STL标准库-容器-map和multimap
技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
map与multimap为关联容器,结构如下
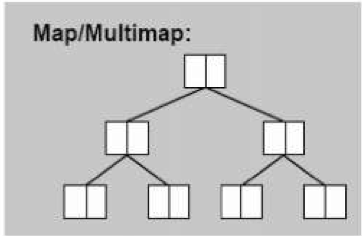
map底层实现依然是rb_tree 他的data可以改,但是key不能改,因此map仍然具有自动排序的功能
我们无法使用迭代器改变元素的key(const key),但是可以改变元素的data.
map的key必须独一无二,multimap的key可以重复
map的定义函数
template <typename _Key, typename _Tp, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,
typename _Alloc = std::allocator<std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> > >
class map
{
public:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef _Tp mapped_type;
typedef std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type;
typedef _Compare key_compare;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
...
}
参数1 class key 键值key
参数2 class T data
参数3 class compare 排序key的函数 默认为less() 升序
参数4 alloc 分配器
map的基本使用
一 定义
//构造函数
map<int, int> c;
c[] = ;
c[] = ;
c[] = ;
c[] = ;
c[] = ;
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //operator =
map<int, int> c1;
c1 = c;
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
二 迭代器操作 map的迭代器就是红黑树的迭代器
//迭代器操作
/*
map<int, int> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
*/ //begin()
map<int, int>::iterator iter;
iter = c.begin();
cout<< "begin(): "<<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl; //end()
iter = c.end();
iter--;
cout<<"end(): " <<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl; //rbegin()反向头迭代器
map<int, int>::reverse_iterator riter;
riter = c.rbegin();
cout << "rbegin(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl; //rend()反向头迭代器
riter = c.rend();
riter--;
cout << "rend(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl; //cbegin() const 迭代器 正向 头迭代器
map<int, int>::const_iterator citer;
citer = c.cbegin();
cout << "cbegin(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl; //cend() const 迭代器 反向 尾迭代器
citer = c.cend();
citer--;
cout<< "cend(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl;
三 容量
//容量
/*
map<int, int> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
*/
//是否为kong
cout << "empty: " << c.empty() <<endl; //元素个数
cout << "size: " << c.size() <<endl; //最大容量
cout << "max_size: " << c.max_size() <<endl;
四 基本操作
//基本操作
/*
map<int, int> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
*/ //operator[] 这个和其他容器的operator有些不同,如果[index] 的index(key) 在map中存在则直接返回该key对应的data ,如果不存在则想该位置插入默认值
cout << "operator[]: " << c[] << endl;
cout << "operator[]: " << c[] << endl; //这时你会发现 map自动插入一个c[10]
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //at() 取data
cout<< "at(): " << c.at() << endl; //插入insert() map 不允许key重复 插入重复key 不会报错但插入不成功
c.insert(pair<int, int>(, ));
cout <<"insetr(): ";
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; map<int, int> c_insert;
map<int, int>::iterator insert_iter = c_insert.begin();
c_insert.insert(insert_iter,pair<int, int>(, ));
cout <<"insetr(): ";
for(auto i : c_insert)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //删除
map<int,int>::iterator erase_iter = c.begin();
c.erase(erase_iter);
cout <<"erase(): ";
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
//指定下表删除
c.erase();
cout <<"erase(): ";
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //指定元素删除
erase_iter = c.find();
if(erase_iter != c.end())
{
cout<<"found index: "<< erase_iter->first <<endl;
c.erase(erase_iter);
}
else{
cout<< "Not found" <<endl;
}
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //交换swap
map<int, int> c_swap1;
c_swap1.insert({pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,)});
map<int, int> c_swap2;
cout<<"swap() before: "<<endl;
cout<<"c_swap1: ";
for(auto i : c_swap1)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; cout<<"c_swap2: ";
for(auto i : c_swap2)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; cout<<"swap() after: ";
c_swap2.swap(c_swap1);
cout<<"c_swap1: ";
for(auto i : c_swap1)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; cout<<"c_swap2: ";
for(auto i : c_swap2)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //清除clear
c_insert.clear();
cout <<"clear(): ";
for(auto i : c_insert)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //elements() 插入 如果存在什么也不做 如果不存在插入
map<int, int>::iterator element_iter = c_swap2.begin(); auto xxx = c_swap2.emplace(pair<int, int>(,));
if(xxx.second)
{
cout << "不存在" <<endl;
}
else
{
cout<< "存在" <<endl;
}
cout <<"elements(): ";
for(auto i : c_swap2)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //emplace_hint() 插入
element_iter = c.emplace_hint(element_iter, pair<int, int>(,));
cout <<"emplace_hint(): ";
if(element_iter != c_swap2.end())
{
cout<< "存在" <<endl;
}
else{
cout << "不存在" <<endl;
}
五 操作函数
//函数
/*
map<int, int> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
*/
//key_comp 返回key排序的函数 返回仿函数
cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回1 因为1<2
cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回0 因为2>1
cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回0 因为1=1 //value_comp 返回取value和key数据包中的 取key函数 返回仿函数
pair<int,int> value_comp_pair = *c.begin();
iter = c.begin();
cout << c.value_comp()(*iter++,value_comp_pair) << endl;
六 算法
//算法
/*
map<int, int> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
*/
//find() 指定key 返回对应pair
cout <<"find(1): " << c.find()->second << endl;; //count() key出现的次数
cout <<"count(1): " << c.count()<< endl;; c.erase(); //lower_bound 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
auto lower_boundObj = c.lower_bound();
if(lower_boundObj->first)
cout<<lower_boundObj->first<<endl;
else
cout<< "Not found lower_boundObj" << endl; for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //upper_bound 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
auto upper_boundObj = c.upper_bound();
if(upper_boundObj->first)
cout<<upper_boundObj->first<<endl;
else
cout<< "Not found upper_bound" << endl; for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl; //equal_range()返回该元素所在区间(闭区间),返回值是一个pair<iterator, iterator>类型,first代表所在区间的起点迭代器,second表示所在区间的终点迭代器 auto equal_rangeObj = c.equal_range();
if(equal_rangeObj.first->first)
{
cout<<equal_rangeObj.first->first<<endl;
}
else
cout<< "NOT equal_rangeObj.first" << endl; if(equal_rangeObj.second->second)
{
cout<<equal_rangeObj.second->first<<endl;
}
else
cout<< "NOT second" << endl;
七 自定义比较函数 map 默认为升序 改为降序
class my_compare_
{
public:
bool operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
map<int, int, my_compare_> c;
c.insert({pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,)});
for(auto i : c)
{
cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
return ;
}
STL标准库-容器-map和multimap的更多相关文章
- STL标准库-容器-set与map
STL标准库-容器-set与multiset C++的set https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7456024.html STL标准库-容器-map和 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流.沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. set与multiset关联容器 结构如下 set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key se ...
- STL标准库-容器-deque
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. deque双向开口可进可出的容器 我们知道连续内存的容器不能随意扩充,因为这样容易扩充别人那去 deque却可以,它创造了内存 ...
- STL标准库-容器-vector
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. 向量容器vector是一个动态数组,内存连续,它是动态分配内存,且每次扩张的原来的二倍. 他的结构如下 一 定义 vector ...
- STL学习笔记— —容器map和multimap
简单介绍 在头文件<map> 中定义 namespace std { template <typename Key, typename T, typename Compare = l ...
- STL标准库-容器-list
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. list 表示非连续的内存区域,并通过一对指向首尾元素的指针双向链接起来,从而允许向前和向后两个方向进行遍历.在list 的任 ...
- STL标准库-容器-rb_tree
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性 红黑树,关联式容器底层实现(map set),在使用中基本运用不到,但是还是想了解一下他的运作方式 Red_Black tree ...
- 关于C++ STL标准库中map 的多元素应用
map的特性是,所有的元素会根据键值自动排序.map的所有元素都是pair,同时拥有实值(value)和键值(key).pair的第一个元素被视为键值,第二个被视为实质piar 的定义 templat ...
- STL标准库-容器适配器
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性 上一节介绍了仿函数适配器,这节主要介绍容器适配器和迭代器适配器的概念,其实容器适配器和迭代器其适配器就是封装了一些其他class ...
随机推荐
- js判断用户是在PC端或移动端访问
js如何判断用户是在PC端和还是移动端访问. 最近一直在忙我们团队的项目“咖啡之翼”,在这个项目中,我们为移动平台提供了一个优秀的体验.伴随Android平台的红火发展.不仅带动国内智能手机行业,而 ...
- HTML&CSS&Javascript脑图
今天看了极客学院的CSS3部分,加上前几天看过的HTML5部分,现在对HTML和CSS的基础有了系统的认识,正好发现这张图,简直Perfect! 感谢脑图的制作人,虽然不知道是谁,但能把HTML.CS ...
- HDU 1879 继续畅通工程(Prim||Kruscal模板题)
原题链接 Prim(点归并) //异或运算:相同为假,不同为真 #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #define maxn 105 us ...
- Apache配置WSGI
Apache配置WSGI 什么是WSGI WSGI被称作web服务器网关接口,在笔者看来其实是基于CGI标准针对Python语言做了一些改进,其主要功能是规范了web 服务器与Pythonj应用程序之 ...
- linux时区问题
时区问题很麻烦- 0.查看时间命令 #date 查看系统时间 #date -s 修改时间,看下面的例子 #// (将系统日期设定为2014年07月16日) #:: (将系统时间设定为下午11::) # ...
- STM32F105 USB管脚Vbus的处理
源:STM32F105 USB管脚Vbus的处理 对于STM32F105/107来说,为了监测USB的连接问题,程序默认是通过Vbus管脚进行检查的.但是Vbus管脚和UART1的TXD复用,导致我们 ...
- PHP设计模式_注册树模式
通过注册树模式可以更加简单快捷的获取对象,在某个地方实例化了一个对象,可以将这个对象“保存”起来(放入可以全局使用的数组里),用的时候只需要提供 保存对象的时候 的那个标识即可,解决全局共享和交换对象 ...
- c++标准库vector&list使用练习
/* vector顺序存储,随机访问快 list链表存储,插入删除快 deque占用内存多,兼具两者优点 注意: 1.vector严格顺序存储 2.list的迭代器只能做++或--运算,要一次移动多个 ...
- 各版本的区别及含义(i386 、x86_64 、ppc )
1.i386:是指兼容Intel 80386处理器 x86或80x86是英代爾Intel首先开发制造的一种微处理器体系结构的泛称.該系列較早期的處理器名稱是以數字來表示,並以“86”作為結尾, ...
- 获取本机IP,返回字符串
public static String GetLocalIp() { String[] Ips = GetLocalIpAddress(); foreach (String ip in Ips) i ...
