【转】What is an entity system framework for game development?
What is an entity system framework for game development?
Last week I released Ash, an entity system framework for Actionscript game development, and a number of people have asked me the question “What is an entity system framework?”. This is my rather long answer.
Entity systems are growing in popularity, with well-known examples like Unity, and lesser known frameworks like Actionscript frameworks Ember2, Xember and my own Ash. There’s a very good reason for this; they simplify game architecture, encourage clean separation of responsibilities in your code, and are fun to use.
In this post I will walk you through how an entity based architecture evolves from the old fashioned game loop. This may take a while. The examples will be in Actionscript because that happens to be what I’m using at the moment, but the architecture applies to all programming language.
This is based on a presentation I gave at try{harder} in 2011.
The examples
Throughout this post, I’ll be using a simple Asteroids game as an example. I like to use Asteroids as an example because it involves simplified versions of many of the systems required in larger games – rendering, physics, ai, user control of a character, non-player characters.
The game loop
To understand why we use entity systems, you really need to understand the old-fashioned game loop. A game loop for Asteroids might look something like this
function update( time:Number ):void
{
game.update( time );
spaceship.updateInputs( time );
for each( var flyingSaucer:FlyingSaucer in flyingSaucers )
{
flyingSaucer.updateAI( time );
}
spaceship.update( time );
for each( var flyingSaucer:FlyingSaucer in flyingSaucers )
{
flyingSaucer.update( time );
}
for each( var asteroid:Asteroid in asteroids )
{
asteroid.update( time );
}
for each( var bullet:Bullet in bullets )
{
bullet.update( time );
}
collisionManager.update( time );
spaceship.render();
for each( var flyingSaucer:FlyingSaucer in flyingSaucers )
{
flyingSaucer.render();
}
for each( var asteroid:Asteroid in asteroids )
{
asteroid.render();
}
for each( var bullet:Bullet in bullets )
{
bullet.render();
}
}
This game loop is called on a regular interval, usually every 60th of a second or every 30th of a second, to update the game. The order of operations in the loop is important as we update various game objects, check for collisions between them, and then draw them all. Every frame.
This is a very simple game loop. It’s simple because
- The game is simple
- The game has only one state
In the past, I have worked on console games where the game loop, a single function, was over 3,000 lines of code. It wasn’t pretty, and it wasn’t clever. That’s the way games were built and we had to live with it.
Entity system architecture derives from an attempt to resolve the problems with the game loop. It addresses the game loop as the core of the game, and pre-supposes that simplifying the game loop is more important than anything else in modern game architecture. More important than separation of the view from the controller, for example.
Processes
The first step in this evolution is to think about objects called processes. These are objects that can be initialised, updated on a regular basis, and destroyed. The interface for a process looks something like this.
interface IProcess
{
function start():Boolean;
function update( time:Number ):void;
function end():void;
}
We can simplify our game loop if we break it into a number of processes to handle, for example, rendering, movement, collision resolution. To manage those processes we create a process manager.
class ProcessManager
{
private var processes:PrioritisedList; public function addProcess( process:IProcess, priority:int ):Boolean
{
if( process.start() )
{
processes.add( process, priority );
return true;
}
return false;
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var process:IProcess in processes )
{
process.update( time );
}
} public function removeProcess( process:IProcess ):void
{
process.end();
processes.remove( process );
}
}
This is a somewhat simplified version of a process manager. In particular, we should ensure we update the processes in the correct order (identified by the priority parameter in the add method) and we should handle the situation where a process is removed during the update loop. But you get the idea. If our game loop is broken into multiple processes, then the update method of our process manager is our new game loop and the processes become the core of the game.
The render process
Lets look at the render process as an example. We could just pull the render code out of the original game loop and place it in a process, giving us something like this
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
public function start() : Boolean
{
// initialise render system
return true;
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
spaceship.render();
for each( var flyingSaucer:FlyingSaucer in flyingSaucers )
{
flyingSaucer.render();
}
for each( var asteroid:Asteroid in asteroids )
{
asteroid.render();
}
for each( var bullet:Bullet in bullets )
{
bullet.render();
}
} public function end() : void
{
// clean-up render system
}
}
Using an interface
But this isn’t very efficient. We still have to manually render all the different types of game object. If we have a common interface for all renderable objects, we can simplify matters a lot.
interface IRenderable
{
function render();
}
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IRenderable>; public function start() : Boolean
{
// initialise render system
return true;
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:IRenderable in targets )
{
target.render();
}
} public function end() : void
{
// clean-up render system
}
}
Then our spaceship class might contain some code like this
class Spaceship implements IRenderable
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number; public function render():void
{
view.x = position.x;
view.y = position.y;
view.rotation = rotation;
}
}
This code is based on the flash display list. If we were blitting, or using stage3d, it would be different, but the principles would be the same. We need the image to be rendered, and the position and rotation for rendering it. And the render function does the rendering.
Using a base class and inheritance
In fact, there’s nothing in this code that makes it unique to a spaceship. All the code could be shared by all renderable objects. The only thing that makes them different is which display object is assigned to the view property, and what the position and rotation are. So lets wrap this in a base class and use inheritance.
class Renderable implements IRenderable
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number; public function render():void
{
view.x = position.x;
view.y = position.y;
view.rotation = rotation;
}
}
class Spaceship extends Renderable
{
}
Of course, all renderable items will extend the renderable class, so we get a simple class heirarchy like this

The move process
To understand the next step, we first need to look at another process and the class it works on. So lets try the move process, which updates the position of the objects.
interface IMoveable
{
function move( time:Number );
}
class MoveProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IMoveable>; public function start():Boolean
{
return true;
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:IMoveable in targets )
{
target.move( time );
}
} public function end():void
{
}
}
class Moveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number;
public var velocity:Point;
public var angularVelocity:Number; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.x * time;
position.y += velocity.y * time;
rotation += angularVelocity * time;
}
}
class Spaceship extends Moveable
{
}
Multiple inheritance
That’s almost good, but unfortunately we want our spaceship to be both moveable and renderable, and many modern programming languages don’t allow multiple inheritance.
Even in those languages that do permit multiple inheritance, we have the problem that the position and rotation in the Moveable class should be the same as the position and rotation in the Renderable class.
One common solution is to use an inheritance chain, so that Moveable extends Renderable.
class Moveable extends Renderable implements IMoveable
{
public var velocity:Point;
public var angularVelocity:Number; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.x * time;
position.y += velocity.y * time;
rotation += angularVelocity * time;
}
}
class Spaceship extends Moveable
{
}
Now the spaceship is both moveable and renderable. We can apply the same principles to the other game objects to get this class hierarchy.

We can even have static objects that just extend Renderable.

Moveable but not Renderable
But what if we want a Moveable object that isn’t Renderable? An invisible game object, for example? Now our class hierarchy breaks down and we need an alternative implementation of the Moveable interface that doesn’t extend Renderable.
class InvisibleMoveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number;
public var velocity:Point;
public var angularVelocity:Number; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.x * time;
position.y += velocity.y * time;
rotation += angularVelocity * time;
}
}

In a simple game, this is clumsy but manageable, but in a complex game using inheritance to apply the processes to objects rapidly becomes unmanageable as you’ll soon discover items in your game that don’t fit into a simple linear inheritance tree, as with the force-field above.
Favour composition over inheritance
It’s long been a sound principle of object-oriented programming to favour composition over inheritance. Applying that principle here can rescue us from this potential inheritance mess.
We’ll still need Renderable and Moveable classes, but rather than extending these classes to create the spaceship class, we will create a spaceship class that contains an instance of each of these classes.
class Renderable implements IRenderable
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number; public function render():void
{
view.x = position.x;
view.y = position.y;
view.rotation = rotation;
}
}
class Moveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number;
public var velocity:Point;
public var angularVelocity:Number; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.x * time;
position.y += velocity.y * time;
rotation += angularVelocity * time;
}
}
class Spaceship
{
public var renderData:IRenderable;
public var moveData:IMoveable;
}
This way, we can combine the various behaviours in any way we like without running into inheritance problems.
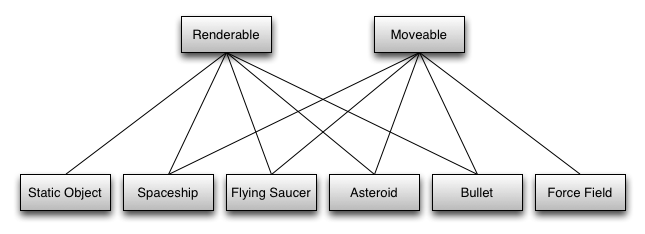
The objects made by this composition, the Static Object, Spaceship, Flying Saucer, Asteroid, Bullet and Force Field, are collectively called entities.
Our processes remain unchanged.
interface IRenderable
{
function render();
}
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IRenderable>; public function update(time:Number):void
{
for each(var target:IRenderable in targets)
{
target.render();
}
}
}
interface IMoveable
{
function move();
}
class MoveProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IMoveable>; public function update(time:Number):void
{
for each(var target:IMoveable in targets)
{
target.move( time );
}
}
}
But we don’t add the spaceship entity to each process, we add it’s components. So when we create the spaceship we do something like this
public function createSpaceship():Spaceship
{
var spaceship:Spaceship = new Spaceship();
...
renderProcess.addItem( spaceship.renderData );
moveProcess.addItem( spaceship.moveData );
...
return spaceship;
}
This approach looks good. It gives us the freedom to mix and match process support between different game objects without getting into spagetti inheritance chains or repeating ourselves. But there’s one problem.
What about the shared data?
The position and rotation properties in the Renderable class instance need to have the same values as the position and rotation properties in the Moveable class instance, since the Move process will change the values in the Moveable instance and the Render process will use the values in the Renderable instance.
class Renderable implements IRenderable
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number; public function render():void
{
view.x = position.x;
view.y = position.y;
view.rotation = rotation;
}
}
class Moveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:Point;
public var rotation:Number;
public var velocity:Point;
public var angularVelocity:Number; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.x * time;
position.y += velocity.y * time;
rotation += angularVelocity * time;
}
}
class Spaceship
{
public var renderData:IRenderable;
public var moveData:IMoveable;
}
To solve this, we need to ensure that both class instances reference the same instances of these properties. In Actionscript that means these properties must be objects, because objects can be passed by reference while primitives are passed by value.
So we introduce another set of classes, which we’ll call components. These components are just value objects that wrap properties into objects for sharing between processes.
class PositionComponent
{
public var x:Number;
public var y:Number;
public var rotation:Number;
}
class VelocityComponent
{
public var velocityX:Number;
public var velocityY:Number;
public var angularVelocity:Number;
}
class DisplayComponent
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
}
class Renderable implements IRenderable
{
public var display:DisplayComponent;
public var position:PositionComponent; public function render():void
{
display.view.x = position.x;
display.view.y = position.y;
display.view.rotation = position.rotation;
}
}
class Moveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.velocityX * time;
position.y += velocity.velocityY * time;
position.rotation += velocity.angularVelocity * time;
}
}
When we create the spaceship we ensure the Moveable and Renderable instances share the same instance of the PositionComponent.
class Spaceship
{
public function Spaceship()
{
moveData = new Moveable();
renderData = new Renderable();
moveData.position = new PositionComponent();
moveData.velocity = new VelocityComponent();
renderData.position = moveData.position;
renderData.display = new DisplayComponent();
}
}
The processes remain unaffected by this change.
A good place to pause
At this point we have a neat separation of tasks. The game loop cycles through the processes, calling the update method on each one. Each process contains a collection of objects that implement the interface it operates on, and will call the appropriate method of those objects. Those objects each do a single important task on their data. Through the system of components, those objects are able to share data and thus the combination of multiple processes can produce complex updates in the game entities, while keeping each process relatively simple.
This architecture is similar to a number of entity systems in game development. The architecture follows good object-oriented principles and it works. But there’s more to come, starting with a moment of madness.
Abandoning good object-oriented practice
The current architecture uses good object-oriented practices like encapsulation and single responsibility – the IRenderable and IMoveable implementations encapsulate the data and logic for single responsibilities in the updating of game entities every frame – and composition – the Spaceship entity is created by combining implementations of the IRenderable and IMoveable interfaces. Through the system of components we ensured that, where appropriate, data is shared between the different data classes of the entities.
The next step in this evolution of entity systems is somewhat counter-intuitive, breaking one of the core tenets of object-oriented programming. We break the encapsulation of the data and logic in the Renderable and Moveable implementations. Specifically, we remove the logic from these classes and place it in the processes instead.
So this
interface IRenderable
{
function render();
}
class Renderable implements IRenderable
{
public var display:DisplayComponent;
public var position:PositionComponent; public function render():void
{
display.view.x = position.x;
display.view.y = position.y;
display.view.rotation = position.rotation;
}
}
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IRenderable>; public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:IRenderable in targets )
{
target.render();
}
}
}
Becomes this
class RenderData
{
public var display:DisplayComponent;
public var position:PositionComponent;
}
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<RenderData>; public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:RenderData in targets )
{
target.display.view.x = target.position.x;
target.display.view.y = target.position.y;
target.display.view.rotation = target.position.rotation;
}
}
}
And this
interface IMoveable
{
function move( time:Number );
}
class Moveable implements IMoveable
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
position.x += velocity.velocityX * time;
position.y += velocity.velocityY * time;
position.rotation += velocity.angularVelocity * time;
}
}
class MoveProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<IMoveable>; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:Moveable in targets )
{
target.move( time );
}
}
}
Becomes this
class MoveData
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent;
}
class MoveProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<MoveData>; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:MoveData in targets )
{
target.position.x += target.velocity.velocityX * time;
target.position.y += target.velocity.velocityY * time;
target.position.rotation += target.velocity.angularVelocity * time;
}
}
}
It’s not immediately clear why we’d do this, but bear with me. On the surface, we’ve removed the need for the interface, and we’ve given the process something more important to do – rather than simply delegate its work to the IRenderable or IMoveable implementations, it does the work itself.
The first apparent consequence of this is that all entities must use the same rendering method, since the render code is now in the RenderProcess. But that’s not actually the case. We could, for example, have two processes, RenderMovieClip and RenderBitmap for example, and they could operate on different sets of entities. So we haven’t lost any flexibility.
What we gain is the ability to refactor our entities significantly to produce an architecture with clearer separation and simpler configuration. The refactoring starts with a question.
Do we need the data classes?
Currently, our entity
class Spaceship
{
public var moveData:MoveData;
public var renderData:RenderData;
}
Contains two data classes
class MoveData
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent;
}
class RenderData
{
public var display:DisplayComponent;
public var position:PositionComponent;
}
These data classes in turn contain three components
class PositionComponent
{
public var x:Number;
public var y:Number;
public var rotation:Number;
}
class VelocityComponent
{
public var velocityX:Number;
public var velocityY:Number;
public var angularVelocity:Number;
}
class DisplayComponent
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
}
And the data classes are used by the two processes
class MoveProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<MoveData>; public function move( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:MoveData in targets )
{
target.position.x += target.velocity.velocityX * time;
target.position.y += target.velocity.velocityY * time;
target.position.rotation += target.velocity.angularVelocity * time;
}
}
}
class RenderProcess implements IProcess
{
private var targets:Vector.<RenderData>; public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:RenderData in targets )
{
target.display.view.x = target.position.x;
target.display.view.y = target.position.y;
target.display.view.rotation = target.position.rotation;
}
}
}
But the entity shouldn’t care about the data classes. The components collectively contain the state of the entity. The data classes exist for the convenience of the processes. So we refactor the code so the spaceship entity contains the components rather than the data classes.
class Spaceship
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent;
public var display:DisplayComponent;
}
class PositionComponent
{
public var x:Number;
public var y:Number;
public var rotation:Number;
}
class VelocityComponent
{
public var velocityX:Number;
public var velocityY:Number;
public var angularVelocity:Number;
}
class DisplayComponent
{
public var view:DisplayObject;
}
By removing the data classes, and using the constituent components instead to define the spaceship, we have removed any need for the spaceship entity to know what processes may act on it. The spaceship now contains the components that define its state. Any requirement to combine these components into other data classes for the processes is some other class’s responsibility.
Systems and Nodes
Some core code within the entity system framework (which we’ll get to in a minute) will dynamically create these data objects as they are required by the processes. In this reduced context, the data classes will be mere nodes in the collections (arrays, linked-lists, or otherwise, depending on the implementation) used by the processes. So to clarify this we’ll rename them as nodes.
class MoveNode
{
public var position:PositionComponent;
public var velocity:VelocityComponent;
}
class RenderNode
{
public var display:DisplayComponent;
public var position:PositionComponent;
}
The processes are unchanged, but in keeping with the more common naming I’ll also change their name and call them systems.
class MoveSystem implements ISystem
{
private var targets:Vector.<MoveNode>; public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:MoveNode in targets )
{
target.position.x += target.velocity.velocityX * time;
target.position.y += target.velocity.velocityY * time;
target.position.rotation += target.velocity.angularVelocity * time;
}
}
}
class RenderSystem implements ISystem
{
private var targets:Vector.<RenderNode>; public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var target:RenderNode in targets )
{
target.display.view.x = target.position.x;
target.display.view.y = target.position.y;
target.display.view.rotation = target.position.rotation;
}
}
}
interface ISystem
{
function update( time:Number ):void;
}
And what is an entity?
One last change – there’s nothing special about the Spaceship class. It’s just a container for components. So we’ll just call it Entity and give it a collection of components. We’ll access those components based on their class type.
class Entity
{
private var components : Dictionary; public function add( component:Object ):void
{
var componentClass : Class = component.constructor;
components[ componentClass ] = component'
} public function remove( componentClass:Class ):void
{
delete components[ componentClass ];
} public function get( componentClass:Class ):Object
{
return components[ componentClass ];
}
}
So we’ll create our spaceship like this
public function createSpaceship():void
{
var spaceship:Entity = new Entity();
var position:PositionComponent = new PositionComponent();
position.x = Stage.stageWidth / 2;
position.y = Stage.stageHeight / 2;
position.rotation = 0;
spaceship.add( position );
var display:DisplayComponent = new DisplayComponent();
display.view = new SpaceshipImage();
spaceship.add( display );
engine.add( spaceship );
}
The core Engine class
We mustn’t forget the system manager, formerly called the process manager.
class SystemManager
{
private var systems:PrioritisedList; public function addSystem( system:ISystem, priority:int ):void
{
systems.add( system, priority );
system.start();
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var system:ISystem in systemes )
{
system.update( time );
}
} public function removeSystem( system:ISystem ):void
{
system.end();
systems.remove( system );
}
}
This will be enhanced and will sit at the heart of our entity system framework. We’ll add to it the functionality mentioned above to dynamically create nodes for the systems.
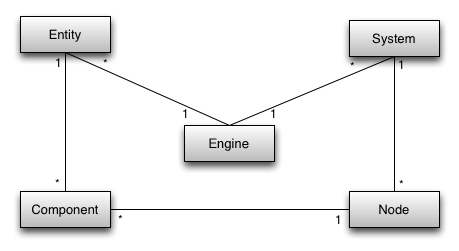
The entities only care about components, and the systems only care about nodes. So to complete the entity system framework, we need code to watch the entities and, as they change, add and remove their components to the node collections used by the systems. Because this is the one bit of code that knows about both entities and systems, we might consider it central to the game. In Ash, I call this the Engine class, and it is an enhanced version of the system manager.
Every entity and every system is added to and removed from the Engine class when you start using it and stop using it. The Engine class keeps track of the components on the entities and creates and destroys nodes as necessary, adding those nodes to the node collections. The Engine class also provides a way for the systems to get the collections they require.
public class Engine
{
private var entities:EntityList;
private var systems:SystemList;
private var nodeLists:Dictionary; public function addEntity( entity:Entity ):void
{
entities.add( entity );
// create nodes from this entity's components and add them to node lists
// also watch for later addition and removal of components from the entity so
// you can adjust its derived nodes accordingly
} public function removeEntity( entity:Entity ):void
{
// destroy nodes containing this entity's components
// and remove them from the node lists
entities.remove( entity );
} public function addSystem( system:System, priority:int ):void
{
systems.add( system, priority );
system.start();
} public function removeSystem( system:System ):void
{
system.end();
systems.remove( system );
} public function getNodeList( nodeClass:Class ):NodeList
{
var nodes:NodeList = new NodeList();
nodeLists[ nodeClass ] = nodes;
// create the nodes from the current set of entities
// and populate the node list
return nodes;
} public function update( time:Number ):void
{
for each( var system:ISystem in systemes )
{
system.update( time );
}
}
}
To see one implementation of this architecture, checkout the Ash entity system framework, and see the example Asteroids implementation there too.
Conclusion
So, to summarise, entity systems originate from a desire to simplify the game loop. From that comes an architecture of entities, which represent the state of the game, and systems, which operate on the state of the game. Systems are updated every frame – this is the game loop. Entities are made up of components, and systems operate on the entities that have the components they are interested in. The engine monitors the systems and the entities and ensures each system has access to a collection of all the entities that have the appropriate components.
However, systems don’t generally care about the entity as a whole, just the specific components they require. So, to optimise the architecture and provide additional clarity, the systems operate on statically typed node objects that contain the appropriate components, where those components all belong to the same entity.
An entity system framework provides the basic scaffolding and core management for this architecture, without providing any actual entity or system classes. You create your game by creating the appropriate entities and systems.
An entity based game engine will provide many standard systems and entities on top of the basic framework.
Three entity system frameworks for Actionscript are my own Ash, Ember2 by Tom Davies and Xember by Alec McEachran. Artemis is an entity system framework for Java, that has also been ported to C#.
My next post covers some of the reasons why I like using an entity system framework for my game development projects.
This entry was tagged Ash, Entity systems, Game development.
104 thoughts on “What is an entity system framework for game development?”
【转】What is an entity system framework for game development?的更多相关文章
- 修改替换/system/framework/framework.jar后重启手机为何没有效果?
自Android 5.0开始android默认使用art(Android4.4开始有实验性质的art),取代原来的Dalvik, art会加载boot.art和boot.oat两个文件(静态编译优化, ...
- 编译android --system,framework
在你的android 目录下: sudo git clone https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest cd manifest git b ...
- [教程] 【【【【odex教程之jar】】】】/system/framework里面的jar做odex g13
dexopt-wrapper core.jar core.odex dexopt-wrapper ext.jar ext.odex dexopt-wrapper framework.jar frame ...
- odex反编译dex异常 Cannot locate boot class path file /system/framework/core.odex
为了将ROM中system/app下的CertInstaller.odex反编译为CertInstaller.dex,输入命令: "java -jar baksmali.jar -x C ...
- Android出现declaration of org.apache.http.message.BasicLineFormatter appears in /system/framework/
这是由于使用了CloseableHttpClient造成的,把 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); Closea ...
- CBES = component-based entity system
比较好的介绍 CBES 的文章 http://www.richardlord.net/blog/what-is-an-entity-framework
- 为什么要在游戏开发中使用ECS模式
http://www.richardlord.net/blog/why-use-an-entity-framework Why use an entity system framework for g ...
- Entity Framework Code First (七)空间数据类型 Spatial Data Types
声明:本文针对 EF5+, Visual Studio 2012+ 空间数据类型(Spatial Data Types)是在 EF5 中引入的,空间数据类型表现有两种: Geography (地理学上 ...
- Entity Framework 的小实例:在项目中添加一个实体类,并做插入操作
Entity Framework 的小实例:在项目中添加一个实体类,并做插入操作 1>. 创建一个控制台程序2>. 添加一个 ADO.NET实体数据模型,选择对应的数据库与表(Studen ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript prototype 属性
prototype 属性使开发人员有能力向对象添加属性和方法. 语法 object.prototype.name=value 实例 在本例中,我们将展示如何使用 prototype 属性来向对象添加属 ...
- noip知识点总结之--贪心
一.什么是贪心 贪心算法嘛... 就是在对某个问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择 In other wors,并不是从整体最优上加以考虑,而是在获得某种意义上的局部最优解 二.贪心算法的适用前 ...
- mongodb 和 mysql 的对照
In addition to the charts that follow, you might want to consider the Frequently Asked Questions sec ...
- js 获得每周周日到周一日期
//得到每周的第一天(周日)function getFirstDateOfWeek(theDate){ var firstDateOfWeek; theDate.setDate(theDate.get ...
- jdk和tomcat环境部署
部署前需要准备的东西: 1.确定操作系统(32位或64位) 2.准备对应的jdk和tomcat软件 3.准备一份环境变量配置说明,省的到时候忘记了 步骤: 1.安装JDK 安装好JDK后,再配置JDK ...
- phonegap开发入门
做了几次开发配置了,但时间一长就忘了,特记录一下. 一.环境变量配置::右击“我的电脑”-->"高级"-->"环境变量" 1.在系统变量里新建JAV ...
- Halcon 映射校正例程注释(MapImage)
*关闭窗口 dev_close_window () dev_close_window () *打开指定大小.颜色背景的窗口 dev_open_window (, , /, /, 'black', Wi ...
- excel的变量
因需要定制游戏的公式,公式是以一个系数乘以等级,我想达到修改系数,每个等级对应的值就立即显示出来, 但把系数写在一个单元格,一拉,系数单元格也会跟着增长行数--不是我想要的: 但只要把系数单元格改成变 ...
- 二模 (11) day1
第一题: 题目大意:用邻接矩阵给出一棵树(边权非负)上N个节点相互之间的最短路距离,求这棵树所有边权的和. 解题过程: 1.暂时还没想出来,待AC. 第二题: 题目大意:给出一些单词,然后建立Trie ...
- ASP.NET MVC 4使用Bundle的打包压缩JS/CSS
打包(Bundling)及压缩(Minification)指的是将多个js文件或css文件打包成单一文件并压缩的做法,如此可减少浏览器需下载多个文件案才能完成网页显示的延迟感,同时通过移除JS/CSS ...
