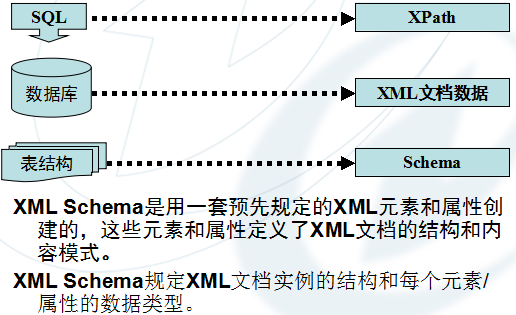
xml之Schema架构
1、什么是Schema架构
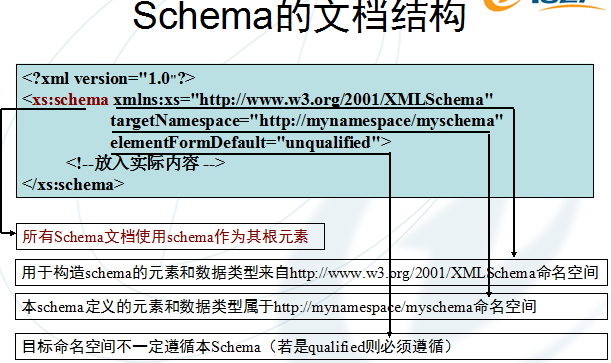
2、Schema文档结构
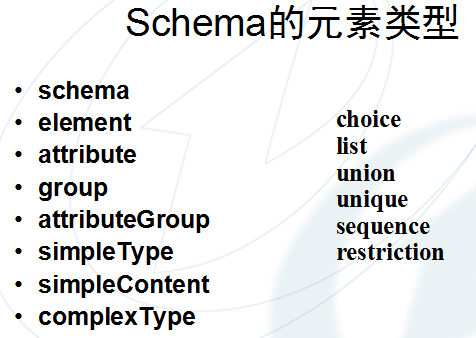
3、Schema元素类型
1》element元素
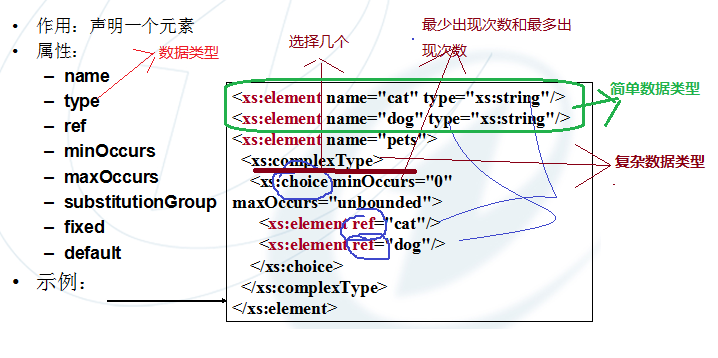
<!--简单数据;类型-->
<xs:element name="dog" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="cat" type="xs:string"></xs:element> <!--复杂数据类型-->
<xs:element name="pets">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="dog" ></xs:element>
<xs:element ref="cat"></xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
element元素
2》group元素
属性:name、ref
<!--group元素-->
<xs:element name="ele1" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="ele2" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
<xs:attribute name="myAttrituate1" type="xs:decimal"></xs:attribute>
<!--group含有 name 和 ref 两个属性-->
<!--位于 根节点schema下面的 group 没有 ref 元素-->
<xs:group name="myGroup1">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="ele1"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="ele3" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group> <xs:complexType name="comp1">
<xs:group ref="myGroup1"></xs:group>
<xs:attribute ref="attr2"></xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
group元素
3》attribute元素(为元素声明属性)
属性:name、type、ref
<xs:attribute name="myAttrituate1" type="xs:decimal"></xs:attribute> <!--attribute元素:含有属性:name/ref/type-->
<xs:attribute name="attr2" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
attribute元素
4》attributeGroup元素
作用:将一组属性声明在一起,一边被复杂类型重复使用
属性:name、ref
<!--attributeGroup元素,含有属性 name / ref-->
<xs:attributeGroup name="myattributeGroup">
<xs:attribute name="attribute1" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="attribute2" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
</xs:attributeGroup> <!--下面这个 attributeGroup 就是 指向 上面的 那个 attributeGroup-->
<xs:attributeGroup name="myattributeRefGroup">
<xs:attributeGroup ref="myattributeGroup"></xs:attributeGroup>
</xs:attributeGroup>
attributeGroup
5》simpleType元素
作用:定义一个简单类型,它决定了元素和属性值的约束和相关信息
属性:name
内容:应用已经存在的简单类型,三种方式
restrict→限定一个范围
list→从列表中选择
union→包含一个值的集合
<!--simpleType元素(决定 元素和属性值的 约束和相关信息)含有属性 name,,含有三种形式的 内容-->
<!--第一种内容 : restriction(限制,简单类型是 在什么)-->
<xs:simpleType name="restrictionSimpleType">
<!--限制 内容在 一定范围内;;注意 base 是不能 缺失的(内容 继承自 什么)-->
<xs:restriction base="xs:integer">
<xs:minInclusive value="0"></xs:minInclusive>
<xs:maxInclusive value="100"></xs:maxInclusive>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType> <!--第二种 内容的 形式 list(列表,,只允许用户 在指定的 列表中间 选择一个值)-->
<xs:simpleType name="listSimpleType">
<xs:list itemType="xs:date"></xs:list> <!--约束 简单类型的 内容只允许 是 日期中的 一个日期-->
</xs:simpleType> <!--第三种 内容的 形式 union(合并,,就是 一个 简单类型 包含 一个 简单类型的集合) --> <!--下面的 这个 例子 非常经典,,一定要记住-->
<xs:simpleType name="roadBikeSize">
<xs:restriction base="xs:positiveInteger"><!--公路自行车的 尺寸-->
<xs:enumeration value="20"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="40"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="60"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType> <xs:simpleType name="mountainbikesize"><!--山地车的 尺寸-->
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="small"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="middle"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="big"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType> <xs:attribute name="sizeOfBike">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:union>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="roadBikeSize"></xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="mountainbikesize"></xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:union>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute> <xs:element name="bike">
<xs:complexType><!--因为 元素 含有属性 ,所以要使用 复杂类型-->
<xs:attribute ref="sizeOfBike"></xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
simpleType三种方式
6》complexType元素
作用:定义一个复合类型,它决定了一组元素和属性值的约束和相关信息
属性:name
<xs:complexType name="sizeOfShoes">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:decimal">
<xs:attribute name="sizing" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType> <xs:element name="shoes" type="sizeOfShoes"></xs:element>
complexType元素
(*)complexType与simpleType区别:
1、simpleType类型的元素中不能包含元素或者属性。
2、当需要声明一个元素的子元素和/或属性时,用complexType;
3、当需要基于内置的基本数据类型定义一个新的数据类型时,用simpleType。
7》simpleContent元素
作用:应用于complexType,对它的内容进行限制和扩展
<xs:element name="shoes2">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent >
<xs:extension base="xs:decimal"><!--这里的 base 继承 是限制 simpleContent 的-->
<xs:attribute name="sizing">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"><!--这里的 base是 限制 simpleType(也就是限制 attribute)-->
<xs:enumeration value="big"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="middle"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="small"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
simpleContent元素
8》choice元素
作用:允许唯一的一个元素从一个组中被选择
属性:maxOccurs、minOccurs
<xs:element name="pets2">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="2"> <!--设置 能够选择的 项数(最少选择一项,最多选择2项)-->
<xs:element name="dog">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="哈巴"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="藏獒"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="cat">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="波斯猫"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="tom"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
choice元素
9》unique元素
作用:定义一个元素或属性值,它必须在特定的范围内
<xs:complexType name="CustomerOrderType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="item" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="itemID" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="CustomerId" type="xs:string"></xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType> <xs:element name="ordersByCustomer">
<xs:complexType><!--下面含有子元素-->
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="customerOrderType" type="CustomerOrderType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"></xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:unique name="oneCustomerOrdersforEachCustomerID">
<xs:selector xpath="mstns:customerOrderType"></xs:selector>
<xs:field xpath="@CustomerId"></xs:field>
</xs:unique>
</xs:element>
unique元素
10》sequence元素
作用:按照顺序出现某些元素
<xs:complexType name="pets">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="dog"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="cat"></xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
sequence元素
4、完整示例代码
<xs:element name="purchaseOrder" type="PurchaseOrderType"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="comment" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="PurchaseOrderType">
<!--下面是子元素:依次出现下面子元素-->
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="shipTo" type="USAAddress"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="billTo" type="USAAddress"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="items" type="Items"></xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="orderDate" type="xs:date"></xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="USAAddress">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="name"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="street"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="city"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="state"></xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="country" type="xs:string" fixed="US"></xs:attribute><!--fixed="US"表示 如果没有 声明此属性,那么默认 就是 US-->
</xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="Items">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="productName" type="xs:string"></xs:element>
<xs:element name="quantity">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:positiveInteger">
<xs:maxExclusive value="100"></xs:maxExclusive>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
示例代码
xml之Schema架构的更多相关文章
- XML和Schema命名空间详解
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/wanghuan203/article/details/9204337 XML和Schema具有无关平台,技术厂商,简单,规范统一等特点,极具开放性, ...
- xml和xsd架构文档相关知识
1.使用架构(XSD)验证XML文件 2.使用自动生成工具: 工具目录:C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v8.0A\bin\NETFX 4. ...
- xml语法、DTD约束xml、Schema约束xml、DOM解析xml
今日大纲 1.什么是xml.xml的作用 2.xml的语法 3.DTD约束xml 4.Schema约束xml 5.DOM解析xml 1.什么是xml.xml的作用 1.1.xml介绍 在前面学习的ht ...
- JavaScripts学习日记——XML DTD Schema
今日关键词: XML DTD Schema 1.XML 1 XML的概述 1.1 什么是XML XML全称为Extensible Markup Language,意思是可扩展的标记语言.XML语法上和 ...
- XML的Schema约束
XSD文档至少要包含:schema根元素和XML模式命名空间的定义.元素定义.需要注意的是XSD中必须定义一个且只能定义一个schema根元素,根元素中包括模式的约束,XML模式命名空间的定义,其他命 ...
- XML和Schema
2017-11-03 19:33:56 XML:Extensible Markup Language,也就是可扩展标记语言.XML工具使处理和转化信息变得十分容易和方便. XML和HTML格式是古老的 ...
- 怎样用Google APIs和Google的应用系统进行集成(5)----怎样把Google Tasks的JSON Schema转换成XML的Schema(XSD)?
前面说了一些Google API的介绍,可是在实际的开发其中,我们可能须要把Google RESTful API返回的JSON数据转换成XML数据输入到第三方系统,这在企业应用集成里面很的常见. 那么 ...
- 怎样用Google APIs和Google的应用系统进行集成(8)----怎样把Google Blogger(博客)的JSON Schema转换成XML的Schema(XSD)?
在Google RESTFul API中,Google Blogger API(Google博客API)应该和我们的生活离得近期:由于差点儿非常多人每天都在看博客,都在写博客,都听说过博客.在前面的G ...
- solrconfig.xml和schema.xml说明
1. solrconfig.xml solrconfig.xml配置文件主要定义了SOLR的一些处理规则,包括索引数据的存放位置,更新,删除,查询的一些规则配置. 1.1. datadir节点 ...
随机推荐
- Django搭建及源码分析(二)
上节针对linux最小系统,如何安装Django,以及配置简单的Django环境进行了说明. 本节从由Django生成的manage.py开始,分析Django源码.python版本2.6,Djang ...
- nodejs前端自动化构建
http://99jty.com/?p=1257 http://www.jankerli.com/?p=1628 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhepama/archive/2013 ...
- What is the difference between differed processing mode and interactive mode?
Every time you access and navigate through the fields on a page in PeopleSoft there are events such ...
- MongoDB 相关下载
MongoDB 下载:http://www.mongodb.org/ 本实例中MongoDB的C#驱动,支持linq:https://github.com/samus/mongodb-csharp M ...
- 关于commons-fileupload组件上传文件中文名乱码问题
java web开发,常用到的文件上传功能,常用的commons-fileupload和commons-io两个jar包.关于如何使用这两个jar来完成文件上传的功能,这里不做详解.使用commons ...
- php 显示内存 释放内存
<?php //这只是个例子,下面的数字取决于你的系统 echo memory_get_usage() . "\n"; // 36640 $a = str_repeat(&q ...
- delphi函数调用约定
指令 参数存放位置 参数传递顺序 参数内存管理 使用地方 Register CPU寄存器 从左到右 被调用者 默认,published属性存取方法必须使用 Pascal 栈 从左到右 被调用者 向后兼 ...
- STM32F4_引领入门
Ⅰ.概述 该文写给那些想学ST芯片开发(或初级学习)的朋友,文章着重细节,或许有点简单. 笔者想告诉那些刚开始学习ST的朋友,不管你使用哪一个系列(F0.F1.F2),哪一种型号芯片,其实学习的方法和 ...
- MVC的Filters(拦截过滤)的Error页面,支持Ajax报错
报错拦截过滤到error页面 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Class, Inherited = true, A ...
- python分片
刚刚学习,很新 >>> numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] >>> numbers[0:10:2] [1,3,5,7,9] >& ...
