从源码看java中Integer的缓存问题
在开始详细的说明问题之前,我们先看一段代码
public static void compare1(){
Integer i1 = 127, i2 = 127, i3 = 128, i4 = 128;
System.out.println(i1 == i2);
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2));
System.out.println(i3 == i4);
System.out.println(i3.equals(i4));
}
这段代码输出的结果是什么呢?
答案是:
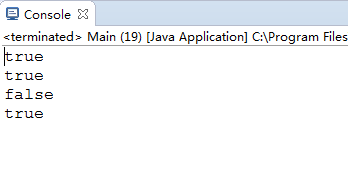
是不是感到奇怪呢?为什么127的时候==是true,128的时候就变成了false?其实要回答这个问题不难。
Integer在赋值的时候会发生自动装箱操作,调用Integer的valueOf方法,那么我们看一下java的源码(1.8):
/**
* Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified
* {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not
* required, this method should generally be used in preference to
* the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely
* to yield significantly better space and time performance by
* caching frequently requested values.
*
* This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127,
* inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range.
*
* @param i an {@code int} value.
* @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}.
* @since 1.5
*/
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
这里根据源码可以看出,在传入的i值在IntegerCache.low和IntegerCache.high之间的时候,会返回IntegerCache.cache数组里面的数,不在这个范围才会new一个Integer对象。接下来我们看一下IntegerCache数组的初始化情况:
/**
* Cache to support the object identity semantics of autoboxing for values between
* -128 and 127 (inclusive) as required by JLS.
*
* The cache is initialized on first usage. The size of the cache
* may be controlled by the {@code -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size>} option.
* During VM initialization, java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high property
* may be set and saved in the private system properties in the
* sun.misc.VM class.
*/ private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[]; static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h; cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++); // range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
} private IntegerCache() {}
}
我们看到IntegerCache的low定义为-128,high默认定义为127.但是high是可以配置的,如果没有配置才是127.我们不去看配置的情况,因为java默认是没有配置的。看一下cache数组,长度为high-low+1,从-128开始到127,存在cache数组内。
从上面的代码中可以看出,java在申请一个大于-128小于127的数时,其实是从cache中直接取出来用的,如果不在这个范围则是new了一个Integer对象。
对于==,他比较的是地址。对于int来说比较的是值。
对于equals,比较的是内容(要看equals的具体实现)。看一下Integer里面的实现:
/**
* Compares this object to the specified object. The result is
* {@code true} if and only if the argument is not
* {@code null} and is an {@code Integer} object that
* contains the same {@code int} value as this object.
*
* @param obj the object to compare with.
* @return {@code true} if the objects are the same;
* {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
它比较的确实是值的大小。
因此i1==i2和i1.equals(i2)都是true
i3==i4为false
i3.equals(i4)为true。
从源码看java中Integer的缓存问题的更多相关文章
- 从字节码看java中 this 的隐式传参
从字节码看java中 this 隐式传参具体体现(和python中的self如出一辙,但是比python中藏得更深),也发现了 static 与 非 static 方法的区别所在! static与非s ...
- JDK1.8源码(二)——java.lang.Integer 类
上一篇博客我们介绍了 java.lang 包下的 Object 类,那么本篇博客接着介绍该包下的另一个类 Integer.在前面 浅谈 Integer 类 博客中我们主要介绍了 Integer 类 和 ...
- 从源码看Android中sqlite是怎么通过cursorwindow读DB的
更多内容在这里查看 https://ahangchen.gitbooks.io/windy-afternoon/content/ 执行query 执行SQLiteDatabase类中query系列函数 ...
- 从源码看Android中sqlite是怎么读DB的(转)
执行query 执行SQLiteDatabase类中query系列函数时,只会构造查询信息,不会执行查询. (query的源码追踪路径) 执行move(里面的fillwindow是真正打开文件句柄并分 ...
- 从源码浅析Java中的Lock和AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
在之前的文章中我也曾经介绍过Lock,像ReentrantLock(可重入锁)和ReentrantReadWriteLock(可重入读写锁),这些所我们在说的时候并没有详细的说明它们的原理,仅仅说明了 ...
- 从源码看Java集合之ArrayList
Java集合之ArrayList - 吃透增删查改 从源码看初始化以及增删查改,学习ArrayList. 先来看下ArrayList定义的几个属性: private static final int ...
- JDK1.8源码(二)——java.lang.Integer类
一.初识 1.介绍 int 是Java八大基本数据类型之一,占据 4 个字节,范围是 -2^31~2^31 - 1,即 -2147483648~2147483647.而 Integer 是 int 包 ...
- 从源码看java线程状态
关于java线程状态,网上查资料很混乱,有的说5种状态,有的说6种状态,初学者搞不清楚这个线程状态到底是怎么样的,今天我讲一下如何看源码去解决这个疑惑. 直接上代码: public class Thr ...
- 从源码看 Vue 中的 Mixin
最近在做项目的时候碰到了一个奇怪的问题,通过 Vue.mixin 方法注入到 Vue 实例的一个方法不起作用了,后来经过仔细排查发现这个实例自己实现了一个同名方法,导致了 Vue.mixin 注入方法 ...
随机推荐
- careercup-高等难度 18.5
18.5 有个内含单词的超大文本文件,给定任意两个单词,找出在这个文件中这两个单词的最短距离(也即相隔几个单词).有办法在O(1)时间里完成搜索操作吗?解法的空间复杂度如何? 解法1:我们假设单词wo ...
- 获取div相对文档的位置
获取div相对文档的位置,两个方法 经测试 document.getElementById("btn").getBoundingClientRect() 在IE6下有2像素的bug ...
- gradle的maven plugin使用
在分布式系统开发中,基于gradle的项目,要共享jar一般是借助maven私服.那么gradle的maven插件如何做到上传binary jar,source jar, javadoc jar到私服 ...
- centos下编译安装mysql5.6
CentOS 6.4下编译安装MySQL 5.6.14 参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiongpq/p/3384681.html 概述: CentOS 6.4下通过yum安装的 ...
- java使用jsp servlet来防止csrf 攻击的实现方法
背景: 1.csrf知识 CSRF(Cross-site request forgery跨站请求伪造,也被称为“one click attack”或者session riding,通常缩写为CSRF或 ...
- tachyon 配置项
Tachyon 配置参数分为4类:Master,Worker, Common (Master and Worker), and User configurations. 环境变量配置文件在$TACHY ...
- WinForm中DefWndProc、WndProc与IMessageFilter的区别
这篇文章主要介绍了WinForm中DefWndProc.WndProc与IMessageFilter的区别,较为详细的分析了WinForm的消息处理机制,需要的朋友可以参考下 一般来说,Win ...
- Intervals poj 1201 差分约束系统
Intervals Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 22503 Accepted: 8506 Descri ...
- 1.4.2 solr字段类型--(1.4.2.6)使用外部文件和程序
1.4.2 solr字段类型 (1.4.2.1) 字段类型定义和字段类型属性. (1.4.2.2) solr附带的字段类型 (1.4.2.3) 使用货币和汇率 (1.4.2.4) 使用Dates(日期 ...
- UVa OJ 10071
Problem B Back to High School Physics Input: standard input Output: standard output A particle has i ...
