof(P[1]),cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
{
if(P[i].x>0)
{
if(P[i].flag==1) now--;
else
{
now++;
ans=max(ans,now);
}
}
else if(P[i].x==0&&P[i].flag==0)
{
now++;
ans=max(ans,now);
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
刘汝佳老师的求交集写的更优美(左端点与左端点比,右端点与右端点比,并且初始区间为【0,+oo】,使得没有我那么多麻烦的判断)
void update(int x, int a, int w, double& L, double& R) {
if(a == 0) {
if(x <= 0 || x >= w) R = L-1; //无解
} else if(a > 0) {
L = max(L, -(double)x/a);
R = min(R, (double)(w-x)/a);
} else {
L = max(L, (double)(w-x)/a);
R = min(R, -(double)x/a);
}
}
【分析】
不难发现,流星的轨迹是没有直接意义的,有意义的只是每个流星在照相机视野内出现的时间段。换句话说,我们把本题抽象为这样一个问题:给出n个开区间(Li,Ri),你的任务是求出一个数t,使得包含它的区间数最多(为什么是开区间呢?请读者思考)。开区间(Li,Ri)是指所有满足Li<x
<Ri的实数x的集合。
把所有区间画到平行于数轴的直线上(免得相互遮挡,看不清楚),然后想象有一条竖直线从左到右进行扫描,则问题可以转化为:求扫描线在哪个位置时与最多的开区间相交,如图1-27所示。
图 1-27
不难发现,当扫描线移动到某个区间左端点的“右边一点点”时最有希望和最多的开区间相交(想一想,为什么)。为了快速得知在这些位置时扫描线与多少条线段相交,我们再一次使用前面提到的技巧:维护信息,而不是重新计算。
我们把“扫描线碰到一个左端点”和“扫描线碰到一个右端点”看成是事件(event),则扫描线移动的过程就是从左到右处理各个事件的过程。每遇到一个“左端点事件”,计数器加1;每遇到一个“右端点事件”,计数器减1。这里的计数器保存的正是我们要维护的信息:扫描线和多少个开区间相交,如图1-28所示。
图 1-28
这样,我们可以写出这样一段伪代码。
将所有事件按照从左到右排序
while(还有未处理的事件) {
选择最左边的事件E
if(E是“左端点事件”) { cnt++; if(cnt > ans) ans= cnt; } //更新计数器和答案
else cnt--;//一定是“右端点事件”
}
这段伪代码看上去挺有道理,但实际上暗藏危险:如果不同事件的端点相同,那么哪个排在前面呢?考虑这样一种情况——输入是两个没有公共元素的开区间,且左边那个区间的右端点和右边那个区间的左端点重合。在这种情况下,两种排法的结果截然不同:如果先处理左端点事件,执行结果是2;如果先处理右端点事件,执行结果是1。这才是正确答案。
这样,我们得到了一个完整的扫描算法:先按照从左到右的顺序给事件排序,对于位置相同的事件,把右端点事件排在前面,然后执行上述伪代码的循环部分。如果你对这个冲突解决方法心存疑虑,不妨把它理解成把所有区间的右端点往左移动了一个极小(但大于0)的距离。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//0<x+at<w
void update(int x, int a, int w, double& L, double& R) {
if(a == 0) {
if(x <= 0 || x >= w) R = L-1; //无解
} else if(a > 0) {
L = max(L, -(double)x/a);
R = min(R, (double)(w-x)/a);
} else {
L = max(L, (double)(w-x)/a);
R = min(R, -(double)x/a);
}
} const int maxn = 100000 + 10; struct Event {
double x;
int type;
bool operator < (const Event& a) const {
return x < a.x || (x == a.x && type > a.type); //先处理右端点
}
} events[maxn*2]; int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
int w, h, n, e = 0;
scanf("%d%d%d", &w, &h, &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x, y, a, b;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &a, &b);
//0<x+at<w, 0<y+bt<h, t>=0
double L = 0, R = 1e9;
update(x, a, w, L, R);
update(y, b, h, L, R);
if(R > L) {
events[e++] = (Event){L, 0};
events[e++] = (Event){R, 1};
}
}
sort(events, events+e);
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
if(events[i].type == 0) ans = max(ans, ++cnt);
else cnt--;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
另外,本题还可以完全避免实数运算,全部采用整数:只需要把代码中的double全部改成int,然后在update函数中把所有返回值乘以lcm(1,2,…,10)=2 520即可(想一想,为什么)。
因为2520 是他们的公倍数 除出来必定是整数
void update(int x, int a, int w, int& L,int& R) {
if(a == 0){
if(x<= 0 || x >= w) R = L-1; //无解
} else if(a> 0) {
L =max(L, -x*2520/a);
R =min(R, (w-x)*2520/a);
} else {
L =max(L, (w-x)*2520/a);
R =min(R, -x*2520/a);
}
}
【转换模型+扫描线】【UVA1398】Meteor的更多相关文章
- 性能测试学习之三—— PV->TPS转换模型&TPS波动模型
PV->TPS转换模型 由上一篇“性能测试学习之二 ——性能测试模型(PV计算模型)“ 得知 TPS = ( (80%*总PV)/(24*60*60*(T/24)))/服务器数量 转换需要注意: ...
- [源码解析] 深度学习流水线并行 PipeDream(3)--- 转换模型
[源码解析] 深度学习流水线并行 PipeDream(3)--- 转换模型 目录 [源码解析] 深度学习流水线并行 PipeDream(3)--- 转换模型 0x00 摘要 0x01 前言 1.1 改 ...
- Uva1398 Meteor
扫描线法. 将流星出现在相机里的时间转化成线段,离散化端点后,扫描何时出现的流星最多.注意边界的不算,所以要先减右端点再加左端点 /*By SilverN*/ #include<iostream ...
- 使用Blender批量导出/转换模型
2.4版本号的Blender API和2.5以上版本号的API有非常大的不同,这里仅仅是提供了思路和2.4版本号的导出方案. 先提供一个脚本,这个是由Blender调用的.用于转换Ogre的Mesh文 ...
- 全参考视频质量评价方法(PSNR,SSIM)以及与MOS转换模型
转载处:http://blog.csdn.NET/leixiaohua1020/article/details/11694369 最常用的全参考视频质量评价方法有以下2种: PSNR(峰值信噪比):用 ...
- 动态规划(模型转换):uvaoj 1625 Color Length
[PDF Link]题目点这里 这道题一眼就是动态规划,然而貌似并不好做. 如果不转换模型,状态是难以处理的. 巧妙地转化:不直接求一种字母头尾距离,而是拆开放到状态中. #include <i ...
- [转]kaldi特征和模型空间转换
转:http://blog.csdn.net/shmilyforyq/article/details/76807431 博主话:这篇博客是对kaldi官网中Feature and model-spac ...
- 3D模型预处理(格式转换:obj转换为gltf)
在cesium中导入模型需要的是gltf或glb格式的文件,cesium官方提供了obj转gltf文件的工具,一个obj2gltf的库,地址为https://github.com/Analytical ...
- Pytorch | BERT模型实现,提供转换脚本【横扫NLP】
<谷歌终于开源BERT代码:3 亿参数量,机器之心全面解读>,上周推送的这篇文章,全面解读基于TensorFlow实现的BERT代码.现在,PyTorch用户的福利来了:一个名为Huggi ...
随机推荐
- [SASS] Make a responsive arrow box
Check the page:http://www.cssarrowplease.com/ In HTML: {{type}} is tow way binding in Angular, three ...
- [core java学习笔记][第十一章异常断言日志调试]
第11章 异常,断言,日志,调试 处理错误 捕获异常 使用异常机制的技巧 使用断言 日志 测试技巧 GUI程序排错技巧 使用调试器 11.1 处理错误 11.1.1异常分类 都继承自Throwable ...
- docker 数据管理
一,介于创建docker容器退出或者删除容器数据无法得以保存以及docker容器中的分区较小的问题存在,未解决该问题,可以使用参考以下几种方法. 1,将宿主的目录挂载到容器中去. docker run ...
- 《JavaScript 闯关记》之基本包装类型
为了便于操作基本类型值,JavaScript 还提供了3个特殊的引用类型:Boolean.Number 和 String.实际上,每当读取一个基本类型值的时候,后台就会创建一个对应的基本包装类型的对象 ...
- .net程序员转战android第三篇---登录模块之静态登录
这一篇我将分2个部分记录登录界面,第一部分是静态登录, 这部分将如何从界面布局.控件使用.文件关系.数据验证.登陆实现等5小块记录. 第二部分是动态登录,这块会基于上面的4小块,在数据验证不是静态数据 ...
- django的Model 模型中常用的字段类型
常用的字段类型: AutoField:自增长字段,通常不用,如果未在Model中显示指定主键,django会默认建立一个整型的自增长主键字段 BooleanField:布尔型,值为True或False ...
- PHP学习笔记二十六【类的重载】
<?php //重载: //函数名一样,通过函数的参数个数或者是参数类型不同,达到调用同一个函数名 Class A{ // public function test1(){ // echo &q ...
- 0124——KVC KVO模式
1.KVC KVC是Key-Value-Coding的简称,它是一种可以直接通过字符串的名 字(key)来访问类属性(实例变量)的机制.而不是通过调用Setter.Getter方法访问.当使用KVO. ...
- 【.Net Remoting-1】
[.NetRemoting]2015.09.16 [分布式应用程序] 应用程序分布在不同计算机上,通过网络来共同完成一项任务 C/S架构[模式] [互操作性,Interoperability]又称[互 ...
- 循环小数 UVa202
输入整数a和b(0<=a<=3000,1<=b<=3000),输出a/b的循环小数表示以及循环节长度. 例如,a=5,b=43,小数表示为0.(1162790697674418 ...


